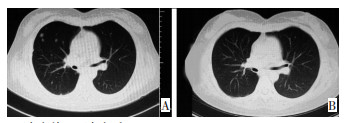
-
-
表 1 埃克替尼治疗23例晚期NSCLC早期临床疗效观察 例(%)
Table 1. Early efficacy of icotinib in 23 advanced NSCLC cases

-
[1] Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 361(10): 947-957. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810699 [2] Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study [J]. Lancet Oncol, 2011, 12(8): 735-742. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70184-X [3] Sun Y, Shi Y, Zhang L, et al. A randomized, double-blind phase Ⅲ study of icotinib versus gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) previously treated with chemotherapy (ICOGEN)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(Suppl): Abstr 7522. [4] Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Collaborative Group. Chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis using updated data on individual patients from 52 randomised clinical trials[J]. BMJ, 1995, 311 (7010): 899-909. doi: 10.1136/bmj.311.7010.899 [5] Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med. 2002, 346(2): 92-98. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011954 [6] Schlessinger J. Ligand-induced, receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor[J]. Cell, 2002, 110(6): 669-672. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00966-2 [7] Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM. Lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med. 2008, 359(13): 1367-1380. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0802714 [8] 王岩, 徐建明, 宋三泰. 表皮生长因子受体靶向药物作用机制与相关标志物的研究进展[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2005, 27(9): 573-576. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0253-3766.2005.09.019 [9] Miller VA, Kris MG, Shah N, et al. Bronchioloalveolar pathologic subtype and smoking history predict sensityvity to gefitinib in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(6): 1103-1109. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.08.158 [10] Mitsudomi T, Kosaka T, Endoh H, et al. Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene predict prolonged survival after Gefitinib treatment in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with postoperative recurrence[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2005, 23(11): 2513-2520. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.00.992 [11] Tokumo M, Toyooka S, Kiurs K, et al. The relationship between epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and clinicopathologic features in non-small cell lung cancers[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2005, 11 (3): 1167-1173. http://ousar.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/files/public/0/8531/20160527182727445879/K003003.pdf [12] Tan F, Shen X, Wang D, et al. Icotinib (BPI-2009H), a novel EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, displays potent efficacy in preclinical studies [J]. Lung Cancer, 2012, 76(2): 177-182. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.10.023 [13] Tamura K, Fukuoka M. Gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. . Expert Opin Pharmacother, 2005, 6(6): 985-993. doi: 10.1517/14656566.6.6.985 [14] 周道平, 聂国庆. 吉非替尼治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌临床观察[J]. 安徽医学, 2008, 29(2): 163-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYX200802029.htm -




 下载:
下载: