Significance of Th17 and FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cells in Pathogenesis of Gastric Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma
-
摘要:
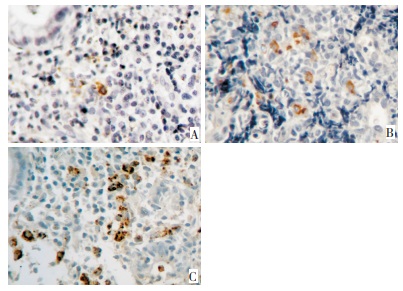
目的 探讨Th17和FOXP3+T(Treg)阳性细胞在慢性胃炎、淋巴细胞性胃炎和胃黏膜相关淋巴组织(MALT)淋巴瘤中的意义。 方法 采用免疫组织化学方法检测18例慢性胃炎、17例淋巴细胞性胃炎和18例低度恶性胃MALT淋巴瘤组织中Th17及FOXP3+T细胞的表达情况。 结果 Th17在慢性胃炎组、淋巴细胞性胃炎组和胃MALT淋巴瘤组阳性细胞数分别为(11.2±2.4)、(15.1±5.3)和(16.8±5.4)个/每高倍镜视野,胃MALT淋巴瘤与慢性胃炎相比,差别有统计学意义(P < 0.05),但胃MALT淋巴瘤与淋巴细胞性胃炎间差别无统计学意义(P>0.05)。FOXP3+T在慢性胃炎组、淋巴细胞性胃炎组和胃MALT淋巴瘤组的细胞数分别为(5.1±2.7)、(22.4±4.0)和(30.8±7.2)个/每高倍镜视野,三组间两两比较差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。FOXP3+T和Th17细胞数量改变在胃MALT淋巴瘤组呈正相关(R=0.308,P < 0.05)。 结论 FOXP3+T和Th17细胞数量在淋巴细胞性胃炎和胃MALT淋巴瘤组织中增多,可能在胃MALT淋巴瘤的发生、发展过程中发挥作用。 -
关键词:
- Th17细胞 /
- FOXP3+调节T细胞 /
- 胃黏膜相关淋巴组织淋巴瘤 /
- 免疫组织化学
Abstract:Objective To investigate the role of Th17 and Treg in chronic gastritis, lymphocytic gastritis, and low-grade gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. Methods The expression of FOXP3+Treg and Th17 in 18 chronic gastritis, 17 lymphocytic gastritis, and 18 gastric MALT lymphoma cases were detected by immunohistochemical staining. Results IL-17 expression increased in the chronic gastritis, lymphocytic gastritis, and gastric MALT lymphoma cases. However, no statistical significance was found in IL-17 expression between lymphocytic gastritis and gastric MALT lymphoma. The expression of FOXP3+Treg cells increased in the chronic gastritis, lymphocytic gastritis, and gastric MALT lymphoma cases (P < 0.05) (corresponding to 30.8 ± 7.2, 22.4 ± 4.0, and 5.1 ± 2.7 per high magnification field, respectively). The density of FOXP3+Treg cells was positively correlated with the expression of IL-17 (r = 0.308, P < 0.05). Conclusion Th17 and Treg may play certain roles in the development of gastric MALT lymphoma. -
表 1 53例病例的临床资料
Table 1. Clinical data of 53 patients

表 2 IL-17和FOXP3+在胃MALT淋巴瘤、淋巴细胞性胃炎和慢性胃炎组织中的表达
Table 2. IL-17 and FOXP3+ expression in gastric MALT lymphoma, lymphocytic gastritis, and chronic gastritis

-
[1] Otter R, Bieger R, Kluin PM, et al. Primary gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in a population-based registry[J]. Br J Cancer, 1989, 60(5): 745-755. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.351 [2] 龚非力. 医学免疫学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 287-296. [3] De Panfilis G, Campanini N, Santini M, et al. Phase-and-stage-related proportions of T cells bearing the transcription factor FOXP3 infiltrate primary melanoma[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2008, 128(3): 676-684. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701046 [4] Strzêpa A, Szczepanik M. IL-17-expressing cells as a potential therapeutic target for treatment of immunological disorders[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2011, 63(1): 30-44. doi: 10.1016/S1734-1140(11)70396-6 [5] Muranski P, Restifo NP. Does IL-17 promote tumor growth[J]. Blood, 2009, 114(2): 231-232. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-215541 [6] Asenjo LM, Gisbert JP. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric MALT lymphoma: a systematic review[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2007, 99(7): 398-404. http://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/diges/v99n7/original5.pdf [7] Kryezek I, Banerjee M, Cheng P, et al. Phenotype, distribution, generation, and functional and clinical relevance of Th17 cells in the human tumor environments[J]. Blood, 2009, 114(6): 1141-1149. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-208249 [8] Kimang'a A, Revathi G, Kariuki S, et al. IL-17A and IL-17F Gene Expression is Strongly Induced in the Mucosa of H. pylori-Infected Subiects From Kenya and Germany[J]. Basic Immunol, 2010, 72(6): 522-528. [9] Shiomi S, Toriie A, Imamura S, et al. IL-17 is involved in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric inflammatory Responses in a Mouse Model[J]. Helicobacter, 2008, 13(6): 518-424. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2008.00629.x [10] 李晓红, 陆秀芳. IL-17在卵巢上皮性癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 中国现代医药志, 2010, 12(10): 52-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHTY201010027.htm [11] 董林, 王艳萍, 王金良, 等. FOXP3的结构、表达调控及在免疫抑制中的功能研究[J]. 现代免疫学, 2011, 31(2): 164-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHMY201102017.htm [12] Kindlund B, Sjöling A, Hansson M, et al. FOXP3-expressing CD4(+) T-cell numbers increase in areas of duodenal gastric metaplasia and are associated to CD4(+) T-cell aggregates in the duodenum of Helicobacter pylori-infected duodenal ulcer patients[J]. Helicobacter, 2009, 14(3): 192-201. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2009.00673.x [13] Kandulski A, Wex T, Kuester D, et al. Naturally occurring regulatory T cells (CD4+, CD25high, FOXP3+) in the antrum and cardia are associated with higher H. pylori colonization and increased gene expression of TGF-betal[J]. Helicobacter, 2008, 13(4): 295-303. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2008.00612.x -




 下载:
下载: