CXCR4 expression of bone marrow CD34+ cells in myelodysplastic syndromes and its correlation with cell migration
-
摘要:
目的 探讨不同危险度骨髓增生异常综合征(myelodysplasticsymdromes,MDS)中骨髓CD34+细胞CXCR4的表达情况及其与细胞迁移率的相关性。 方法 收集40例骨髓增生异常综合征患者的骨髓标本,根据IPSS积分系统进行危险度分组。低危组20例:IPSS积分0~1.5分;高危组20例:IPSS积分≥1.5分;同时采集10例健康者的骨髓标本作为对照。分离纯化骨髓CD34+细胞,通过流式细胞术检测CXCR4膜蛋白的表达;研究SDF-1α趋化作用下CD34+细胞的迁移率及CD34+细胞对骨髓基质细胞的迁移率。 结果 高危组MDS患者CD34+细胞CXCR4的表达率明显高于低危组和正常对照组(P < 0.000 1);低危组和正常对照组之间CXCR4的表达率无显著性差异(P>0.05)。高危组CD34+细胞对SDF-1α及骨髓基质细胞的迁移率显著高于低危组及正常组(均P < 0.000 1),且其对骨髓基质细胞的迁移率与CXCR4的表达呈正相关(P=0.000 1)。 结论 高危组MDS患者CD34+细胞CXCR4的表达量及其对骨髓基质细胞的迁移率均明显高于低危组患者,且其迁移率随CXCR4表达量的增加而升高,不同风险组的MDS患者存在SDF-1及其受体CXCR4表达和功能上的差异,SDF-1及其受体CXCR4在MDS发病中具有重要作用。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the expression of CXCR4 and the migration rate of bone marrow stromal CD34+ cells in different risk groups with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) using correlation analysis. Methods Forty MDS patients were divided into low- and high-risk groups based on the International Prognosis Scoring System (IPSS). The former was composed of 20 patients with IPSS < 1.5, whereas the latter was composed of 20 patients with IPSS ≥1.5. Bone marrow (BM) samples of these patients and 10 normal controls were collected. CD34+ cells were separated and purified. The expression of CXCR4 was determined by flow cytometry. The migration rate of CD34+ cells on the chemotactic effect of SDF-1α and on the effect of bone marrow stromal cells were measured. Results The expression rate of CXCR4 was higher in the high-risk MDS group than in the low-risk and control groups (P < 0.000 1). No significant differences existed between the low-risk and the control groups (P>0.05). The migration rate of CD34+ cells on the effects of SDF-1α and marrow stromal cells were significantly increased in the high-risk MDS group compared with those in the low-risk and control groups (P < 0.000 1). Migration rate of CD34+ cells on the effect of marrow stromal cells was positively correlated with CXCR4 expression (P=0.000 1). Conclusion The CXCR4 expression and migration rates of CD34+ cells on the effect of marrow stromal cells are significantly higher in the high-risk MDS group than in the low-risk group. Migration rate has a positive correlation with the CXCR4 expression, which further indicates that MDS is a heterogeneous group of hematopoietic stem cell malignancies. The expression and function of SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4 differ within each group with various risks. SDF-1 and CXCR4 may be involved in MDS pathogenesis. -
Key words:
- myelodysplastic syndrome /
- CXCR4 /
- SDF-1 /
- marrow stromal cell migration
-
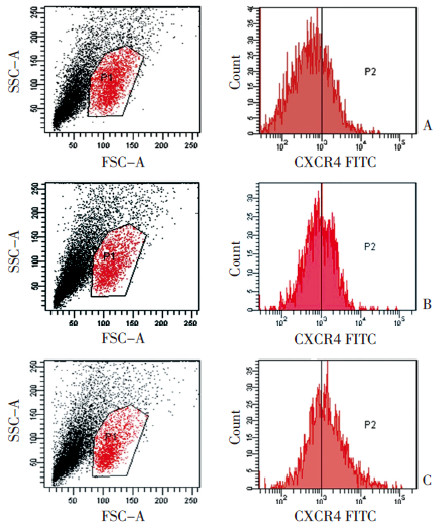
图 1 骨髓CD34+细胞中CXCR4的表达率
Figure 1. Expression rate of CXCR4 in bone marrow CD34+ cells
A: Expression rate of CXCR4 in CD34+ + cells of a normal control was 19.2%;B: Expression rate of CXCR4 in CD34+ cells of a low-risk patient was 30.1%;C: Expression rate of CXCR4 in CD34+ cells of a high-risk pa⁃ tient was 72.8%
-
[1] Czader M, Orazi A. World Health Organization classification of myelodysplasticsyndromes[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2012, 18(22): 3149-3162. doi: 10.2174/1381612811209023149 [2] Tormo M, Marugán I, Calabuig M. Myelodysplastic syndromes: an update on molecular pathology[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2010, 12 (10): 652-661. doi: 10.1007/s12094-010-0574-9 [3] Cheng M, Qin G. Progenitor cell mobilization and recruitment: SDF-1, CXCR4, α 4-integrin, and c-kit[J]. Prog Biology Transl Sci, 2012, 111: 243-264. [4] Teicher BA, Fricker SP. CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2010, 16(11): 2927-2931. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2329 [5] Nervi B, Ramirez P, Rettig MP, et al. Chemosensitization of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) following mobilization by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100[J]. Blood, 2009, 113(24): 6206-6214. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-162123 [6] Vianello F, Villanova F, Tisato V, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells non-selectively protect chronic myeloid leukemia cells from imatinib-induced apoptosis via the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis[J]. Haematologica, 2010, 95(7): 1081-1089. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.017178 [7] Tauro S, Hepburn MD, Peddie CM, et al. Functional disturbance of marrow stromal microenvironment in the myelodysplastic syndromes[J]. Leukemia, 2002, 16(5): 785-790. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402440 [8] Tauro S, Hepburn MD, Bowen DT, et al. Assessment of stromal function, and its potential contribution to deregulation of hematopoiesis in the myelodysplastic syndromes[J]. Haematologica, 2001, 86(10): 1038-1045. [9] Kastrinaki MC, Pontikoglou C, Klaus M, et al. Biologic characteristics of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in myelodysplastic syndromes[J]. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 2011, 6(2): 122-130. doi: 10.2174/157488811795495422 [10] Varga G, Kiss J, Várkonyi J, et al. Inappropriate Notch activity and limited mesenchymal stem cell plasticity in the bone marrow of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2007, 13(4): 311-319. doi: 10.1007/BF02940310 [11] Matsuda M, Morita Y, Hanamoto H, et al. CD34+ progenitors from MDS patients are unresponsive to SDF-1, despite high levels of SDF-1 in bone marrow plasma[J]. Leukemia, 2004, 18(5): 1038-1040. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403301 [12] Yang R, Pu J, Guo J, et al. The biological behavior of SDF-1/CXCR4 in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome[J]. Med Oncol, 2012, 29(2): 1202-1208. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-9943-7 [13] Zhang Y, Guo Q, Zhao H, et al. Expression of CXCR4 is an independent prognostic factor for overall survival and progression-free survival in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome[J]. Med Oncol, 2013, 30(1): 341-344. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0341-6 -




 下载:
下载: