Application of the intelligent management platform for the whole course of cancer in patients with breast cancer
-
摘要:
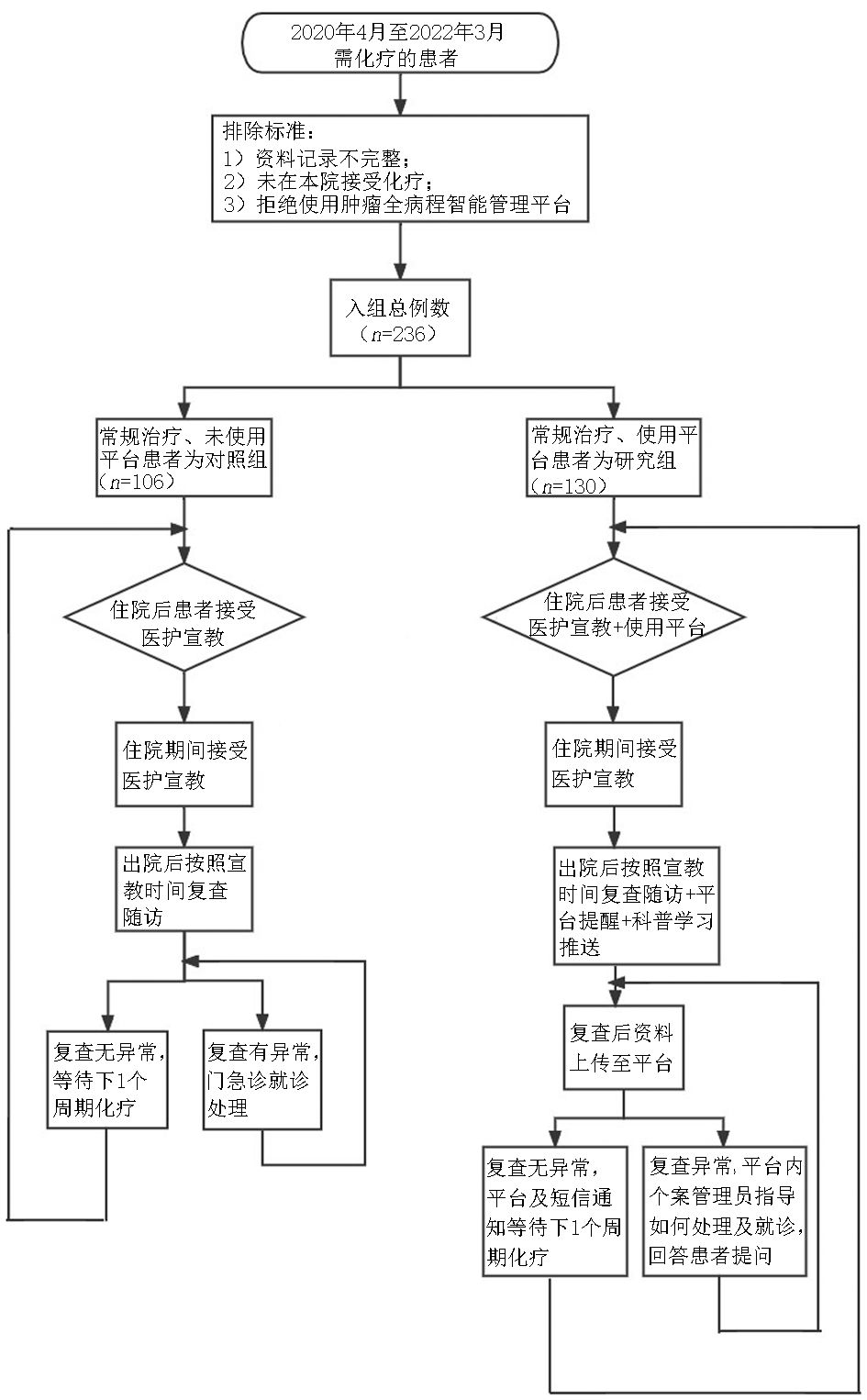
目的 探讨肿瘤全病程智能管理平台在乳腺癌化疗患者管理中的应用及效果。 方法 选取2020年4月至2022年3月于浙江大学医学院附属第一医院行乳腺癌术后化疗的患者236例,分为研究组130例及对照组106例,评价使用该平台对于患者管理的效果。 结果 研究组中患者化疗后出现中性粒细胞低合并发热的例数及其住院例数、严重不良反应导致住院例数均减少,对化疗不良反应处理的及时性有优势,与对照组相比差异均具有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。 结论 该平台应用于乳腺癌化疗患者的管理中,有利于督促患者及时就诊,减少严重不良反应导致住院的例数,促进患者康复。 -
关键词:
- 肿瘤全病程智能管理平台 /
- 乳腺癌 /
- 化疗 /
- 不良反应 /
- 住院例数
Abstract:Objective To explore the application of the intelligent management platform for the whole course of cancer in the management of patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Methods From April 2020 to March 2022, 236 patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy in The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine were enrolled. There were 130 and 106 patients in the study and control groups, respectively, to evaluate the effectiveness of using this platform for patient management. Results The number of neutropenia with fever cases, the number of hospitalized patients, and the number of hospitalized patients with severe adverse reactions decreased in the study group compared with those in the control group, and had an advantage in receiving timely treatment for adverse reactions of chemotherapy. The above data showed statistically significant differences between the two groups (P<0.05). Conclusions The platform was able to aid in the management of patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy, which is conducive to urging patients to visit the doctor in time, reduce the number of patients with serious adverse reactions, and promote the rehabilitation of patients. -
表 1 两组患者一般资料的比较
项目 对照组(n=106) 研究组(n=130) χ² P 年龄(岁) 0.60 0.44 <50 55(51.89) 74(56.92) ≥50 51(48.11) 56(43.08) 学历 0.03 0.87 高中以下 47(44.34) 59(45.38) 高中及以上 59(55.66) 71(54.62) 婚姻 0.01 0.92 已婚 95(89.62) 117(90.00) 未婚、离婚或丧偶 11(10.38) 13(10.00) 新辅助化疗 1.05 0.31 是 27(25.47) 41(31.54) 否 79(74.53) 89(68.46) 术后病理TNM分期(期) 2.06 0.56 Ⅰ 37(34.91) 44(33.85) Ⅱ 54(50.94) 73(56.15) Ⅲ 12(11.32) 12(9.23) Ⅳ 3(2.83) 1(0.77) HR阳性 0.42 0.52 是 65(61.32) 85(65.38) 否 41(38.68) 45(34.62) HER-2阳性 0 0.96 是 38(35.85) 47(36.15) 否 68(64.15) 83(63.85) 三阴性乳腺癌 0.09 0.77 是 22(20.75) 25(19.23) 否 84(79.25) 105(80.77) Ki-67数值(%)* 0.01 0.90 ≤20 26(24.53) 31(23.85) >20 80(75.47) 99(76.15) 采用一级预防 0.32 0.57 是 52(49.06) 59(45.38) 否 54(50.94) 71(54.62) ( )内单位为%;*:本院病理科将20%作为Ki-67高低表达的区分值 表 2 两组患者化疗方案的比较
化疗方案 对 照 组(n=106) 研究组(n=130) AC 4(3.77) 7(5.38) AC-T 38(35.85) 47(36.16) AC-TH 3(2.83) 3(2.31) AC-THP 7(6.60) 5(3.85) TC 20(18.87) 22(16.92) TCH 5(4.72) 2(1.54) TCb 0 2(1.54) TCbH 6(5.66) 9(6.92) TCbHP 11(10.38) 15(11.54) TH 0 7(5.38) 其他 12(11.32) 11(8.46) ( )内单位为%;A:蒽环类; C:环磷酰胺; T:紫杉类; Cb:卡铂; H:曲妥珠单抗; P:帕妥珠单抗 表 3 两组化疗方案的完成率和复查依从性的比较
项目 对照组(n=106) 研究组(n=130) χ² P 化疗方案完成率 0 1.00 完成+化疗进行中 104(98.11) 128(98.46) 未完成 2(1.89) 2(1.54) 复查依从性 - 0.42 每次都复查 105(99.06) 127(97.69) 偶尔不复查 1(0.94) 3(2.31) 经常不复查 0 0 从不复查 0 0 ( )内单位为% 表 4 两组中化疗不良反应的比较
项目 对照组(n=106) 研究组(n=130) χ² P 出现不良反应 2.26 0.13 是 97(91.51) 125(96.15) 否 9(8.49) 5(3.85) 因严重不良反应导致住院 6.02 0.01 有 17(16.04) 8(6.15) 无 89(83.96) 122(93.85) 出现中性粒细胞低合并发热 4.12 0.04 是 16(15.09) 9(6.92) 否 90(84.91) 121(93.08) 因不良反应更改或推迟化疗方案 2.15 0.14 是 10(9.43) 6(4.62) 否 96(90.57) 124(95.38) ( )内单位为% -
[1] 胡佳琪,耿怡丹,张玺,等.个案管理模式在乳腺癌患者中的应用研究进展[J].承德医学院学报,2022,39(2):159-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6879.2022.2.cdyxyxb202202020 [2] 张怡,梁悦.乳腺癌致病因素及早期诊断研究进展[J].首都食品与医药,2016,23(16):27-29. [3] 王宏.乳腺癌个案管理提高化疗完成率临床应用效果[J].岭南现代临床外科,2016,16(4):413-415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2016.04.010 [4] Basch E, Deal AM, Kris MG, et al. Symptom monitoring with patient-reported outcomes during routine cancer treatment: a randomized controlled trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(6):557-565. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.0830 [5] Jin LJ, Zhao YY, Wang P, et al. Efficacy of the whole-course case management model on compliance and satisfaction of breast cancer patients with whole-course standardized treatment[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022:2003324. [6] Chai Y, Li L, Wu YL, et al. The effects of case management for breast cancer patients: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2022, 101(9):e28960. [7] Tolstrup LK, Pappot H, Bastholt L, et al. Patient-reported outcomes during immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma: mixed methods study of patients' and clinicians' experiences[J]. J Med Internet Res, 2020, 22(4):e14896. [8] 周建红,罗文苹,张日光,等.聚乙二醇化重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子的临床应用进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(15):3067-3072. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.15.029 [9] 蒋向玲,陈春兰,覃惠英,等.肿瘤个案管理模式在鼻咽癌患者全程管理中的实践效果[J].中国实用护理杂志,2019,35(29):2274-2279. [10] Bennett AV, Jensen RE, Basch E. Electronic patient-reported outcome systems in oncology clinical practice[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2012, 62(5):337-347. [11] Seow H, Sussman J, Martelli-Reid L, et al. Do high symptom scores trigger clinical actions? An audit after implementing electronic symptom screening[J]. J Oncol Pract, 2012, 8(6):e142-e148. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2011.000525 [12] Kroenke K, Krebs EE, Wu JW, et al. Telecare collaborative management of chronic pain in primary care: a randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 2014, 312(3):240-248. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.7689 [13] 邓婷,巴一.肿瘤患者支持治疗的进展[J].中国肿瘤临床,2022,49(9):434-437. [14] Berry DL, Blumenstein BA, Halpenny B, et al. Enhancing patient-provider communication with the electronic self-report assessment for cancer: a randomized trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(8):1029-1035. [15] Iivanainen S, Alanko T, Vihinen P, et al. Follow-up of cancer patients receiving anti-PD-(L)1 therapy using an electronic patient-reported outcomes tool (KISS): prospective feasibility cohort study[J]. JMIR Form Res, 2020, 4(10):e17898. -




 下载:
下载: