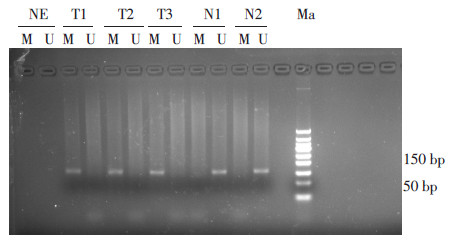
-
摘要:
目的 探讨胃癌组织中微小RNA-375(miRNA-375)基因表达与基因甲基化调控的相关性。 方法 2011年3月至8月在天津医科大学总医院通过胃镜检查收集90例新鲜组织活检标本, 分为2组, 胃癌组54例, 非癌对照组36例。应用实时荧光定量反转录PCR检测miRNA-375基因表达, 甲基化特异性PCR检测miRNA-375基因启动子区CpG岛甲基化。 结果 胃癌组miR NA-375基因表达下调, 与非癌对照组相比差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);胃癌组和非癌对照组miRNA-375基因启动子区高甲基化阳性率分别为62.96%(34/54)和22.22%(8/36), 差异有统计学意义(χ2=14.405, P < 0.05)。中高分化胃癌组织中miRNA-375基因表达高于低分化组, 差异有统计学意义(t=2.634, P=0.011);miRNA-375基因启动子区甲基化阳性率中高分化组与低分化组分别为44.44%(8/18)和72.22%(26/36), 差异有统计学意义(χ2=3.971, P=0.046)。 结论 癌组织中存在miRNA-375基因异常低表达及启动子区的高甲基化, miRNA-375基因高甲基化可能抑制miRNA-375基因表达, 在胃癌发生发展中发挥重要作用。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to explore aberrant DNA methylation of microRNA-375(miRNA-375) gene and its expression in gastric carcinoma tissues. Methods A total of 90 subjects were divided into two groups: gastric carcinoma(n=54) and non-cancer control(n = 36).The expression of miRNA-375 gene was detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction.The DNA methylation of the CpG island promoters of miRNA-375 was detected by the DNA methylation specific polymerase chain reaction in gastric carcinoma and non-cancer control mucosa. Results The expression of miRNA-375 in the gastric carcinoma significantly decreased compared with the non-cancer control(P=0.000, P < 0.05).The positive rate of the hypermethylation of miRNA-375 gene(62.96%) in the gastric carcinoma was significantly higher than that in the non-cancer control(22.22%)(χ2=14.405, P=0.000, P < 0.05).The expression of miRNA-375 gene in well-differentiated carcinoma was significantly higher than that in poorly differentiated carcinoma.A statistically significant difference was found between the two groups(t=2.634, P=0.011, P < 0.05).The positive rate of DNA hypermethylation of miRNA-375 gene(44.44%, 8/18) in well-differentiated carcinoma was significantly higher than that in poorly differentiated carcinoma(72.22%, 26/36)(χ2=3.971, P=0.046, P < 0.05). Conclusion The aberrant hypermethylation of the CpG island promoters of miRNA-375 gene and their lower expression in gastric carcinoma may play a crucial role in carcinogenesis and gastric carcinoma development. -
Key words:
- stomach neoplasms /
- microRNA /
- gene expression /
- methylation
-
表 1 胃癌组及非癌对照组miRNA-375基因的表达
Table 1. Expression of miRNA-375 gene in gastric carcinoma group and non-cancer control group

表 2 miRNA-375基因表达及基因甲基化与胃癌临床病理特征的关系
Table 2. The relationship of miRNA-375 gene expression and methylation with clinicopathological characteristics of gastric cancer

-
[1] He XX, Chang Y, Meng FY, et al. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growthin vitro and in vivo[J]. Oncogene, 2012, 31(28): 3357-3369. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.500 [2] Li X, Lin R, Li J. Epigenetic silencing of MicroRNA-375 regulatesPDK1 expression in esophageal cancer[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2011, 56(10): 2849-2856. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1711-1 [3] Wang F, Li Y, Zhou J, et al. MiR-375 Is Down-Regulated in Squamous Cervical Cancer and Inhibits Cell Migration and Invasion viaTargeting Transcription Factor SP1[J]. Am J Pathol, 2011, 179(5): 2580-2588. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.07.037 [4] Zhang X, Yan Z, Zhang J, et al. Combination of hsa-miR-375and hsa-miR-142-5p as a predictor for recurrence risk in gastriccancer patients following surgical resection[J]. Ann Oncol, 2011, 22(10): 2257-2266. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq758 [5] 周永宁, 徐采朴, 房殿春. CpG岛甲基化与胃肠道肿瘤[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2003, 11(01): 65-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXHB200301018.htm [6] Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets[J]. Proc NatlAcad Sci U S A, 2006, 103(7): 2257-2261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510565103 [7] Tsukamoto Y, Nakada C, Noguchi T, et al. MicroRNA-375 isdownregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival bytargeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta[J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(6): 2339-2349. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2777 [8] Ding L, Xu Y, Zhang W, et al. MiR-375 frequently downregulated in gastric cancer inhibits cell proliferation by targeting JAK2[J]. Cell Res, 2010, 20(7): 784-793. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.79 [9] O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, et al. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression[J]. Nature, 2005, 435(7043): 839-843. doi: 10.1038/nature03677 [10] Fabbri M. miRNAs and cancer epigenetics[J]. Curr Opin investingDrugs, 2008, 9(6): 583-590. [11] 刘文天, 焦焕利, 杨玉龙, 等. P16基因高甲基化在胃癌发展中的作用[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2007, 15(26): 2839-2843. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXHB200726020.htm [12] Boland CR, Shin SK, Goel A. Promoter methylation in the genesisof gastrointestinal cancer[J]. Yonsei Med J, 2009, 50(3): 309-321. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.3.309 [13] 李阳, 岳宏宇, 刘文天, 等. 胃癌组织中微RNA-34b/c和微RNA-124a基因的甲基化[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2011, 91(23): 1640-1642. [14] Tsukamoto Y, Nakada C, Noguchi T, et al. MicroRNA-375 isdownregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival bytargeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta[J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(6): 2339-2349. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2777 [15] Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Inoue N, et al. MicroRNA signatures inHelicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa[J]. INT J Cancer, 2011, 128(2): 361-370. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25348 -




 下载:
下载: