-
摘要:
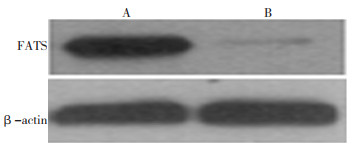
目的 研究脆性位点相关抑癌基因(fraglie-site associated tumor suppressor, FATS)在非小细胞肺癌以及癌旁正常组织的mRNA和蛋白表达水平, 探讨FATS在非小细胞肺癌发生发展中的作用。 方法 通过实时定量PCR技术和Western blot技术分析检测天津医科大学附属肿瘤医院2003年5月至2007年10月间91例非小细胞肺癌患者FATS基因和蛋白表达水平, 并且研究其表达水平与患者临床预后的关系。 结果 实时定量PCR和Western blot结果均显示非小细胞肺癌患者肿瘤组织FATS表达量明显低于其配对的癌旁正常组织(P=0.001)。FATS基因低表达患者与高表达患者在总生存期差异有统计学意义(P=0.030)。Cox多因素分析显示FATS基因的表达是非小细胞肺癌独立的预后因素(OR=2.250;95%CI: 1.054~4.805;P=0.036)。 结论 FATS低表达与非小细胞肺癌的发生发展具有高度相关性, FATS表达作为非小细胞肺癌的独立预后因素, 有望成为新的肿瘤标记物, 为临床诊治提供新的靶点。 Abstract:Objective To compare the levels of FATS mRNA and protein in non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC) and paired normal tissues and to investigate the function of FATS in NSCLC. Methods The mRNA and protein expression levels of the FATS gene in 91 NSCLC patients were determined using quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR(qRT-PCR) and Western blot analysis.The relationship between FATS expression and the prognosis of these patients was investigated. Results The qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis showed that FATS expression was significantly lower in NSCLC tissue than in the paired paraneoplastic tissue(P=0.001).The differences in the overall survival of patients with low and high FATS expression were statistically significant(P=0.030).Multivariate analysis indicated that the FATS expression was an independent prognostic factor for NSCLC(odds ratio, 2.250;95%confidence interval, 1.054-4.805;P=0.036). Conclusion FATS expression is clinically significant and appears to be a new independent marker for NSCLC. -
Key words:
- NSCLC /
- Prognosis /
- FATS /
- mRNA expression
-
表 1 FATS mRNA在NSCLC及癌旁正常组织的表达量 x±s
Table 1. FATS mRNA expression in NSCLC specimens and normal lung tissue

表 2 FATS表达与临床病理因素的关系 例
Table 2. Association of FATS expression with clinical characteristics

表 3 NSCLC患者总生存期Cox多因素分析及3年生存率
Table 3. Cox multivariate analysis of OS and 3-year DFS of NSCLC patients

-
[1] Grills C, Jithesh PV, Blayney J, et al. Gene expression meta-analysis identifies VDAC1 as a predictor of poor outcome in early stage non-small cell lung cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(1): el4635. http://uir.ulster.ac.uk/33864/1/2011-0131-plos-one-VDAC1-lung-journal.pone.0014635.PDF [2] Maione P, Rossi A, Sacco PC, et al. Advances in chemotherapy in advanced non—small—cell lung cancer[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother, 2010, 11(18): 2997-3007. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.511615 [3] Pfister DG, Johnson DH, Azzoli CG, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology treatment of unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer guideline: update 2003[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(2): 330-353. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.09.053 [4] Oliver TG, Mercer KL, Sayles LC, et al. Chronic cisplatin treatment promotes enhanced damage repair and tumor progression in a mouse model of lung cancer[J]. Genes Dev, 2010, 24(8): 837-852. doi: 10.1101/gad.1897010 [5] Li Z, Zhang Q, Mao JH, et al. An HDACl—binding domain within FATS bridges p21 turnover to radiation—induced tumorigenesis[J]. Oncogene, 2010, 29(18): 2659-2671. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.19 [6] Giangreco A, Groot KR, Janes SM. Lung cancer and lung stem cells: strange bedfellows[J]? Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2007, 175 (6): 547-553. [7] Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming(seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2007, 2(8): 706-714. [8] Gasser S, Raulet D. The DNA damage response, immunity and cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2006, 16(5): 344-347. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.07.004 [9] Drusco A, Pekarsky Y, Costinean S, et al. Common fragile site tumor suppressor genes and corresponding mouse models of cancer[J]. J Biomed Biotechnol, 2011, 984505. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/6dc2/1c7929caa9554137b96520d9b6a6dc8a48dd.pdf [10] Zhang X, Zhang Q, Zhang J, et al. FATS is a transcriptional target of p53 and associated with antitumor activity[J]. Mol Cancer, 2010, 16(9): 244. doi: 10.1186%2F1476-4598-9-244.pdf -




 下载:
下载: