In Vitro Effect of TNF-α Expression Induced by Bradykinin in Glioma Cells on the Blood-Tumor Barrier
-
摘要:
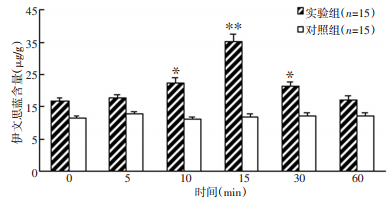
目的 探讨缓激肽(bradykinin,BK)诱发胶质瘤细胞释放的肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)对体外血瘤屏障的影响及其作用机制。 方法 分别用缓激肽和生理盐水作用于C6胶质瘤细胞及神经胶质细胞后,放射免疫法检测0、5、10、15、30和60 min时培养液内TNF-α的浓度。用原代培养的脑微血管内皮细胞(BMEC)和C6细胞共培养构建血瘤屏障模型。将缓激肽处理C6细胞不同时间点的条件培养液(C6CM)作用于屏障模型后,动态观察屏障的通透性及跨内皮阻抗(TER)的改变,并用免疫荧光技术检测脑微血管内皮细胞的紧密连接蛋白occludin的表达,RT-PCR法检测屏障模型脑微血管内皮细胞中核因子-κB(NF-κB)的变化。 结果 缓激肽作用于C6细胞后,培养液内TNF-α浓度较对照组明显增加(P < 0.05),而神经胶质细胞无明显变化。C6CM作用于血瘤屏障模型后,血瘤屏障通透性增加,跨内皮阻抗减小,而内皮细胞间的紧密连接蛋白occludin表达和核因子-κB的转录水平降低,直至30min后NF-κB转录水平逐渐增强。 结论 缓激肽诱发了胶质瘤细胞释放TNF-α,释放的TNF-α可通过NF-κB影响紧密连接蛋白occludin表达而影响血瘤屏障通透性。 Abstract:Objective To assess the in vitro effect and mechanism of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF - α) expression induced by bradykinin (BK) in glioma cells on the blood-tumor barrier (BTB). Methods A radioimmunoassay was used to dynamically monitor the TNF-α content in a nutrient fluid at 0, 5, 10, 15, 30, and 60 min time points after BK treatment of C6 cells and glial cells. An in vitro BTB model was established using a coculture of brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMEC) and C6 cells. The effect of a BK- treated C6 conditioned medium (C6CM) on the levels of nuclear transcription factor kappa B (NF - κB) mRNA was investigated by PCR. The occludin expression, as well as the transendothelial resistance (TER) and permeability of BTB, was also investigated via the immunofluorescence technique. Results The TNF-α content in the nutrient fluid of the C6 cells clearly increased after BK treatment compared with that of the control group; however, the glial cells showed no such result. C6CM acted on BTB in vitro, resulting in the decrease in the NF - κB mRNA and occludin expression levels until the minimum was reached at 15 min. Meanwhile, the permeability of BTB increased, whereas TER decreased. Conclusion BK induced the C6 cells to release TNF-α. TNF-α in turn inhibited NF-κB transcription and reduced the occludin expression. These mechanisms may explain the effects of TNF-α on the opening of BTB using BK. -
Key words:
- Bradykinin /
- Tumor necrosis factor-α /
- Blood-tumor barrier model /
- Tight junction protein
-
表 1 缓激肽处理不同时间C6细胞培养液中TNF-α含量变化(μg/L,x±s,n=15)
Table 1. Contents of TNF-α in the nutrient fluid of C6 cells by BK(μg·L-1, x±s, n=15)

-
[1] Côté J, Savard M, Bovenzi V, et al. Selective tumor blood-brain barrier opening with the kinin B2 receptor agonist[Phe(8)psi(CH(2) NH)Arg(9)]-BK in a F98 glioma rat model: an MRI study[J]. Neuropeptides, 2010, 44(2): 177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.12.009 [2] Qin LJ, Gu YT, Zhang H, et al. Bradykinin-induced blood-tumor barrier opening is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2009, 450 (2): 172-175. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.10.080 [3] Hurst RD, Fritz IB. Properties of an immortalized vascular endothelial/ glioma cell co-culture model of the blood-brain barrier[J]. J Cell Physiol, 1996, 167(1): 81-88. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199604)167:1<81::AID-JCP9>3.0.CO;2-8 [4] Harford-Wright E, Lewis KM, Vink R. Towards drug discovery for brain tumours: interaction of kinins and tumours at the blood brain barrier interface[J]. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov, 2011, 6(1): 31-40. doi: 10.2174/157488911794079118 [5] Thompson EM, Frenkel EP, Neuwelt EA. The paradoxical effect of bevacizumab in the therapy of malignant gliomas[J]. Neurology, 2011, 76(1): 87-93. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318204a3af [6] Raslan F, Schwarz T, Meuth SG, et al. Inhibition of bradykinin receptor B1 protects mice from focal brain injury by reducing blood– brain barrier leakage and inflammation[J]. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metabol, 2010, 30(8): 1477-1486. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.28 [7] Zweckberger K, Plesnila N. Anatibant, a selective non-peptide bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, reduces intracranial hypertension and histopathological damage after experimental traumatic brain injury[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2009, 454(2): 115-117. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.02.014 [8] Qin LJ, Gu YT, Zhang H, et al. Bradykinin-induced blood-tumor barrier opening is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2009, 450(2): 172-175. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.10.080 [9] Wachtel M, Bolliger MF, Ishihara H, et al. Down-regulation of occludin expression in astrocytes by tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is mediated via TNF type-1 receptor and nuclear factor-kappaB activation[J]. J Neurochem, 2001, 78(1): 155-162. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00399.x [10] Kazumasa M, Mikio F, Yoshida Y, et al. Molecular architecture of tight junctions of periderm differs from that of the maculae occludentes of epidermis[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2002, 118(6): 1073-1079. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.01774.x -




 下载:
下载: