Clinical value of low dose 99mTc-MIBI double phase tomographic imaging in diagnosis of breast cancer
-
摘要:
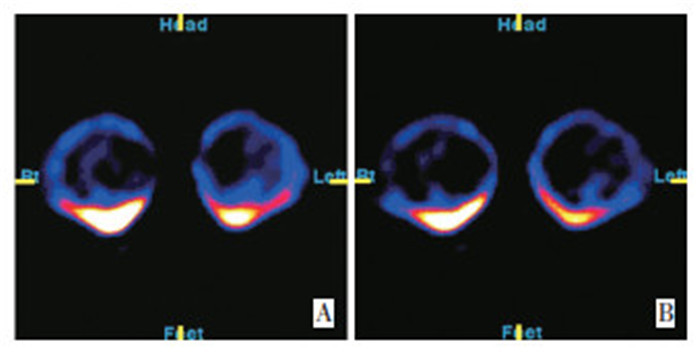
目的 探讨低剂量99mTc-甲氧基异丁基异腈(MIBI)半定量分析在乳腺断层双时相显像诊断乳腺癌中的临床意义。 方法 109例乳房肿块患者和26例正常对照者为临床研究对象, 使用自制乳腺显像装置进行早期和延迟图像采集, 图像行半定量分析(SQA), 并与病理检查结果对照。 结果 正常对照组、良性病变组、乳腺癌组的早期相T/NT比值分别为1.09±0.18、1.77±1.36、3.98±3.11, 3组比较, 差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。正常对照组的早期相与延迟相T/NT比值差异无统计学意义[(1.09±0.18)vs.(1.08±0.19), P > 0.05];良性病变组下降, 差异有统计学意义[(1.77±1.36)vs.(1.28±0.83), P < 0.05];乳腺癌组下降不明显, 差异无统计学意义[(3.98±3.11)vs.(3.04±2.46), P > 0.05]。半定量分析诊断乳腺癌的灵敏度为97.67%(42/43), 特异性为81.82%(54/66), 准确性为88.07%(96/109), 阳性预测值为77.78%(42/54), 阴性预测值为98.18%(54/55)。 结论 低剂量99mTc-MIBI乳腺断层双时相显像是诊断乳腺癌的一种行之有效的方法, 对鉴别乳腺良恶性病变有很好的临床应用价值。 -
关键词:
- 乳腺肿瘤 /
- 低剂量99mTc-MIBI /
- 半定量分析
Abstract:Objective This study aims to investigate the clinical significance of the semi-quantitative analysis of low-dose 99mTc-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile(MIBI) double phase tomographic imaging in breast cancer diagnosis. Methods A total of 109 patients with breast lesions and 26 normal breasts underwent double-phase 99mTc-MIBI tomographic imaging using a self-designed imaging device.The early and the delayed tumor to non-tumor ratios(T/NT) were calculated by semi-quantitative image analysis(SQA).The results were compared with that of the pathological results. Results The early phase T/NT ratios in the normal control, benign, and breast cancer groups were 1.09±0.18, 1.77±1.36, and 3.98±3.11, respectively.The difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05).The difference of the early and delayed phase T/NT ratios in the normal control group was not statistically significant(1.09±0.18 vs.1.08±0.19, > 0.05).The difference in the benign group was statistically significant(1.77±1.36 vs.1.28±0.83, P < 0.05), whereas that of the breast cancer group was not statistically significant(3.98±3.11 vs.3.04±2.46, P > 0.05).The sensitivity of the semi-quantitative analysis in the diagnosis of breast cancer was 97.67%, the specificity was 81.82%, and the accuracy was 88.07%.The positive and negative values were 77.78%(42/54) and 98.18%(54/55), respectively. Conclusion Low dose 99mTc-MIBI double-phase tomography imaging is an effective method to detect breast cancer, and has great clinical value in the differentiation of malignant and benign breast lesions. -
Key words:
- mammary neoplasms /
- low dose99mTc-MIBI /
- semi-quantitative analysis
-
表 1 109例乳腺肿块放射性浓聚显像情况
Table 1. Radioactive concentration imaging of breast mass in 109 cases

表 2 各组乳腺断层早期和延迟相T/NT比值
Table 2. T/NT ratios of the early and the delayed imaging in each group

表 3 9mTc-MIBI双时相断层显像半定量分析结果与组织病理学结果对照
Table 3. Contrast between the results of 99mTc-MIBI tomographic imaging and histopathology

-
[1] 文美玲. 99m Tc-MIBI乳腺断层双时相显像与乳腺钼靶X线照相在乳腺癌诊断中的价值[J]. 南华大学学报, 2008, 36(2): 175-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYYY200802009.htm [2] 刘保军, 李娟. 99m Tc-MIBI亲肿瘤显像对乳腺肿物良恶性鉴别诊断的价值[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2009, 31(1): 50-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNXY201912003.htm [3] Habib S, Maseeh-uz-Zaman, Hameed A, et al. Diagnostic accura cy of Tc-99m-MIBI for breast carcinoma in correlation with mam mography and sonography[J]. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak, 2009, 19(10): 622-626. [4] Kim IJ, Kim YK, Kim SJ. Detection and prediction of breast cancer using double phase Tc-99m MIBI scintimammography in compari son with MRI[J]. Onkologie, 2009, 32(10): 556-560. doi: 10.1159/000232316 [5] Berghammer P, Sinzinger H. The efficacy of 99m Tc-MIBI scinti mammography in the evaluation of breast lesions and axillary in volvement[J]. Hell J Nucl Med, 2011, 14(1): 83-84. [6] Ozülker T, Ozülker F, Ozpa aci T, et al. The efficacy of 99m Tc-MI BI scintimammography in the evaluation of breast lesions and axillary involvement: a comparison with X-rays mammography, ultra sonography and magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Hell J Nucl Med, 2010, 13(2): 144-153. [7] Huang D, Zhao F, Zhang Y. The clinical usefulness of 99m Tc-Tetro fosmin scintigraphy in the diagnosis of lung neoplasmas and medias tinal lymphoid node involvement[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Techno log Med Sci, 2008, 28(5): 608-612. doi: 10.1007/s11596-008-0527-5 [8] Sadeghi R, Zakavi SR, Forghani MN, et al. The efficacy of Tc-99m sestamibi for sentinel node mapping in breast carcinomas: comparison with Tc-99m antimony sulphide colloid[J]. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur, 2010, 13(1): 1-4. [9] Usmani S, Khan HA, Javed A, et al. Functional breast imaging with 99m Tc-Mibi for detection of primary breast lesion and axillary lymph node metastases[J]. Gulf J Oncolog, 2008, 7(4): 52-57. [10] DeCesare A, De Vincentis G, Gervasi S, et al. Single-photon-emis sion computed tomography(SPECT) with technetium-99m sestamibi in the diagnosis of small breast cancer and axillary lymph node involvement[J]. World J Surg, 2011, 35(12): 2668-2672. doi: 10.1007/s00268-011-1267-4 [11] Fallahi B, Beiki D, Mousavi SA, et al. 99m Tc-MIBI whole body scin tigraphy and P-glycoprotein for the prediction of multiple drug re sistance in multiple myeloma patients[J]. Hell J Nucl Med, 2009, 12(3): 255-264. [12] 刘保军, 李娟. 99m Tc-MIBI乳腺癌显像与P-gp、GST-π及Bcl-2表达的关系[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2009, 31(4): 435-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6309.2009.04.006 [13] Taibi N, Aka P, Kirsch-Volders M, et al. Radiobiological effect of 99mTechnetium-MIBI in human peripheral blood lymphocytes: ex vivo study using micronucleus/FISH assay[J]. Cancer Lett, 2006, 20(1): 68-78. -




 下载:
下载: