Expression and significance of L1-CAM in invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast
-
摘要:
目的 探讨L1细胞黏附分子(L1 cell adhesion molecules, L1-CAM)在乳腺浸润性微乳头状癌(Invasive micropapillarycarcinoma, IMPC)中的表达及其临床意义。 方法 应用免疫组织化学SP法, 检测97例乳腺IMPC中L1-CAM表达, 并以95例浸润性导管癌非特殊型(invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified, IDC-NOS)作为对照组。分析L1-CAM在IMPC的表达及与临床病理学特征和预后的关系。 结果 L1-CAM表达于肿瘤细胞膜及间质中的脉管内皮细胞, 在IMPC组主要表达于肿瘤细胞集团内细胞间的相互连接面。L1-CAM在IMPC中的表达率(50.5%)显著高于IDC-NOS组(18.9%), 并与IMPC的组织学分级、脉管侵犯、淋巴结转移、间质内脉管的L1-CAM表达及肿瘤细胞的P53表达呈正相关(P < 0.05), 与ER、PR表达呈负相关(P < 0.05)。单因素分析结果显示, IMPC患者中L1-CAM表达阳性患者预后不良。多因素分析结果显示IMPC中L1-CAM表达是影响患者术后生存的独立预后因素。 结论 L1-CAM可能在IMPC集团性生长、侵袭、转移中发挥重要作用, 可作为IMPC预后预测的标志物及靶向治疗研究的新靶点。 -
关键词:
- 乳腺浸润性微乳头状癌 /
- L1细胞粘附分子 /
- 淋巴结转移
Abstract:Objective The study aims to investigate the expression of L1 cell adhesion molecules(L1-CAM) in invasion micropapillary carcinoma(IMPC) and to analyze its clinical significance. Methods L1-CAM expression was analyzed in 97 IMPC cases and 95 invasive ductal carcinoma–not otherwise specified(IDC-NOS) cases via immunohistochemistry. The correlation of L1-CAM expression with clinicopathologic characteristics, which include the prognosis IMPC patients, was determined. Results The rate of L1-CAM expression in IMPC(50.5%) is significantly higher than that of IDC-NOS(18.9%). L1-CAM expression is also associated with histological grade, vessel invasion, lymph node metastasis, L1-CAM vessels, and protein p53 expression(P < 0.05), whereas it is negatively associated with ER and PR(P < 0.05). L1-CAM was predominantly expressed in the cell-cell interface of the cell clusters of IMPC and in the stroma vascular endothelial cells. Univariate analysis results indicate that expression of L1 is a risk factor that can predict the survival of IMPC patients(P < 0.05). Multivariate analyses results from a Cox's proportional hazards model show that a high expression of L1-CAM is an independent risk factor for the death of IMPC patients. Conclusion This study suggests that L1-CAM expression may have an important function in collective cell growth and is significantly associated with tumor invasion and metastasis. L1-CAM can be considered as biomarkers of prognosis and as a new target for IMPC therapy. -
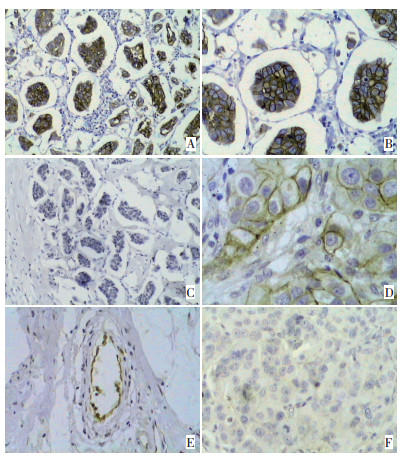
图 1 L1-CAM在浸润性微乳头状癌及浸润性导管癌中的表达
Figure 1. L1-CAM expression in IMPC and IDC-NOS
A: Positive L1-CAM expression in IMPC(SP × 200). Strong membrane staining was mainly found in the interface of the cell clusters of IMPC; B: Positive L1-CAM expression in IMPC(SP×400); C: Negative L1-CAM expression in IMPC(SP×200); D: Positive L1-CAM expression in IDC-NOS (SP×400). Strong membrane staining was observed in tumor cells; E: Positive L1-CAM expression in the endothelial cells of IMPC(SP×400); F: Negative L1-CAM expression in IDC-NOS(SP×400)
表 1 L1-CAM表达和乳腺IMPC临床病理学特征的关系
Table 1. Correlations between L1-CAM expression and clinicopathologic features in IMPC cases

表 2 97例乳腺IMPC患者预后的临床变量多因素分析
Table 2. Multivariate analysis of clinicopathologic variables as prognostic factors for overall survival in 97 IMPC cases

-
[1] Tavassoli FA, Devilee P. WHO classification of tumor. Pathology and genetics, tumor of the breast and female genital organ[M]. Lyon: IARC Press, 2003, 26(7): 926-931. [2] 付丽, 松山郁生, 付笑影, 等. 乳腺浸润性微乳头状癌的形态改变与生物学行为的关系[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2004, 33(1): 21-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHBL200401006.htm [3] 范宇, 郎荣刚, 王颖, 等. 乳腺浸润性微乳头状癌上皮性钙黏附素的表达及意义[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2004, 33(4): 308-311. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0529-5807.2004.04.002 [4] Hortsch M. Structural and functional evolution of the L1 family: are four adhesion molecules better than one[J]? Mol Cell Neurosci, 2000, 15(1): 1-10. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1044743199908096 [5] Guo X, Chen L, Lang R, et al. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: association of pathologic features with lymph node metastasis[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2006, 126(5): 740-746. doi: 10.1309/AXYY4AJTMNW6FRMW [6] Walsh PC. Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase: a new molecular marker for prostate cancer[J]. J Urol, 2002, 168(4 Pt 1): 1635. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11956072/ [7] Linnemann D, Bock E. Expression of the cell adhesion molecules N-CAM and L1 in B16 melanoma cells[J]. Med Biol, 1986, 64(6): 345-349. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3821197/ [8] Schroder C, Schumacher U, Fogel M, et al. Expression and prognostic value of L1-CAM in breast cancer[J]. Oncol Rep, 2009, 22 (5): 1109-1117. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19787228/ [9] Voura EB, Ramjeesingh RA, Montgomery AM, et al. Involvement of integrin alpha(v)beta(3) and cell adhesion molecule L1 in transendothelial migration of melanoma cells[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2001, 12 (9): 2699-2710. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.9.2699 [10] Stoeck A, Schlich S, Issa Y, et al. L1 on ovarian carcinoma cells is a binding partner for Neuropilin-1 on mesothelial cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2006, 239(2): 212-226. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.08.005 [11] Stoletov K, Kato H, Zardouzian E, et al. Visualizing extravasation dynamics of metastatic tumor cells[J]. J Cell Sci, 2010, 123(13): 2332-2341. doi: 10.1242/jcs.069443 [12] Schafer H, Dieckmann C, Korniienko O, et al. Combined treatment of L1CAM antibodies and cytostatic drugs improve the therapeutic response of pancreatic and ovarian carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2012, 319(1): 66-82. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.12.035 [13] Shtutman M, Levina E, Ohouo P, et al. Cell adhesion molecule L1 disrupts E-cadherin-containing adherens junctions and increases scattering and motility of MCF7 breast carcinoma cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2006, 66(23): 11370-11380. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2106 [14] Thiery JP, Chua K, Sim WJ, et al. [Epithelial mesenchymal transition during development in fibrosis and in the progression of carcinoma][J]. Bull Cancer, 2010, 97(11): 1285-1295. doi: 10.1684/bdc.2010.1206 [15] Li W, Liu F, Lei T, et al. The clinicopathological significance of CD44+/CD24-/low and CD24+ tumor cells in invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2010, 206(12): 828-834. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2010.09.008 [16] Gavert N, Vivanti A, Hazin J, et al. L1-mediated colon cancer cell metastasis does not require changes in EMT and cancer stem cell markers[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2011, 9(1): 14-24. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0406 [17] Kaifi JT, Strelow A, Schurr PG, et al. L1 (CD171) is highly expressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumors[J]. Mod Pathol, 2006, 19 (3): 399-406. https://www.nature.com/articles/3800547 [18] Friedli A, Fischer E, Novak-Hofer I, et al. The soluble form of the cancer-associated L1 cell adhesion molecule is a pro-angiogenic factor[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2009, 41(7): 1572-1580. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1357272509000107 [19] Chen L, Fan Y, Lang RG, et al. Breast carcinoma with micropapillary features: clinicopathologic study and long-term follow-up of 100 cases[J]. Int J Surg Pathol, 2008, 16(2): 155-163. doi: 10.1177/1066896907307047 -




 下载:
下载: