Methylation profile of tumor suppressor genes in the cell-free DNA of plasma in hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要:
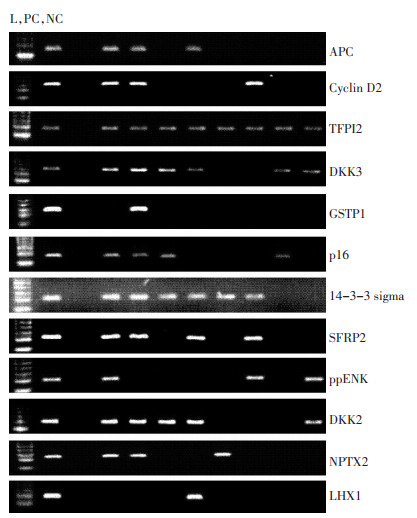
目的 在外周血游离DNA中筛选肝癌特异的甲基化谱。 方法 收集55例肝癌和54例慢性肝病患者血浆标本,应用甲基化特异性PCR方法检测血浆游离DNA的12个抑癌基因甲基化状态。 结果 在肝癌组中,APC、p16、GSTP1、Cyclin D2、LHX1、TFPI2、DKK2、DKK3、SFRP2、14-3-3 sigma、ppENK、NPTX2基因的甲基化频率分别为78.18%、63.64%、58.18%、49.09%、49.09%、47.27%、40.00%、18.18%、16.36%、9.09%、7.27%和5.45%,而在慢性肝病组中,各基因的甲基化频率分别为27.78%、22.22%、7.41%、3.70%、16.67%、37.04%、37.04%、11.11%、20.37%、7.41%、7.41%和9.26%。APC、Cyclin D2、TFPI2、DKK3和GSTP1基因在肝癌组中的甲基化频率高于慢性肝病组(P < 0.01)。将它们组成5基因甲基化谱,肝癌组甲基化指数(中位值为0.6,IQR 0.4~0.8)显著高于慢性肝病组(中位值为0.2,IQR 0~0.2)。在肝癌组中,甲基化指数与患者年龄具有相关性,年龄大者甲基化指数较高,而甲基化指数与其它临床病理参数未见相关性。甲基化指数与肝癌患者的无瘤生存期及总体生存期均未见相关性。 结论 该甲基化谱可能成为肝癌辅助诊断的核酸标志物。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to detect the special methylation profile in peripheral blood for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Methods The methylation status of 12 tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) in the plasma of 55 HCCs and 54 chronic liver diseases (CLDs) was tested by methylation-specific PCR (MSP). Results In HCC, the methylation frequencies were 78.18% in APC, 63.64% in cyclin D2, 58.18% in TFPI2, 49.09% in DKK3, 49.09% in GSTP1, 47.27% in p16, 40.00% in Sigma 14-3-3, 18.18% in SFRP2, 16.36% in ppENK, 9.09% in DKK2, 7.27% in NPTX2, and 5.45% in LHX1. In CLD, the methylation frequencies were 27.78% in APC, 22.22% in cyclin D2, 7.41% in TFPI2, 3.70% in DKK3, 16.67% in GSTP1, 37.04% in p16, 37.04% in Sigma 14-3-3, 11.11% in SFRP2, 20.37% in ppENK, 7.41% in DKK2, 7.41% in NPTX2, and 9.26% in LHX1. The methylation frequencies of APC, cyclin D2, TFPI2, DKK3, and GSTP1 were higher in HCC than in CLD (P < 0.01). The methylation index (MI) of the five-gene methylation profile was statistically higher in HCC (median, 0.6; IQR, 0.4-0.8) than CLD (median, 0.2; IQR, 0-0.2) (P < 0.01). In HCC, MI was statistically related to the patient's age. Older patients with HCC had a higher MI. No significant correlation was observed between MI and other clinicopathological data. Moreover, MI was not related to the disease free survival and the overall survival in HCC. Conclusion This five-gene methylation profile may be a promising biomarker for the assistant diagnosis of HCC. -
Key words:
- hepatocellular carcinoma /
- tumor suppressor gene /
- methylation /
- plasma
-
表 1 MSP反应各基因甲基化引物序列及退火温度
Table 1. Primer sequences for PCR

表 2 不同组12个基因甲基化频率比较 例(%)
Table 2. Methylation frequencies of 12 genes in different groups (n%)

表 3 肝癌组MI与患者整体生存和无瘤生存期相关性分析
Table 3. Relation of MI with survival time in HCC

-
[1] Lang H, Gang C, Hongping Y, et al. Clinicopathological significance of RASSF1A reduced expression and hypermethylation in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatol Int, 2010, 4: 423-432. doi: 10.1007/s12072-010-9164-8 [2] Chan KC, Lai PB, Mok TS, et al. Quantitative analysis of circulating methylated DNA as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Clin Chem, 2008, 54(9): 1528-1536. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.104653 [3] Zhang YJ, Wu HC, Shen J, et al. Predicting hepatocellular carcinoma by detection of aberrant promoter methylation in serum DNA [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2007, 13(8): 2378-2384. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1900 [4] Chang H, Yi B, Li L, et al. Methylation of tumor associated genes in tissue and plasma samples from liver disease patients[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2008, 85(2): 96-100. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2008.07.001 [5] Huang ZH, Hu Y, Hua D, et al. Quantitative analysis of multiple methylated genes in plasma for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2011, 91(3): 702-707. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2011.08.004 [6] Zhang YJ, Rossner P Jr, Chen Y, et al. Aflatoxin B1 and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon adducts, p53 mutations and p16 methylation in liver tissue and plasma of hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. Int J Cancer, 2006, 119(5): 985-991. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21699 [7] Iyer P, Zekri AR, Hung CW, et al. Concordance of DNA methylation pattern in plasma and tumor DNA of Egyptian hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2010, 88(1): 107-111. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2009.09.012 [8] Wong I, Dennis Y, Winnie Y, et al. Frequent p15 promoter methylation in tumor and peripheral blood from hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2000, 6: 3516-3521. [9] Wang JH, Qin Y, Li B, et al. Detection of aberrant promoter methylation of GSTP1 in the tumor and serum of Chinese human primary hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. Clinical Biochemistry, 2006, 39: 344-348. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2006.01.008 [10] Tsutsui M, Iizuka N, Moribe T, et al. Methylated cyclin D2 gene circulating in the blood as a prognosis predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2010, 411(7-8): 516-520. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2010.01.004 [11] 齐翀, 李建芳, 瞿颖, 等. 胃癌血清肿瘤相关基因超甲基化检测及其意义[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2007, 34(22): 1275-1279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2007.22.004 [12] Leon SA. Free DNA in the serum of caneer patients and the effect of therapy[J]. Cancer Res, 1977, 37: 646-650. [13] Martin W, Usha M. Circulating methylated DNA: a new generation of tumor markers[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2006, 12(24): 7205-7208. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2531 [14] Sun FK, Fan YC, Zhao J, et al. Detection of TFPI2 methylation in the serum of hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2013, 58(4): 1010-1015. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2462-3 [15] Yang B, Du Z, Gao YT, et al. Methylation of Dickkopf-3 as a prognostic factor in cirrhosis-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2010, 16(6): 755-763. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i6.755 [16] Colnot S, Decaens T, Niwa-Kawakita M, et al. Liver-targeted disruption of Apc in mice activates beta-catenin signaling and leads to hepatocellular carcinomas[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2004, 101: 17216-17221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404761101 [17] Niehrs C. Function and biological roles of the Dickkopf family of Wnt modulators[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25: 7469-7481. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210054 [18] Ahuja N, Li Q, Mohan AL, et al. Aging and DNA methylation in colorectal mucosa and cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 1998, 58(23): 5489-5494. -




 下载:
下载: