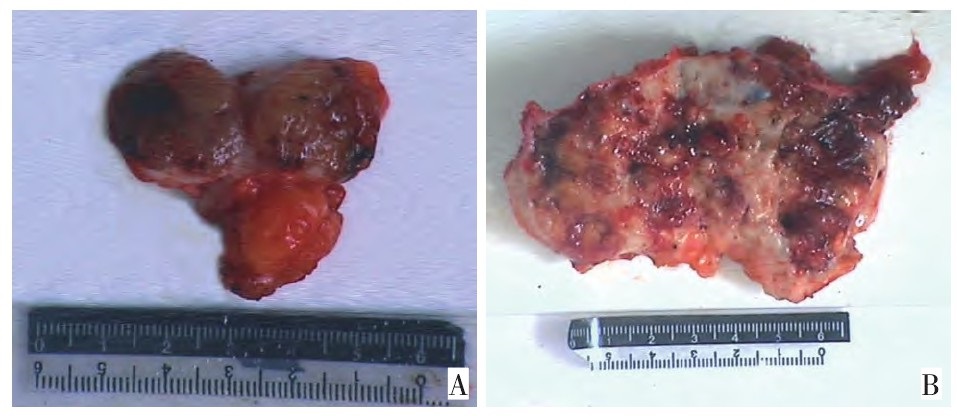
Clinicopathologic characteristics and molecular phenotype of breast mucinous carcinoma and its clinical significance
-
摘要:
目的 探讨乳腺黏液癌(mucinous carcinoma, MC)的临床病理特征、分子表型及预后情况。 方法 收集天津医科大学附属肿瘤医院2004年1月至2010年12月间经手术切除、病理证实的乳腺黏液癌242例, 并随机选取同时期的乳腺浸润性导管癌(invasive ductal carcinoma, IDC)300例作为对照, 回顾性分析其临床病理资料及预后情况。 结果 乳腺单纯型黏液癌与混合型黏液癌在淋巴结转移、超声诊断准确率、p53表达及无病生存率方面差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05), 而在年龄、月经状况、家族史、肿瘤直径、总生存率方面差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。乳腺黏液癌与浸润性导管癌的分子分型、总生存率、无病生存率差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 乳腺黏液癌预后较好, 单纯型黏液癌与混合型黏液癌有不同的临床病理特征及预后, 对乳腺黏液癌进行亚型分型对指导临床治疗及预测预后有重要意义。 Abstract:Objective To study the clinicopathologic characteristics, molecular phenotypes, and prognosis of breast mucinous carcinoma(MC). Methods Data from 242 metastatic breast cancer(MBC) patients who underwent surgery between January 2004 and December 2010 were reviewed.Cases of invasive ductal carcinoma(IDC) of the breast during the corresponding period were randomly selected as matched controls.The clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis were retrospectively analyzed. Results Statistical analysis showed that pure MC differed from mixed MC with respect to lymph node status, ultrasound diagnosis, and expression of p53 and disease-free survival rate(DFS)(P < 0.05).No significant difference was observed in terms of age, menstrual status, family history, tumor size, and overall survival rate(OS)(P > 0.05).MBC was associated with better OS and DFS than IDC, and their molecular phenotypes were significantly different(P < 0.05). Conclusion MBC has a better prognosis than IDC.Distinct clinicopathologic characteristics and prognoses exist for pure MC and mixed MC.Successful diagnosis of breast MC is critical for clinical treatment guidance and prognosis establishment. -
Key words:
- mucinous carcinoma(MC) of the breast /
- molecular phenotype /
- prognosis
-
表 1 单纯型和混合型黏液癌的临床病理特征比较
Table 1. Comparison of the clinical and pathological features of pure MC and mixed MC

-
[1] Bae SY, Choi MY, Cho DH, et al. Mucinous carcinoma of thebreast in comparisonwith invasive ductal carcinoma: clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis[J]. J Breast Cancer, 2011, 14(4): 308-313. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2011.14.4.308 [2] Bussolati G, Sapino A. Mucinous carcinoma and carcinomas withsigmet-ring-cell differentiation. In: Lakhani SR, Ellis OI, SchnittSJ, et al. WHO Classification of Tumors of the Breast[M]. Lyon: Editors IARC Press, 2012: 60-61. [3] Park S, Koo J, Kim JH, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics ofmucinous carcinoma of the breast in Korea: comparison with invasive ductal carcinoma-not otherwise specified[J]. Korean Med Sci, 2010, 25(3): 361-368. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.361 [4] Castaneda CA, Andrés E, Barcena C, et al. Behaviour of breast cancer molecular subtypes through tumour progression[J]. Clin TranslOncol, 2012, 14(6): 481-485. [5] Di Saverio S, Gutierrez J, Avisar E. A retrospective review withlong term follow up of 11, 400 cases of pure mucinous breast carcinoma[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2008, 111(3): 541-547. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9809-z [6] Li CI, Uribe DJ, Daling JR. Clinical characteristics of different histologic types of breast cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2005, 93(9): 1046-1052. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602787 [7] Bal A, Joshi K, Sharma SC, et al. Prognostic significance of micropapillary pattern in pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast[J]. Int JSurg Pathol, 2008, 16(3): 251-256. doi: 10.1177/1066896908314784 [8] Vo T, Xing Y, Meric-Bernstam F, et al. Long-term outcomes inpatients with mucinous, medullary, tubular, and invasive ductal carcinomas after lumpectomy[J]. Am J Surg, 2007, 194(4): 527-531. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.06.012 [9] Dhillon R, Depree P, Metcalf C, et al. Screen-detected mucinousbreast carcinoma: potential for delayed diagnosis[J]. Clin Radiol, 2006, 6l(5): 423-430. [10] Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, et al. Repeated observation ofbreast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003, 100(14): 8418-8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0932692100 [11] 张勤, 刘红. P53在三阴性乳腺癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2011, 38(4): 214-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2011.04.010 -




 下载:
下载: