Expression and clinicopathologic significance of Cdc42 and WAVE1 in non-small cell lung cancer
-
摘要:
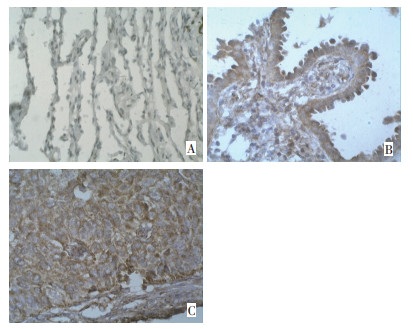
目的 探讨Cdc42和WAVE1在非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)中的表达及其临床意义。 方法 采用免疫组织化学法检测106例经石蜡包埋的NSCLC组织及46例癌旁正常肺组织中Cdc42和WAVE1的表达情况。 结果 Cdc42和WAVE1在NSCLC组织中的表达明显高于正常肺组织。Cdc42的表达强度与肿瘤的分化程度、TNM分期及淋巴结转移情况之间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);WAVE1的表达强度与TNM分期及淋巴结转移情况之间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。NSCLC组织中Cdc42和WAVE1的表达呈正相关(r=0.469,P < 0.01)。Cdc42高表达组的3年生存率(44.16%)低于低表达组(72.41%),WAVE1高表达组的3年生存率(39.44%)亦低于低表达组(77.14%),且差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。淋巴结转移、Cdc42和WAVE1共同高表达是影响NSCLC患者预后的独立因素。 结论 Cdc42和WAVE1在NSCLC组织中异常高表达,且呈现较好的相关性,可能共同参与并促进NSCLC的恶性进程,检测两者的表达会对NSCLC患者的临床病理学特征及预后起一定的提示作用。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression and clinical significance of cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42) and WASP family verprolin-homologous protein l (WAVE1) in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Methods The expression of Cdc42 and WAVE1 was detected in 106 paraffin-embedded NSCLC tissues and 46 adjacent normal lung tissues (control group) using immunohistochemistry. Results The expression levels of Cdc42 and WAVE1 was distinctly higher in NSCLC than in the control group. The expression of Cdc42 in NSCLC significantly correlated with tumor differentiation, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis (P < 0.05). The expression of WAVE1 in NSCLC was significantly correlated with TNM stage and lymph node metastasis (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). The expression of Cdc42 was significantly correlated with WAVE1 in NSCLC (r=0.469, P < 0.01). The 3-year survival rates were significantly lower in the group with high Cdc42 expression (44.16%) than in the low expression group (72.41%; P < 0.01). Similarly, the 3-year survival rates were significantly lower among patients with high WAVE1 expression (39.44%) than in those with low expression (77.14%; P < 0.01). Lymph node metastasis and the common high Cdc42 and WAVE1 expression were independent prognostic factors for NSCLC. Conclusion The Cdc42 expression is correlated with WAVE1 expression. They may act together and have an important function in NSCLC. The expression of both Cdc42 and WAVE1 in NSCLC tissue may be used as markers for assessing the clinicopathologic features and prognosis. -
Key words:
- Cdc42 /
- WAVE1 /
- non-small cell lung cancer /
- immunohistochemistry
-
表 1 Cdc42和WAVE1的表达与NSCLC患者临床病理特征的关系 例
Table 1. Comparison of the expression intensity of Cdc42 and WAVE1 with different clinicopathologic characteristics in NSCLC groups (n)

表 2 NSCLC组织中Cdc42与WAVE1的相关性 例
Table 2. Correlation between the expression of Cdc42 and WAVE1 in NSCLC (n)

表 3 Cox比例风险回归模型分析结果
Table 3. Analytical result of Cox proportional hazards model for various prognostic factors in patients with NSCLC

-
[1] 陈万青, 张思维, 邹小农. 中国肺癌发病死亡的估计和流行趋势研究[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2010, 13(5): 488-493. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.05.20 [2] Stengel K, Zheng Y. Cdc42 in oncogenic transformation, invasion, and tumorigenesis[J]. Cell Signal, 2011, 23(9): 1415-1423. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.04.001 [3] Yamazaki D, Kurisu S, Takenawa T. Regulation of cancer cell motility through actin reorganization[J]. Cancer Sci, 2005, 96(7): 379-386. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00062.x [4] Horiuchi A, Imai T, Wang C, et al. Up-regulation of small GTPases, RhoA and RhoC, is associated with tumor progression in ovarian carcinoma[J]. Lab Invest, 2003, 83(6): 861-870. doi: 10.1097/01.LAB.0000073128.16098.31 [5] Au CW, Siu MK, Liao X, et al. Tyrosine kinase B receptor and BDNF expression in ovarian cancers-effect on cell migration, angiogenesis and clinical outcome[J]. Cancer Lett, 2009, 281(2): 151-161. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.025 [6] Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A. Rho GTPases in cell biology[J]. Nature, 2002, 420(6916): 629-635. doi: 10.1038/nature01148 [7] Balasubramanian MK, Tao EY. Timing it right: precise ON/OFF switches for Rho1 and Cdc42 GTPases in cytokinesis[J]. J Cell Biol, 2013, 202(2): 187-189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201306152 [8] Chander H, Truesdell P, Meens J, et al. Transducer of Cdc42-dependent actin assembly promotes breast cancer invasion and metastasis[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(25): 3080-3090. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.317 [9] Zhang JY, Zhang D, Wang EH. Overexpression of small GTPases directly correlates with expression of δ-catenin and their coexpression predicts a poor clinical outcome in nonsmall cell lung cancer[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2013, 52(5): 338-347. doi: 10.1002/mc.21854 [10] Gao L, Bai L, Nan QZ. Activation of Rho GTPase Cdc42 promotes adhesion and invasion in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Med Sci Monit Basic Res, 2013, 25(19): 201-207. [11] Hu J, Mukhopadhyay A, Craig AW. Transducer of Cdc42-dependent actin assembly promotes epidermal growth factor-induced cell motility and invasiveness[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(3): 2261-2272. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.157974 [12] Baranwal S, Alahari K. Rho GTPase effector functions in tumor cell invasion and metastasis[J]. Curr Drug Targets, 2011, 12(8): 1194-1201. doi: 10.2174/138945011795906534 [13] Ye DZ, Field J. PAK signaling in cancer[J]. Cell Logist, 2012, 2(2): 105-116. doi: 10.4161/cl.21882 [14] Burns S, Cory GO, Vainchenker W, et al. Mechanisms of WASp-mediated hematologic and immunologic disease[J]. Blood, 2004, 104(12): 3454-3462. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1678 [15] Zhang J, Tang L, Shen L, et al. High level of WAVE1 expression is associated with tumor aggressiveness and unfavorable prognosis of epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2012, 127(1): 223-230. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.06.008 [16] Yang MH, Zhao MY, Wang Z, et al. WAVE1 regulates P-glycoprotein expression via Ezrin in leukemia cells[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2011, 52(2): 298-309. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2010.538776 -




 下载:
下载: