Effect of EGFR-TKI retreatment following chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients who underwent EGFR-TKI
-
摘要:
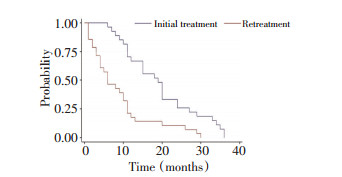
目的 表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor,EGFR-TKI)治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)虽疗效显著,且安全性好,但最终都会发生耐药。EGFR-TKI耐药机制复杂,应对困难,本研究旨在探讨EGFR-TKI治疗晚期NSCLC获得性耐药的患者,化疗后再次应用EGFR-TKI的疗效。 方法 前瞻性对EGFR-TKI治疗晚期NSCLC长期获益后获得性耐药的27例患者,先化疗,后再次应用EGFR-TKI治疗,吉非替尼250 mg qd或厄洛替尼150 mg qd至疾病进展;依据RECIST标准评价疗效,比较再使用原EGFR-TKI与另一种EGFR-TKI的疗效。 结果 27例患者全为晚期肺腺癌,完全缓解(CR)为1例(3.7%)、部分缓解(PR)为8例(29.6%)、稳定(SD)为14例(51.9%)、进展(PD)为4例(14.8%),有效率(RR)为33.3%,疾病控制率(DCR)为85.2% (95% CI为62~94),mPFS为6个月。13例再用原EGFR-TKI (同药组) CR为1例(7.6%),PR为2例(15.4%)、SD为8例(61.5%),RR为23%,PD为2例(15.4%),DCR为86.4%,其mPFS为5个月;14例再用另一种EGFR-TKI (换药组) CR为0例,PR为6例(42.8%),SD为6例(42.8%),进展为2例(14.3%),RR为42.8%,其mPFS为9.5个月,DCR为85.7%,两组DCR比较无显著性差异(P>0.05),两组的mPFS比较有显著性差异(P < 0.05);mPFS换药组明显长于同药组。 结论 EGFR-TKI治疗晚期NSCLC长期获益后获得性耐药的患者,先化疗、后再次应用EGFR-TKI,大部分患者仍能取得一定疗效。 Abstract:Objective Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-activating mutations have higher response rate and more prolonged survival following treatment with single-agent EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) compared with patients with wild-type EGFR. However, all patients treated with reversible inhibitors develop acquired resistance over time. The mechanisms of resistance are complicated. The lack of established therapeutic options for patients after a failed EGFR-TKI treatment poses a great challenge to physicians in managing this group of lung cancer patients. This study evaluates the influence of EGFR-TKI retreatment following chemotherapy after failure of initial EGFR-TKI within at least six months on NSCLC patients. Methods The data of 27 patients who experienced treatment failure from their initial use of EGFR-TKI within at least 6 months were analyzed. After chemotherapy, the patients were retreated with EGFR-TKI (gefitinib 250 mg qd or erlotinib 150 mg qd), and the tumor progression was observed. The patients were assessed for adverse events and response to therapy. Targeted tumor lesions were assessed with CT scan. Results Of the 27 patients who received EGFR–TKI retreatment, 1 (3.7%) patient was observed in complete response (CR), 8 (29.6%) patients in partial response (PR), 14 (51.9%) patients in stable disease (SD), and 4 (14.8%) patients in progressive disease (PD). The disease control rate (DCR) was 85.2% (95% CI = 62%-94%). The median progression-free survival (mPFS) was 6 months (95% CI = 1-29). Of the 13 patients who received the same EGFR-TKI, 1 patient in CR, 3 patients in PR, 8 patients in SD, and 2 patients in PD were observed. The DCR was 84.6%, and the mPFS was 5 months. Of the 14 patients who received another EGFR-TKI, 0 patient in CR, 6 patients in PR, 6 patients in SD, and 2 patients in PD were observed. The DCR was 85.7%, and the mPFS was 9.5 months. Significant difference was found between the 2 groups in progression-free survival but not in response rate or disease control rate. Conclusion Retreatment of EGFR-TKIs can be considered an option after failure of chemotherapy for patients who were previously controlled by EGFR-TKI treatment. -
表 1 27例NSCLC患者基线特征及以往治疗情况
Table 1. Demographic characteristics and summary of prior therapy for NSCLC

-
[1] Tomizawa Y, Fujita Y, Tamura A, et al. Effect of gefitinib re-challenge to initial gefitinib responder with non-small cell lung cancer followed by chemotherapy[J]. Lung Cancer, 2010, 68(2):269-272. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=785e848a3caa80af5b40a6cb069faca3 [2] Hata A, Katakami N, Yoshioka H, et al. Erlotinib after gefitinib failure in relapsed non-small cell lung cancer: clinical benefit with optimal patient selection[J]. Lung Cancer, 2011, 74(2):268-273. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.03.010 [3] 安同彤, 黄真, 王玉艳, 等.晚期非小细胞肺癌初始治疗后再次应用EGFR-TKI的疗效观察[J].中国肺癌杂志, 2011, 14(3):261-265. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2011.03.22An TT, Huang Z, Wang YY, et al. Retreatment with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor after initial failure in advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Chin J Lung Cancer, 2011, 14(3):261-265. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2011.03.22 [4] Song ZB, Yu YF, Chen ZW, et al. Erlotinib as a salvage treatment for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer after failure of gefitinib treatment[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2011, 124(15):2279-2283. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhcmj201115007 [5] Saito H, Murakami S, Kondo T, et al. Effectiveness of erlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer in cases of gefitinib resistance after treatment of more Than 6 Months[J]. Onkologie, 2012, 35 (1-2):18-22. doi: 10.1159/000335736 [6] Oh IJ, Ban HJ, Kim KS, et al. Retreatment of gefitinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who previously controlled to gefitinib: A single-arm, open-label, phase Ⅱ study[J]. Lung Cancer, 2012, 77(1):121-127. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.01.012 [7] Nishinoa K, Imamuraa F, Moritab S, et al. A retrospective analysis of 335 Japanese lung cancer patients who responded to initial gefitinib treatment[J]. Lung Cancer, 2013, 18(8):4411-4417. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fee70f49e723c349e3c98fbdc008a5e3 [8] Tomizawa Y, Fujita Y, Tamura A, et al. Effect of gefitinib re-challenge to initial gefitinib responder with non-small cell lung cancer followed by chemotherapy[J]. Lung Cancer, 2010, 68(2):269-272. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=785e848a3caa80af5b40a6cb069faca3 [9] 孙燕, 石远凯.临床肿瘤内科手册[M].第五版, 人民卫生出版社, 北京: 1997, 49-51.Sun Y, Shi YK. Reasonable medication[M]. Manual of Clinical Oncology(Fifth edition). People's medical publishing house, Beijing, 1997, 49-51. [10] Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D, et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2011, 23(75):75ra26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e7e96e7b5700809c2551366b832fde36 [11] Servidei T, Riccardi A, Mozzetti S, et al. Chemoresistant tumor cell lines display altered epidermal growth factor receptor and HER3 signaling and enhanced sensitivity to gefitinib[J]. Int J Cancer, 2008, 123(12):2939-2949. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23902 [12] Van Schaeybroeck S, Karaiskou-McCaul A, Kelly D, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor activity determines response of colorectal cancer cells to gefitinib alone and in combination with chemotherapy[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2005, 11(20):7480-7489. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0328 [13] Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2005, 353(2):123-132. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050753 [14] Tang C, Li X, Guo W, et al. How to make the Choice in the Retreatment of EGFR-TKI for Advanced NSCLC Patients Who Benefited from Prior Gefitinib Therapy: the Original Drug or Switching to A Second EGFR-TKI[J]? Chin J Lung Cancer, 2013, 16(7):345-352. [15] Tang C, Li X, Guo W, et al. How to Make the choice in the retreatment of EGFR-TKI for advanced NSCLC patients who benefited from prior gefitinib therapy: the original drug or switching to a second EGFR-TKI[J]? zhongguo FeiAi za zhi, 2013, 16(7):345-352. -




 下载:
下载: