Clinical decision making in the management of sigmoid carcinoma complicated by malignant obstruction
-
摘要:
目的 乙状结肠癌并发恶性肠梗阻是结肠癌治疗过程中一个潜在且棘手的临床问题,本文旨在探索乙状结肠癌恶性肠梗阻综合治疗的策略和经验。 方法 回顾和报告北京大学肿瘤医院1例乙状结肠癌并发恶性肠梗阻的综合治疗过程。 结果 晚期转移性乙状结肠癌合并肠梗阻时以支持治疗为主,支持手段有肠梗阻导管置入或肠道支架置入,通过合理的支持治疗缓解急性肠梗阻,提供更安全的手术时机及抗肿瘤综合治疗的机会。营养支持治疗是恶性肠梗阻及抗肿瘤治疗贯穿全程的关键部分,是患者治疗获益的基础保障。 结论 肿瘤原发灶导致的恶性肠梗阻可通过肠梗阻导管、肠道支架缓解肠梗阻及完善肠道准备,后择期行手术切除解决梗阻因素。肠道支架的置入在恶性结肠癌肠梗阻中推荐,但需把握适应证及医疗条件以恰当选择。 Abstract:Objective Sigmoid carcinoma complicated with malignant obstruction is a potential and intractable clinical problem encountered during the treatment of colon cancer. This study aimed to explore clinical treatment strategies and experiences involving the management of malignant obstruction as a result of sigmoid colon carcinoma. Methods We reviewed a case of sigmoid colon carcinoma with malignant obstruction in Peking University Cancer Hospital and reported the treatment strategies implemented. Results Patients with advanced metastatic sigmoid colon carcinoma and resultant obstruction were mainly administered by supportive treatment, which included intestinal obstruction decompression using a tube or stent. Relief of acute obstruction using appropriate supportive therapies provides safer opportunities for both surgery and comprehensive antitumor therapy. Nutritional support is essential throughout the course of obstruction treatment and is a key component of successful antitumor therapy. Conclusions Malignant obstructions caused by primary gastrointestinal tumors may be alleviated via intestinal obstruction decompression using tubes or stents. This allows for improved bowel preparation prior to surgical resection of the primary obstructive tumor. Intestinal stenting is recommended for the decompression of obstructive malignant colon cancers, although contraindications and medical comorbidities should be considered to ensure that the appropriate treatment modality is selected. -
表 1 患者治疗期间膳食及营养支持方案
时期 膳食 口服营养剂 肠外营养 不全性肠梗阻期 普食 + − 完全性肠梗阻期 禁食 − + 肠梗阻缓解期 少渣流食→半流食 + +→− 乙状结肠癌姑息手术围术期 术前 禁食 − + 术后 禁食→流食→半流食 + +→− 抗肿瘤治疗期 普食 + − 表 2 患者影像学检查及评效
项目 2021年1月20日
(基线)2021年4月7日
(4个周期治疗后)2021年6月25日
(术后基线)2021年8月27日
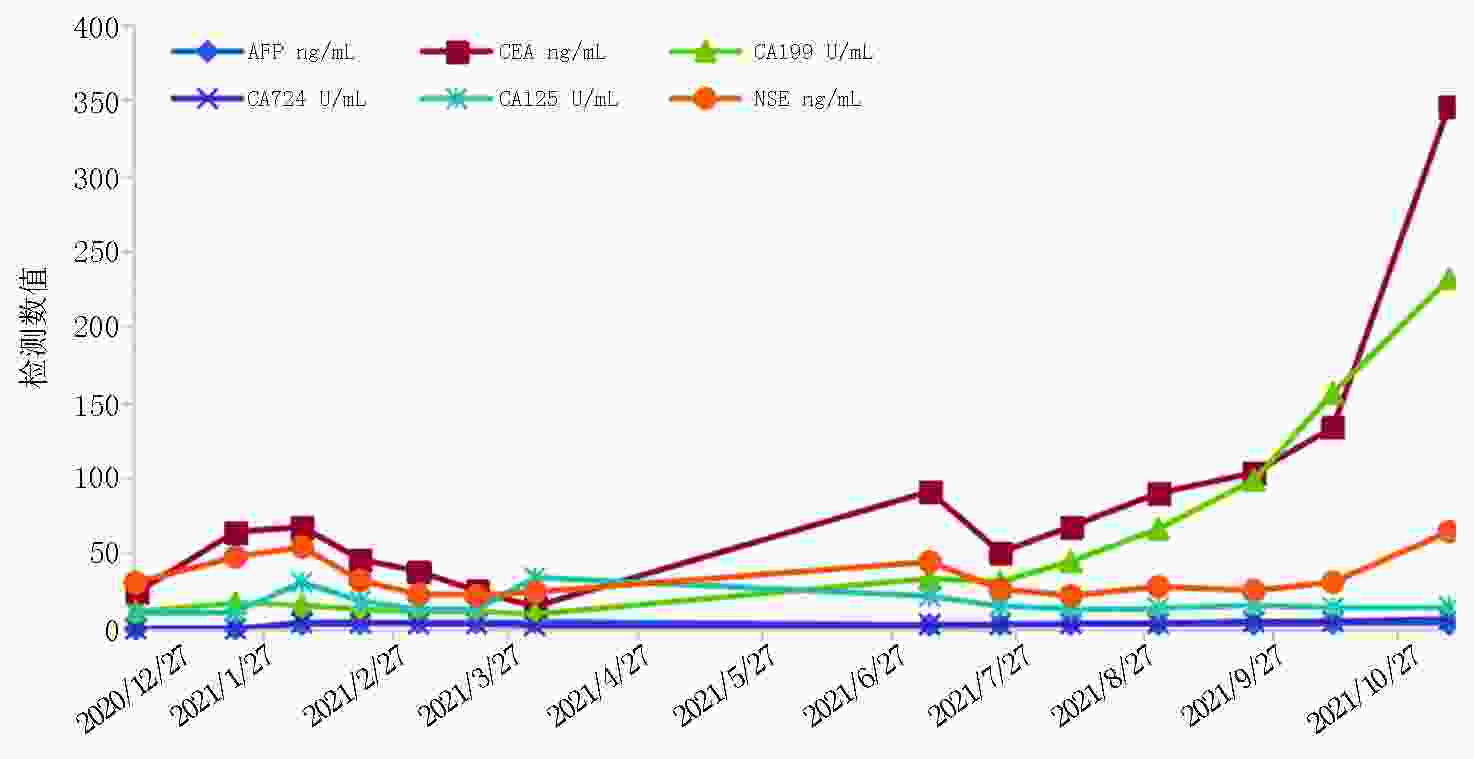
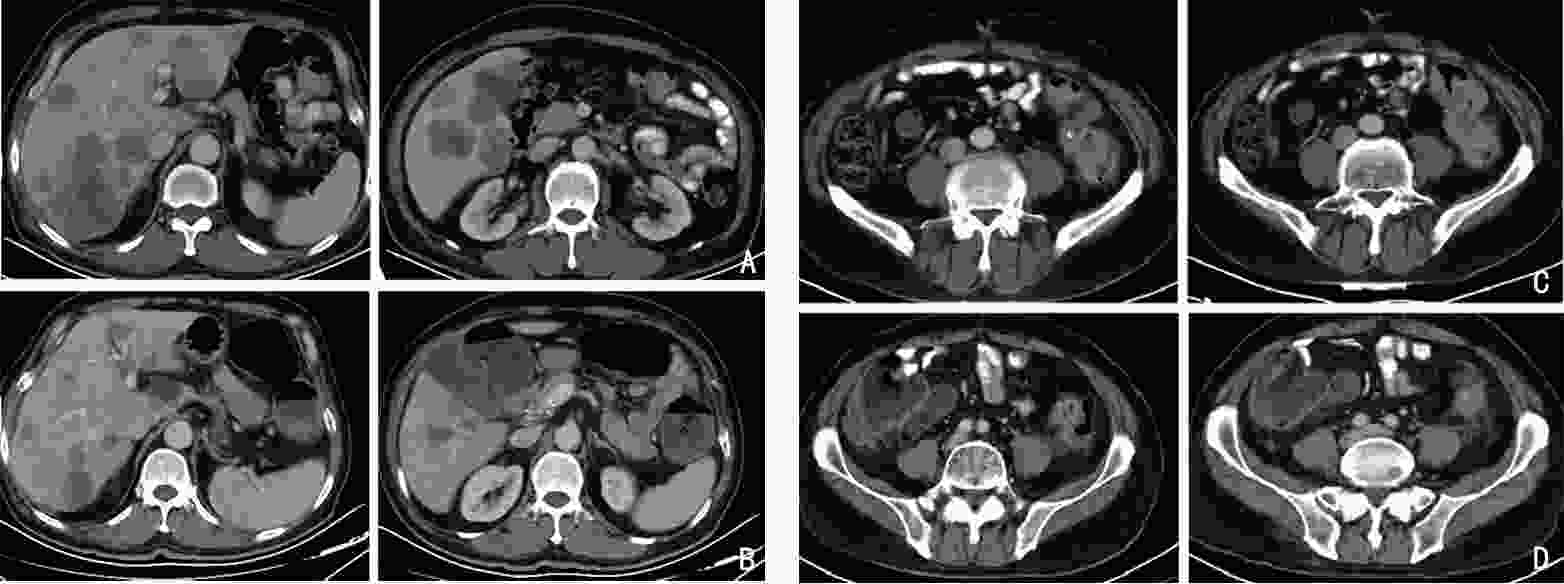
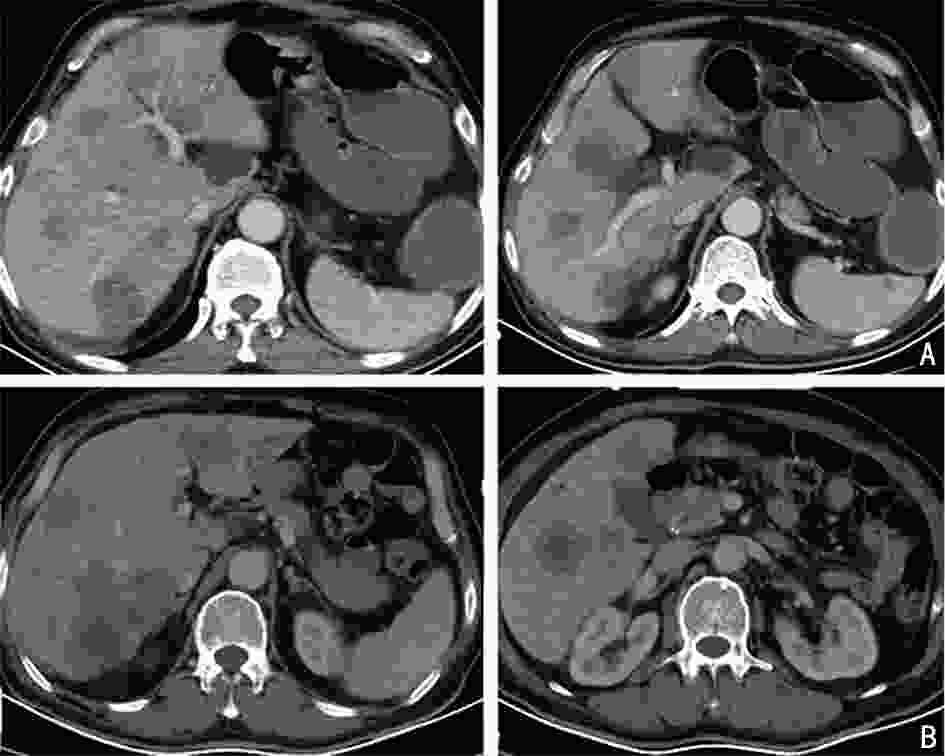
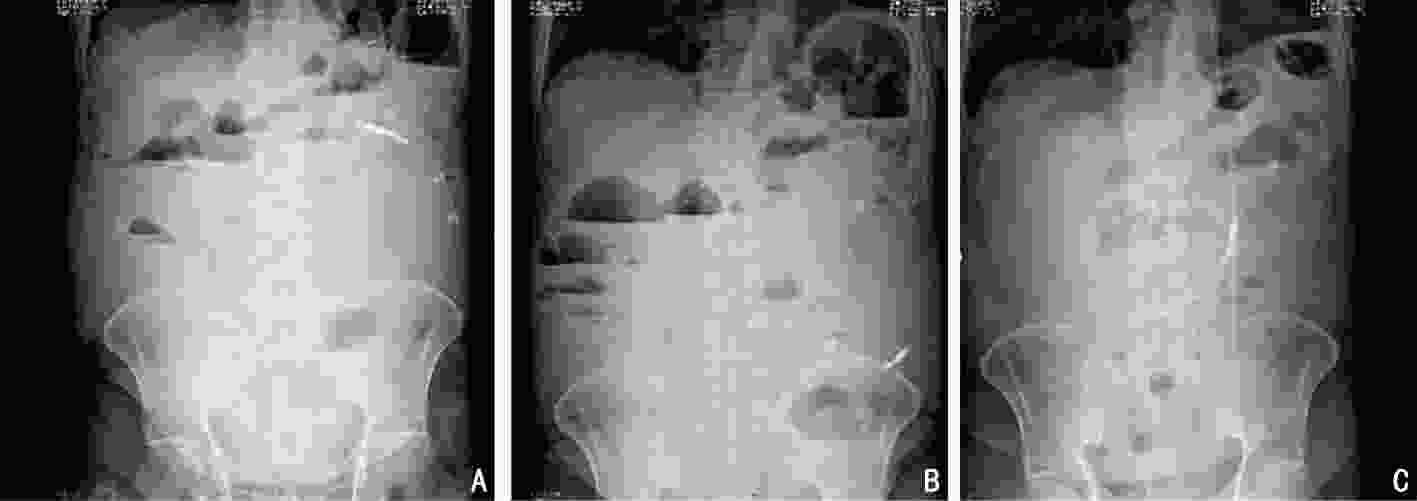
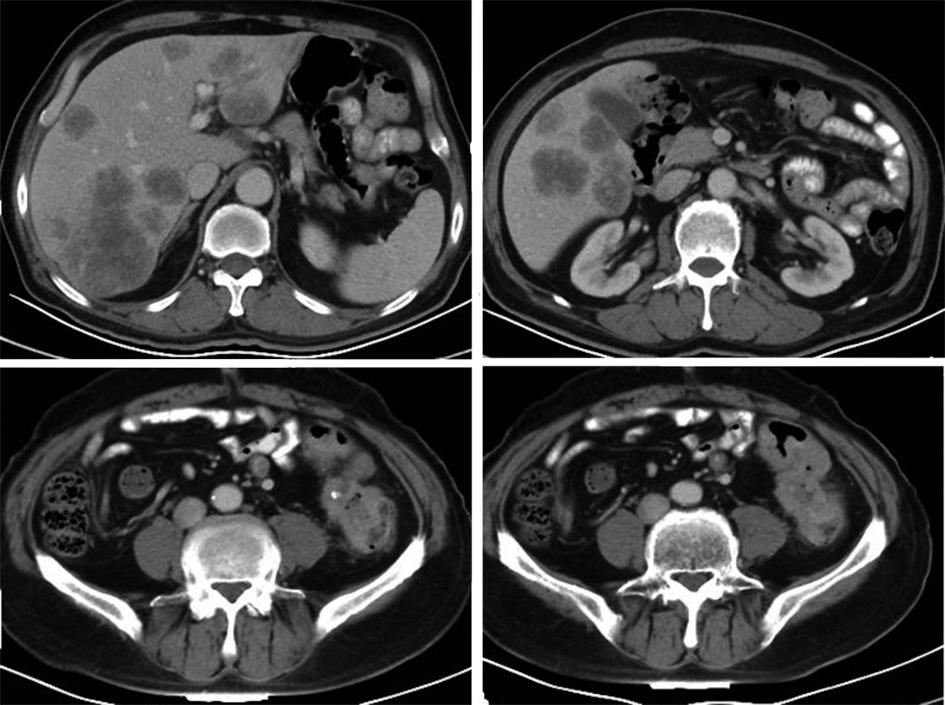
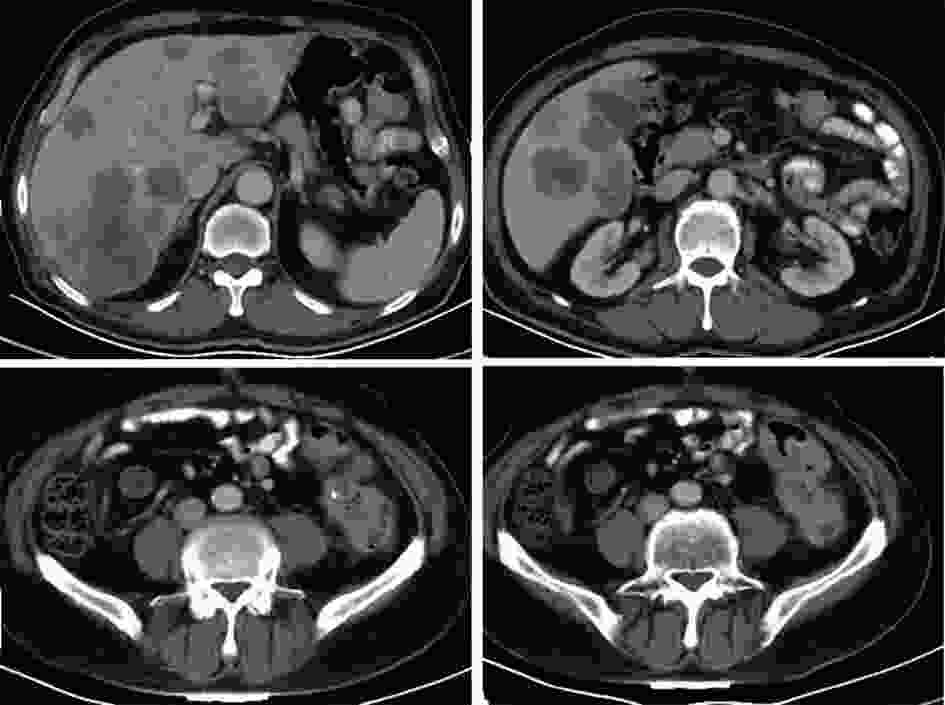
(8个周期/术后3个周期治疗后)降乙结肠交界 肠壁不均匀增厚(14 mm) 肠壁增厚加重,近端结肠扩张,结肠内容物增多(19 mm) 术后,吻合口未见异常 术后,吻合口未见异常 肝转移 肝内多发稍低密度结节,部分融合 肝多发占位缩小 肝内多发占位增大 肝多发占位缩小 腹膜 − 局部增厚 − 腹膜密度较高 评效 肝脏肿瘤负荷重,>60%肝脏受累 PR 肝病灶增大 PR -
[1] Yeo CT, Merchant SJ. Considerations in the management of malignant bowel obstruction[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 2021, 30(3):461-474. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2021.02.003 [2] Ukkonen M, Kivivuori A, Rantanen T, et al. Emergency abdominal operations in the elderly: A multivariate regression analysis of 430 consecutive patients with acute abdomen[J]. World J Surg, 2015, 39(12):2854-2861. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-3207-1 [3] Davis M, Hui D, Davies A, et al. Medical management of malignant bowel obstruction in patients with advanced cancer: 2021 MASCC guideline update[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2021, 29(12):8089-8096. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06438-9 [4] Winner M, Mooney SJ, Hershman DL, et al. Incidence and predictors of bowel obstruction in elderly patients with stage Ⅳ coloncancer: a population-based cohort study[J]. JAMA Surg, 2013, 148(8):715-722. [5] Bento JH, Bianchi ET, Tustumi F, et al. Surgical management of malignant intestinal obstruction: outcome and prognostic factors[J]. Chirurgia (Bucur), 2019, 114(3):343-351. doi: 10.21614/chirurgia.114.3.343 [6] 中国医师协会外科医师分会,中国医师协会外科医师分会肿瘤外科医师委员会,中国医师协会外科医师分会多学科综合治疗专业委员会.恶性肿瘤相关急腹症多学科管理中国专家共识[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2020,23(5):421-437. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20200330-00170 [7] Krouse RS. Malignant bowel obstruction[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2019, 120(1):74-77. doi: 10.1002/jso.25451 [8] van Hooft JE, Veld JV, Arnold D, et al. Self-expandable metal stents for obstructing colonic and extracolonic cancer: European society of gastrointestinal endoscopy (ESGE) guideline-update 2020[J]. Endoscopy, 2020, 52(5):389-407. doi: 10.1055/a-1140-3017 [9] van Hooft JE, Bemelman WA, Oldenburg B, et al. Colonic stenting versus emergency surgery for acute left-sided malignant colonic obstruction: a multicentre randomised trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2011, 12(4):344-352. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70035-3 [10] Song LM, Baron TH. Stenting for acute malignant colonic obstruction: a bridge to nowhere[J]? Lancet Oncol, 2011, 12(4):314-315. [11] Pal A, Saada J, Kapur S, et al. Technical and clinical outcomes after colorectal stenting in malignant large bowel obstruction: A single-center experience[J]. Ann Coloproctol, 2021, 37(2):85-89. [12] Dolan PT, Abelson JS, Symer M, et al. Colonic stents as a bridge to surgery compared with immediate resection in patients with malignant large bowel obstruction in a NY state database[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2021, 25(3):809-817. [13] Arezzo A, Forcignanò E, Bonino MA, et al. Long-term oncologic results after stenting as a bridge to surgery versus emergency surgery for malignant left-sided colonic obstruction: a multicenter randomized controlled trial (ESCO trial)[J]. Ann Surg, 2020, 272(5):703-708. [14] Hill J, Kay C, Morton D, et al. CREST: Randomised phase III study of stenting as a bridge to surgery in obstructing colorectal cancer-Results of the UK ColoRectal Endoscopic Stenting Trial (CREST)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(15_suppl):3507. [15] ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Harrison ME, Anderson MA, et al. The role of endoscopy in the management of patients with known and suspected colonic obstruction and pseudo-obstruction[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2010, 71(4):669-679. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2009.11.027 [16] 中国抗癌协会,中国抗癌协会肿瘤营养与支持治疗专业委员会,中国抗癌协会癌症康复与姑息治疗专业委员会,等.营养风险筛查[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志,2016,3(2):100-101. [17] 中国抗癌协会,中国抗癌协会肿瘤营养与支持治疗专业委员会,中国抗癌协会癌症康复与姑息治疗专业委员会,等.口服营养补充指南[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志,2015,2(4):33-34. -



 下载:
下载: