-
摘要:
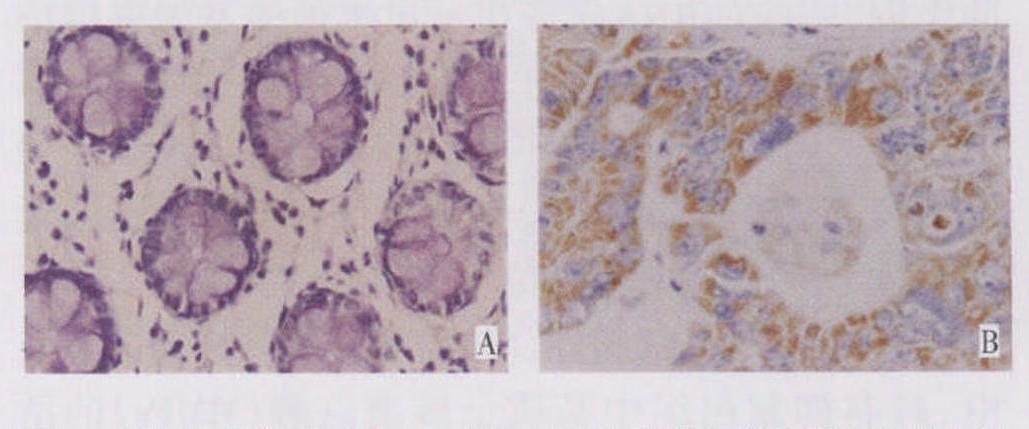
目的 探讨miR-222(Homo sapiens miR-222)与基质金属蛋白酶抑制因子3(Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3, TIMP3)在胃癌组织中的表达及其临床意义。 方法 分别运用原位杂交、免疫组化检测胃癌组织及癌旁组织中miR-222与TIMP3的表达水平, 分析miR-222、TIMP3之间的相关性以及与胃癌临床病理参数的关系。 结果 原位杂交检测显示, 在62例胃癌组织中miR-222阳性表达率为86.67%, 与癌旁对照组22.58%比较, 差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。免疫组化结果显示, 在62例胃癌组织中TIMP3阳性表达率为19.35%, 与癌旁对照组75.81%比较, 差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。相关性分析表明, miR-222的表达与TIMP3的表达呈负相关(P < 0.05);光密度值检测发现, miR-222的表达随着胃癌临床分期和浸润深度的演进而增加, 且胃癌中有淋巴结转移的miR-222的表达显著高于无淋巴结转移组(P < 0.01);TIMP3的表达随着胃癌临床分期和浸润深度的演进而下调, 胃癌中有淋巴结转移的TIMP3的表达均显著低于无淋巴结转移组(P < 0.01)。 结论 在胃癌组织中高表达的miR-222和TIMP3蛋白低表达可能是胃黏膜恶性转变以及胃癌发生浸润转移的重要生物学标志, 检测miR-222和TIMP3对预测结肠癌浸润转移有重要意义。 -
关键词:
- 微小RNA /
- 基质金属蛋白酶抑制因子3 /
- 胃癌 /
- 临床意义
Abstract:Objective To investigates the expression of miR-222 and TIMP3 in gastric cancer, as well as their clinical significance. Methods In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry were used to detect the expression of miR-222 and TIMP3 in gastric cancer specimens, respectively.The correlations among the miR-222, TIMP3 protein, and clinicopathological parameters of gastric cancer were analyzed. Results In situ hybridization showed that the positive expression rate of miR-222 was 86.67 % and 22.58%in gastric cancer and the adjacent tissue, respectively.In the assay of immunohistochemistry, the positive expression rate of TIMP3 was 19.35 % and 75.81 % in gastric cancer and the adjacent tissue, respectively.Significant differences(P < 0.01) were found between the two aforementioned groups.The correlation analysis indicated that the expression of miR-222 had a close negative correlation with that of TIMP3 in gastric cancer(P < 0.01).The up-regulation of miR-222 expression was associated with an advanced clinical stage, infiltrating depth, and lymph node metastasis in the cancer(P < 0.01).Conversely, the down-regulation of the TIMP3 expression was associated with an advanced clinical stage, infiltrating depth, and lymph node metastasis in the cancer(P < 0.01). Conclusion The high expression of miR-222 and the low expression of the TIMP3 protein may be important biological markers for malignant transformation in the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer.The detection of miR-222 and TIMP3 expression in gastric cancer is significantly important for improving the prediction of invasion and metastasis. -
Key words:
- MiR-222 /
- TIMP3 protein /
- Gastric cancer /
-
表 1 胃癌中miR-222和TIMP3表达与临床病理参数的关系
Table 1. Correlations of miR-222 and TIMP3 expression with pathological parameters of gastric cancer

表 2 胃癌组织miR-222和TIMP3蛋白之间的表达关系 例
Table 2. The relations between the expression of miR-222 and TIMP3 in gastric cancer

-
[1] Wong QW, Ching AK, Chan AW, et al. MiR-222 overexpression confers cell migratory advantages in hepatocellular carcinoma through enhancing AKT signaling [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2010, 16(3): 867-875. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1840 [2] Chun-Zhi Z, Lei H, An-Ling Z, et al. MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 regulate gastric carcinoma cell proliferation and radioresistance by targeting PTEN[J]. BMC Cancer, 2010, 10: 367. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-367 [3] Galardi S. Mercatelli N, Farace MG. et al. NF-kappa B and c-Jun induce the expression of the oncogenic miR-221 and miR-222 in prostate carcinoma and glioblastoma cells[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2011, 39(9): 3892-3902. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr006 [4] Röhrs S. Dirks WG. Meyer C. et al. Hypomethylauon and expression of BEX2, IGSF4 and TIMP3 indicative of MLL translocations in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Mol Cancer, 2009, 8: 86. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-86 [5] Masson D, Rioux-Ledercq N. Fergelot P. et al. Loss of expression of TIMP3 in dear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2010, 46(8): 1430-1437. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.01.009 [6] Garofalo M, Di Leva G, Romano G, et al. miR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation[J]. Cancer Cell. 2009, 16(6): 498-509. [7] Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, el al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers[J]. Nature, 2005, 435(7043): 834-838. doi: 10.1038/nature03702 [8] Rigoutsos I, Furnari F. Gene-expression forum: Decoy for microRNAs[J]. Nature, 2010, 465(7301): 1016-1017. doi: 10.1038/4651016a [9] Zhang L, Deng T, Li X, et al. microRNA-141 is involved in a nasopharyngeal carcinoma-related genes network[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2010, 31(4): 559-566. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp335 [10] Deng X, Bhagat S, Dong Z, et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase -3 induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells and confers increased sensitivity to paclitaxel[J]. Eur J Cancer. 2006, 42(18): 3267-3273. [11] 谭志琴, 刘伏香, 唐海林, 等. 子宫内膜癌患者血清中hsa-miR-155的表达及其临床意义[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2010, 45(10): 772-774. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2010.10.012 -




 下载:
下载: