Prognostic Significance of Preoperative Serum Albumin Levels in Patients with Rectal Carcinoma
-
摘要:
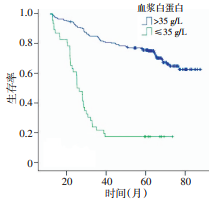
目的 观察直肠癌患者术前血清白蛋白水平的预后意义, 并探讨其可能机制。 方法 依据术前血清白蛋白水平, 将2004年1月至2007年6月于哈尔滨医科大学附属第三医院接受直肠癌根治术的338例患者分为两组: A组, 血清白蛋白≤35 g/L; B组, 血清白蛋白 > 35 g/L, 并对两组的临床病理特征进行统计学分析, 以比较两组患者间的预后及临床病理特征差异。 结果 统计结果显示血清白蛋白水平与肿瘤直径及浸润深度相关(P < 0.05);A组直肠癌患者5年生存率显著低于B组患者(P < 0.001);并且在多因素分析模型中, 术前血清白蛋白水平是影响接受直肠癌根治术的患者术后生存期的独立预后因素(P < 0.001)。 结论 术前血清白蛋白水平是影响直肠癌根治术患者总生存期的重要指标。 Abstract:Objective The objectives of this study were to determine the relationship between the level of preoperative serum albumin in rectal carcinoma patients and their postoperative overall survival as well as discuss the probable underlying mechanism. Methods Based on their preoperative serum albumin levels, 338 rectal carcinoma patients who underwent radical surgery from 2004 to 2007 in the Third Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University were included in this study. They were divided into two groups (group A: serum albumin, ≤35 g/L; group B: serum albumin, > 35 g/L), which we compared in univariate and multivariate statistical models. We then analyzed differences in their clinical pathological features and prognosis. Results The statistical results showed that the level of serum albumin is correlated with the diameter and the depth of infiltration of the rectal carcinoma (P < 0.05). The 5-year overall survival of the patients from group A was remarkably shorter than that of the patients from group B (P < 0.001). According to the multivariate analy- sis, the level of preoperative serum albumin served as an independent prognostic factor in the patients who underwent radical resection of their rectal carcinoma (P < 0.001). Conclusion The level of preoperative serum albumin is an independent prognostic factor correlated with the postoperative overall survival of rectal carcinoma patients. -
Key words:
- Rectal carcinoma /
- Serum albumin /
- Prognosis
-
表 1 直肠癌患者术前血清白蛋白水平与临床病理特征的关系 例
Table 1. Relationship between preoperative serum albumin levels and clinical pathological features of rectal carcinoma patients

表 2 直肠癌术后预后相关因素的多因素分析
Table 2. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in patients with rectal carcinoma

-
[1] Bauer J, Capra S. Comparison of a malnutrition screening tool with subjective global assessment in hospitalised patients with cancer-sensitivity and specificity[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr, 2003, 12(3): 257-260. [2] Fuhrman MP, Charney P, Mueller CM. Hepatic proteins and nutrition assessment[J]. J Am Diet Assoc, 2004, 104(8): 1258-1264. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2004.05.213 [3] Alves A, Panis Y, Mathieu P, et al. Postoperative mortality and morbidity in French patients undergoing colorectal surgery: results of a prospective multicenter study[J]. Arch Surg, 2005, 140(3): 278-283. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.140.3.278 [4] Sarfati D, Hill S, Blakely T, et al. The effect of comorbidity on the use of adjuvant chemotherapy and survival from colon cancer: a retrospective cohort study[J]. BMC Cancer, 2009, 20(9): 116. [5] Elahi MM, McMillian DC, McArdle CS, et al. Score based on hypoalbunemia and elevated C-reactive protein predicts survival in patients with advanced gastrointestinal cancer[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2004, 48(2): 171-173. doi: 10.1207/s15327914nc4802_6 [6] Dixon MR, Haukoos JS, Udani SM, et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen and albumin predict survival in patients with advanced colon and rectal cancer[J]. Arch Surg, 2003, 138(9): 962-966. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.138.9.962 [7] Clark TG, Stewart ME, Altman DG, et al. A prognostic model for ovarian cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2001, 85(7): 944-952. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2001.2030 [8] Levis A, Ficara F, Marmont F, et al. Prognostic significance of serum albumin in chronic lymphocytic leukemia[J]. Haematologica, 1991, 76(2): 113-119. [9] Parker D, Alison DL, Barnard DL, et al. Prognosis in low grade Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: relevance of the number of sites involved, absolute lymphocyte count and serum immunoglobulin level[J]. Hematol Oncol, 1994, 12(1): 15-27. doi: 10.1002/hon.2900120104 [10] Lai CC, You JF, Yeh CY, et al. Low preoperative serum albumin in colon cancer: a risk factor for poor outcome[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2011, 26(4): 473-481. doi: 10.1007/s00384-010-1113-4 [11] Yeun JY, Kaysen GA. Factors influencing serum albumin in dialysis patients[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 1998, 32(6 Suppl 4): S118-S125. [12] Lohsiriwat V, Chinswangwatanakul V, Lohsiriwat S, et al. Hypoalbuminemia is a predictor of delayed postoperative bowel function and poor surgical outcomes in right-sided colon cancer patients[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr, 2007, 16(2): 213-217. [13] Al-Shaiba R, McMillan DC, Angerson WJ, et al. The relationship between hypoalbunemia, tumour volume and the systemic inflamatory response in patients with colorectal liver metastases[J]. Br J Cancer, 2004, 91(2): 205-207. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601886 [14] Koike Y, Miki C, Okugawa Y, et al. Preoperative C-reactive protein as a prognostic and therapeutic marker for colorectal cancer[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2008, 98(7): 540-544. doi: 10.1002/jso.21154 [15] Yuan XY, Zhang CH, He YL, et al. Is albumin administration beneficial in early stage of postoperative hypoalbuminemia following gastrointestinal surgery? A prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Am J Surg, 2008, 196(5): 751-755 doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.10.030 -




 下载:
下载: