-
摘要:
目的 分析脊柱骨巨细胞瘤的影像学表现及进行临床相关性研究, 提高对该病的诊断及临床治疗。 方法 回顾性分析11例经病理证实的脊柱骨巨细胞瘤的影像学资料。 结果 11例肿瘤中位于颈椎2例, 胸椎4例, 腰椎2例, 骶椎3例。术后复发3例, 伴动脉瘤样骨囊肿3例。X线及CT表现为偏心性溶骨性破坏, 病灶内密度较均匀, 8例伴发病理骨折, 3例复发病例的影像学表现为虫蚀状溶骨性破坏, 边界不清。MR表现为T1WI呈等低信号, T2WI上表现为混杂高信号, 3例伴动脉瘤样骨囊肿的表现为多囊状高信号。 结论 脊柱骨巨细胞瘤影像学表现有一定的特征性, 对诊断、治疗及术后处理有重要价值。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to analyze imaging findings of giant cell tumor of the spine and its clinical correlational study. Methods We retrospectively analyzed the imaging features of 11 cases giant cell tumor of the spine confirmed by pathology. Results In the 11 cases, 2 were located in the cervical vertebra, 4 in the thoracic vertebra, 2 in the lumbar vertebra, 3 in the sacral vertebra.Three of the postoperative cases were recurrence and three had aneurysm bone cyst.On X-ray and computed tomography images, the tumors showed expanding bone destruction and uniform density in lesion.Pathological fracture occurred in eight cases.Imaging findings of three recurrence cases showed moth-eaten osseous destruction and unclear boundary.Magnetic resonance images displayed homogeneous intermediate signal on T1WI and miscellaneous high signal on T2WI.Three cases with aneurysm bone cyst exhibited high signal of multiple cystic. Conclusion Giant cell tumor of the spine exhibited some characteristic features of imaging.Therefore, making a correct diagnosis and administering appropriate treatments and postoperative processing procedures are necessary. -
Key words:
- spine /
- giant cell tumor of bone /
- tomography /
- magnetic resonance imaging
-
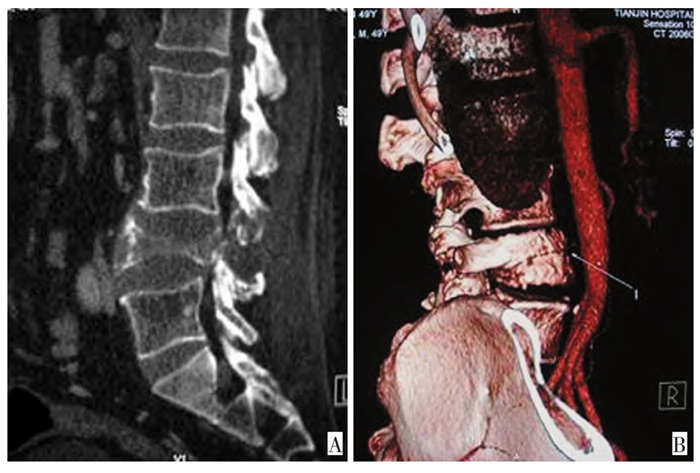
图 1 腰4椎体巨细胞瘤术后复发
Figure 1. Post-operative recurrence of giant cell tumor of the fourth lum-bar vertebral body
A: MPR reconstruction showed that the fourth lumbar vertebral body andattachment structure exhibited osseous destruction.The fourth lumbar ver-tebral body was flattened and the boundary of destructive area was notclear; B: CTA showed that the tumor blood supply was rich.The tumorblood supply artery was also observed
图 2 胸11椎体骨巨细胞瘤伴动脉瘤样骨囊肿及病理骨折
Figure 2. Giant cell tumor of the eleventh thoracic vertebral body with an-eurysms bone cyst and pathologic fracture
A: MR images showed that the eleventh thoracic vertebral body was flattenedsimilar to a"dumbbell", and respectively showed low signal on T1WI andmixed high signal on T2WI.B: Soft tissue masses were observed on thevertebral side.Compression of the spinal cord was also observed
-
[1] Lee MJ, Sallomi DF, Munk PL, et al. Pictorial review: giant cell tu mors of bone[J]. Clinical Radiology, 1998, 53: 481-489. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9260(98)80166-9 [2] Hunter C L, Pacione D, Hornyak M, et al. Giant-cell tumors of thecervical spine: case report. [J]. Neurosurgery, 2006, 59: 1150-1154. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000245587.23710.A6 [3] Samartzis D, Foster W C, Padgett D, et al. Giant cell tumor of thelumbar spine: operative management via spondylectomy andshort-segment, 3-column reconstruction with pedicle recreation[J]. Surgical Neurology, 2008, 69: 138-142. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2007.01.038 [4] 陈东, 张义质, 傅嘉庆, 等. 脊椎骨巨细胞瘤的MRI诊断价值[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2006, 25(3): 260-263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9324.2006.03.016 [5] 杜联军, 丁晓毅, 江浩, 等. 脊柱骨巨细胞瘤的影像学表现及临床意义[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2006, 22(3): 300-303. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2006.03.015 [6] Ozaki T, Liljeqvist UIF, Halm H, et al. Giant cell tumor of thespine[J]. Clin Orthopa Relat Res, 2002, 401(8): 194-201. [7] Refai D, Dunn G P, Santiago P. Giant cell tumor of the thoracicspine: case report and review of the literature[J]. Surgical Neurolo gy, 2009, 71: 228-233. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2007.07.056 [8] 董书堃, 郑铭豪, 沈溪明, 等. 影响骨巨细胞瘤预后的临床和病理因素研究[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2002, 29(12): 837-840. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2002.12.001 [9] 丁晓毅, 陆勇, 颜凌, 等. 骨巨细胞瘤常见和典型的MRI表现分析[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2008, 27(1): 66-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS200801022.htm [10] 韩月东, 张学昕, 徐朝霞. 骨巨细胞瘤的MRI表现与病理基础研究[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2002, 8(21): 699-701. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYFS200208030.htm [11] 王林森, 主编. 骨肿瘤影像诊断学图谱[M], 第1版. 天津科学技术出版社, 2004: 312-329. [12] Sanjay BKS, Sim FH, Unni KK, et al. Giant-cell tumors of the spine[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1993, 75(1): 148-154. [13] Fidler MW. Surgical treatment of giant cell tumors of the thoracic andlumbar spine: report of nine patients[J]. Eur Spine J, 2001, 10(1): 69-77. doi: 10.1007/s005860000206 [14] Aprile I, Scott CA, Cervesato D, et al. Two rare lumbar tumors withunusual MRI characteristics[J]. Neuroradiology, 2000, 42: 458-461. doi: 10.1007/s002340000306 [15] Sciot R, Dorfman H, Brys P, et al. Cytogenetic-morphologic corre lations in aneurismal bone cyst, giant cell tumor of bone and com bined lesions. A report from the CHAMP study group[J]. ModPathol, 2000, 13(11): 1206-1210. [16] Swanger R, Maldjian C, Murali R, et al. Three cases of benign gi ant cell tumor with unusual imaging features[J]. Clinical Imaging, 2008, 32: 407-410. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2007.12.003 [17] Shimada Y, Hongo M, Miyakoshi N, et al. Giant cell tumor of fifthlumbar vertebrae: two cases reports and review of the literature[J]. Spine, 2007, 7: 499-505. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2006.01.016 [18] Mestiri M, Bouabdellah M, Bouzidi R, et al. Giant cells tumor recur rence at the third lumbar vertebra[J]. Orthopaedics & Traumatolo gy: Surgery & Research, 2010, 96: 905-909. [19] Yasko AW. Giant cell tumor of bone[J]. Curr Oncol Rep, 2002, 4(6): 520-526. doi: 10.1007/s11912-002-0067-2 [20] Campanacci M, Baldini N, Boriani S, et al. Giant cell tumor of bone[J]. J Bone joint Surg Am, 1987, 69: 106-114. doi: 10.2106/00004623-198769010-00018 [21] Junming M, Cheng Y, Dong C, et al. Giant cell tumor of the cervicalspine: a series of 22 cases and outcomes[J]. Spine, 2008, 33: 280-288. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318162454f [22] Bennett CJ, Marcus RB, Million RR, et al. Radiation therapy for gi ant cell tumor of bone[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 1993, 26(2): 299-304. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(93)90210-M [23] Luther N, Bilsky M H, Hartl R. Giant cell tumor of the spine[J]. Neurosurg Clin N Am, 2008, 19: 49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2007.09.009 -




 下载:
下载: