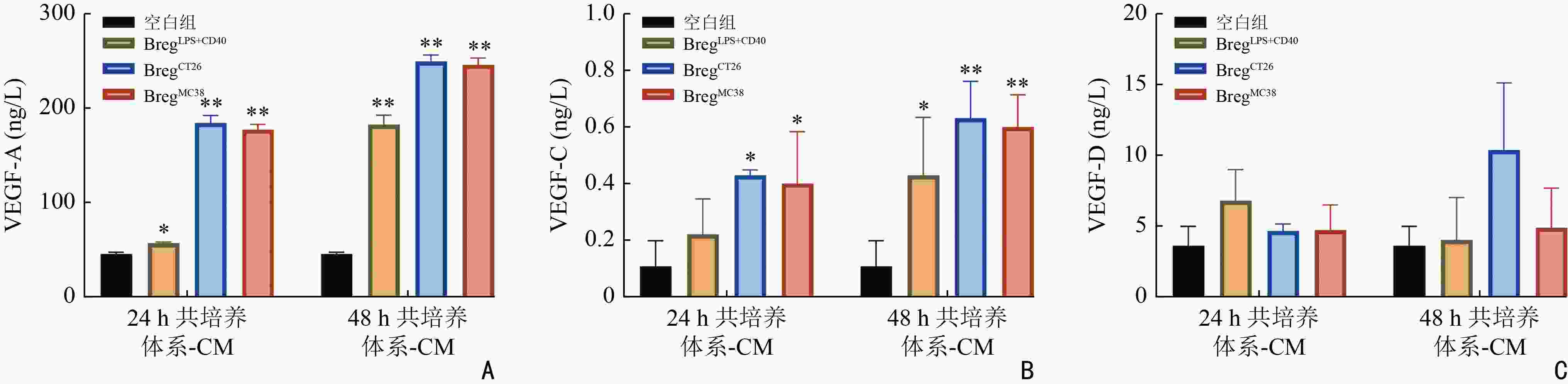
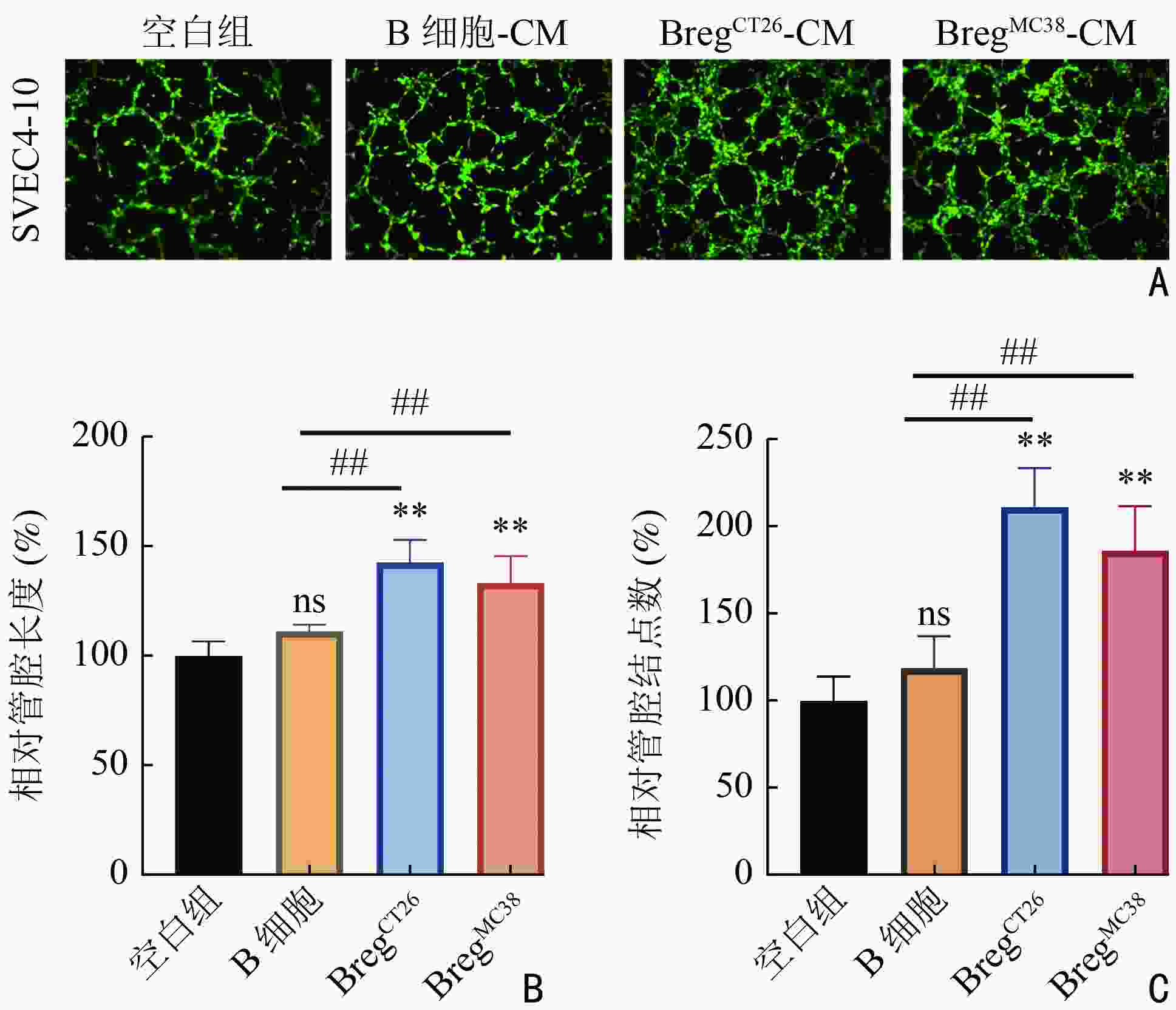
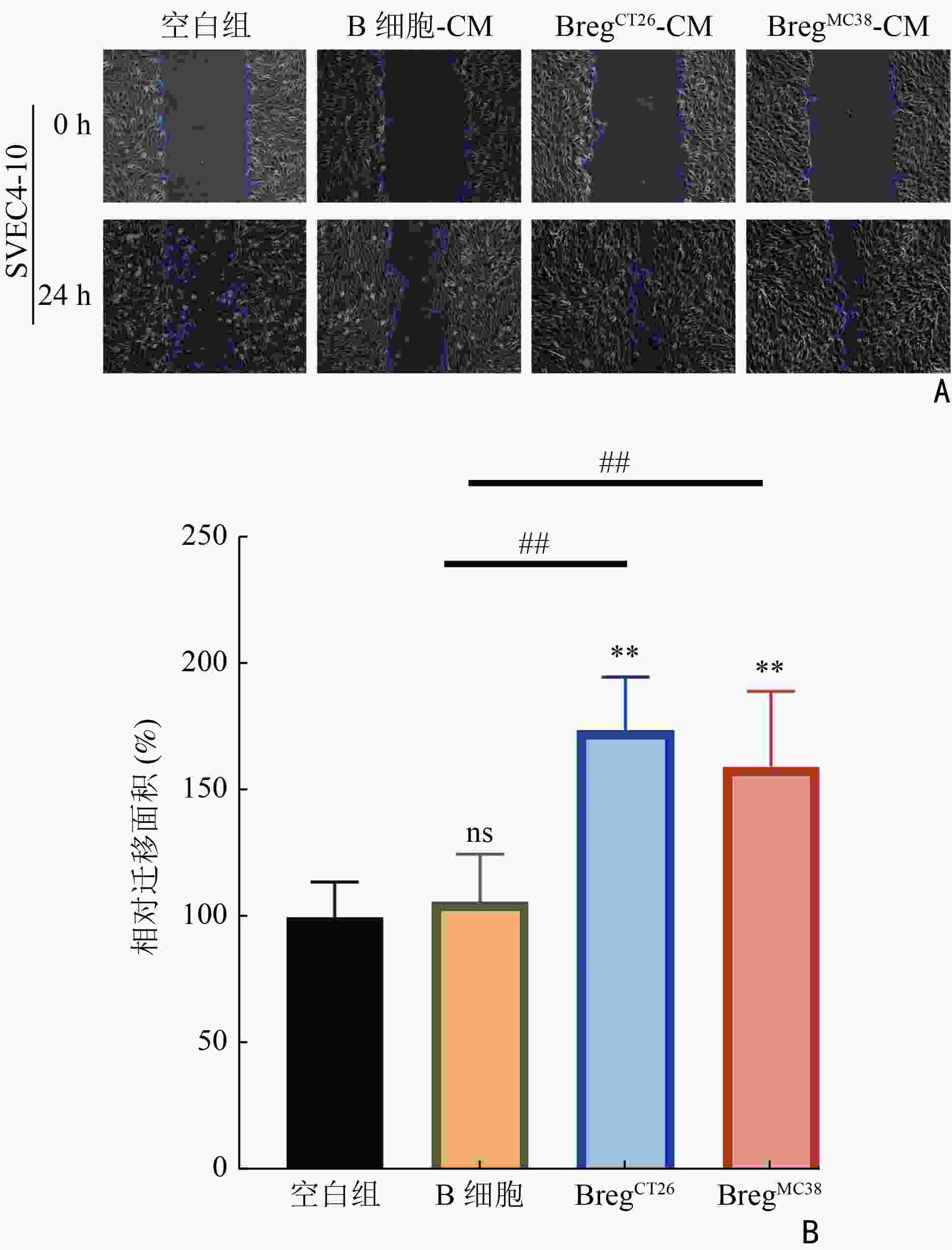
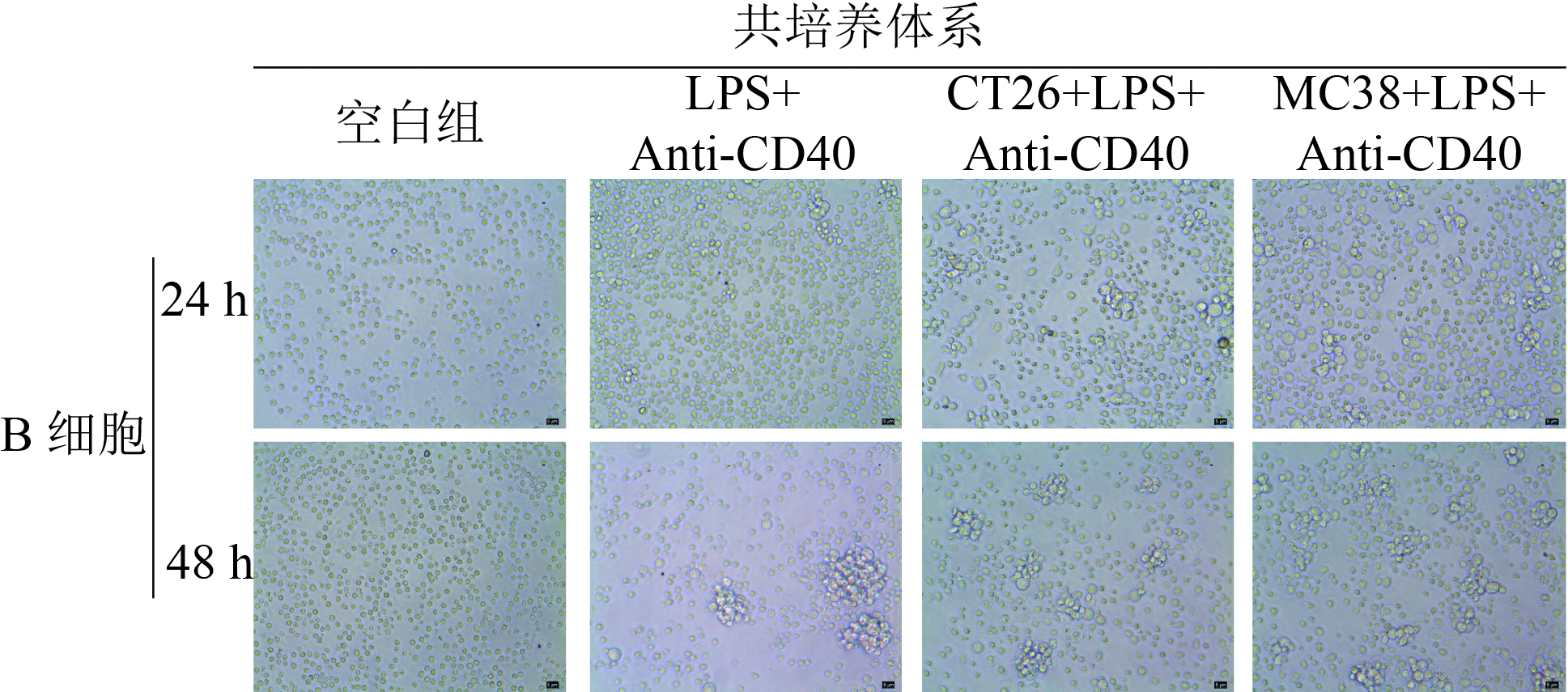
|
[1]
|
Zhou HB, Lei PJ, Padera TP. Progression of metastasis through lymphatic system[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(3):627. doi: 10.3390/cells10030627
|
|
[2]
|
Mizoguchi A, Mizoguchi E, Takedatsu H, et al. Chronic intestinal inflammatory condition generates IL-10-producing regulatory B cell subset characterized by CD1d upregulation[J]. Immunity, 2002, 16(2):219-230. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00274-1
|
|
[3]
|
Shang J, Zha HR, Sun YF. Phenotypes, functions, and clinical relevance of regulatory B cells in cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11:582657.
|
|
[4]
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3):209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
|
|
[5]
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(1):7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654
|
|
[6]
|
Gunderson LL, Jessup JM, Sargent DJ, et al. Revised TN categorization for colon cancer based on national survival outcomes data[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28(2):264-271. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.24.0952
|
|
[7]
|
Zhang C, Zhang L, Xu TL, et al. Mapping the spreading routes of lymphatic metastases in human colorectal cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1):1993. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15886-6
|
|
[8]
|
Karaman S, Detmar M. Mechanisms of lymphatic metastasis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2014, 124(3):922-928. doi: 10.1172/JCI71606
|
|
[9]
|
Ganti SN, Albershardt TC, Iritani BM, et al. Regulatory B cells preferentially accumulate in tumor-draining lymph nodes and promote tumor growth[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5:12255. doi: 10.1038/srep12255
|
|
[10]
|
Ruddell A, Harrell MI, Furuya M, et al. B lymphocytes promote lymphogenous metastasis of lymphoma and melanoma[J]. Neoplasia, 2011, 13(8):748-757. doi: 10.1593/neo.11756
|
|
[11]
|
Wang SS, Liu W, Ly D, et al. Tumor-infiltrating B cells: their role and application in anti-tumor immunity in lung cancer[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2019, 16(1):6-18. doi: 10.1038/s41423-018-0027-x
|
|
[12]
|
Rosser EC, Mauri C. Regulatory B cells: origin, phenotype, and function[J]. Immunity, 2015, 42(4):607-612. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.04.005
|
|
[13]
|
Pace G, Valeri V. Use of cocultures for the study of cellular interactions influencing B-cell regulatory functions[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2270:263-282.
|
|
[14]
|
Mion F, Martinis E, Pucillo CEM, et al. Purification of murine and human IL-10-producing B cells from different anatomical compartments[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2270:61-76.
|
|
[15]
|
Guo R, Wang WX, Yu LZ, et al. Different regulatory effects of CD40 ligand and B-cell activating factor on the function of B cells[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 91:107337. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107337
|
|
[16]
|
Lee-Chang C, Bodogai M, Martin-Montalvo A, et al. Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by resveratrol-mediated inactivation of tumor-evoked regulatory B cells[J]. J Immunol, 2013, 191(8):4141-4151. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300606
|
|
[17]
|
Premkumar K, Shankar BS. TGF-βR inhibitor SB431542 restores immune suppression induced by regulatory B-T cell axis and decreases tumour burden in murine fibrosarcoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2021, 70(1):153-168.
|
|
[18]
|
Qiu ZY, Li Q, Lu YX, et al. Clinical significance and prognostic value of circulating B10 cells in colorectal cancer[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol, 2022, 18(2):e157-e162.
|




 下载:
下载: