Comparison of patient survival on adjuvant FOLFOX6 and XELOX chemotherapy after resection for gastric cancer
-
摘要:
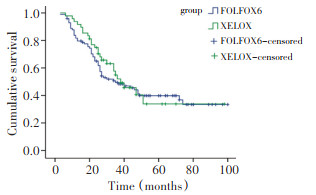
目的 比较可切除胃癌患者术后分别采用奥沙利铂联合5-氟尿嘧啶/亚叶酸钙(FOLFOX6)与奥沙利铂联合卡培他滨(XELOX)两种方案辅助化疗的生存差异。 方法 147例Ⅰ~Ⅲ期胃癌术后(R0切除)患者接受治疗, 其中FOLFOX6组99例, XELOX组48例, 比较两组不良反应率和生存率。 结果 FOLFOX6组白细胞减少及肝功能异常的发生率明显高于XELOX组(P < 0.05), XELOX组手足综合征(HFS)的发生明显高于FOLFOX6组(P=0.016), 其它不良反应的比较, 包括贫血、血小板减少、恶心呕吐、腹泻、肾功能异常、外周神经毒性、口腔黏膜炎等差异无统计学意义(P<0.05)。FOLFOX6组与XELOX组1、3、5年无病生存率(DFS)分别为81.7%、49.5%、39.8%和93.8%、52.1%、33.8%, 两组中位无病生存时间(mDFS)分别为35、38个月, 差异无统计学意义(P=0.672);FOLFOX6组与XELOX组1、3、5年总生存率(OS)分别为98.0%、68.1%、44.6%和97.8%、78.7%、44.7%, 两组中位总生存时间(mOS)分别为55、58个月, 比较亦无显著性差异(P=0.194)。 结论 两种化疗方案对胃癌患者远期生存的影响无显著性差异。 Abstract:Objective To compare the survival of resected gastric cancer patient treated with oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFOX6) with those treated with oxaliplatin and capecitabine (XELOX). Methods A total of 147 resected gastric cancer patients accepted the treatment. Among them, 99 were treated with FOLFOX6 and 48 were treated with XELOX. Adverse events and survival rates of the two groups were compared. Results Incidence of leukopenia and hepatic dysfunction in the FOLFOX6 group was significantly higher than that of the XELOX group (P < 0.05), whereas hand-foot syndrome in the XELOX group was significantly higher than that of the FOLFOX6 group (P=0.016). By contrast, the incidence of other adverse events, such as anemia, thrombocytopenia, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, kidney dysfunction, peripheral neurovirulence, and oral mucositis, was not significantly different (P<0.05) between the two groups. After 1, 3, and 5 years, disease-free and overall survivals between the two groups were not significantly different (P<0.05). Conclusion The effects of FOLFOX6 and XELOX adjuvant chemotherapies on long-term survival of resected gastric cancer patients were found to have no significant difference. -
Key words:
- gastric cancer /
- adjuvant chemotherapy /
- oxaliplatin /
- 5-fluorouracil /
- capecitabine /
- survival
-
表 1 两组患者一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data obtained from FOLFOX6- and XELOX-treated groups

表 2 两组患者不良反应比较
Table 2. Comparison of adverse events observed from FOLFOX6- and XELOX-treated groups

-
[1] Thrumurthy SG, Chaudry MA, Hochhauser D, et al. The diagnosis and management of gastric cancer[J]. BMJ, 2013, 347:f6367. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f6367 [2] Nagini S. Carcinoma of the stomach: A review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, molecular genetics and chemoprevention[J]. World J Gastrointest Oncol, 2012, 4(7):156-169. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v4.i7.156 [3] Miceli R, Tomasello G, Bregni G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer: Current evidence and future challenges[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(16):4516-4525. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4516 [4] Zhao SL, Fang JY. The role of postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy following curative resection for gastric cancer: a meta-analysis [J]. Cancer Invest, 2008, 26(3):317-325. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=37fc37e8472cd0863002686a6691afb5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] Liu TS, Wang Y, Chen SY, et al. An updated meta-analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy after curative resection for gastric cancer[J]. Eur Surg Oncol, 2008, 34(11):1208-1216. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2008.02.002 [6] Sun P, Xiang JB, Chen ZY. Meta-analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy after radical surgery for advanced gastric cancer[J]. Br J Surg, 2009, 96(1):26-33. doi: 10.1002/bjs.6408 [7] Bang YJ, Kim YW, Yang HK, et al. Adjuvant capecitabine and oxaliplatin for gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy (CLASSIC): a phase 3 open-label, randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2012, 379(9813):315-321. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61873-4 [8] Noh SH, Park SR, Yang HK, et al. Adjuvant capecitabine and oxaliplatin (xelox) for gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy: final results from the CLASSIC trial[J]. Ann Oncol, 2013, 24:iv14. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(11)61873-4/fulltext [9] Shah MA, Schwartz GK. Treatment of metastatic esophagus and gastric cancer[J]. Semin Oncol, 2004, 31(4):574-587. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2004.04.013 [10] Hirsch BR, Zafar SY. Capecitabine in the management of colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2011, 3:79-89. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=943b5bdb35d2fae20eb3cb944cfc117e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] Kang YK, Kang WK, Shin DB, et al. Capecitabine/cisplatin versus 5-fluorouracil/cisplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a randomized phase Ⅲ noninferiority trial[J]. Ann Oncol, 2009, 20(4):666-673. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn717 [12] Alcindor T, Beauger N. Oxaliplatin: a review in the era of molecularly targeted therapy[J]. Curr Oncol, 2011, 18(1):18-25. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=943b5bdb35d2fae20eb3cb944cfc117e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] Montagnani F, Turrisi G, Marinozzi C, et al. Effectiveness and safety of oxaliplatin compared to cisplatin for advanced unresectable gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2011, 14(1):50-55. doi: 10.1007/s10120-011-0007-7 [14] 张瑞雪,闫 涵,王 民,等.XELOX方案与FOLFOXs 方案治疗中国晚期胃癌患者的 Meta 分析[J].首都医科大学学报, 2013,34(3):422-427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2013.03.019Zhang RX, Yan H, Wang M, et al. A meta-analysis on the effects of regimen XELOX versus FOLFOXs for treatment of Chinese patients with metastatic gastric cancer[J]. J Cap Med Univ, 2013, 34 (3):422-427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2013.03.019 [15] Wu Y, Wei ZW, He YL, et al. Efficacy of adjuvant XELOX and FOLFOX6 chemotherapy after D2 dissection for gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(21):3309-3315. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3309 -




 下载:
下载: