The significance of breast mammography assisted by hook-wire localization biopsy for BI-RADS Ⅳ and above negative breast lesions
-
摘要:
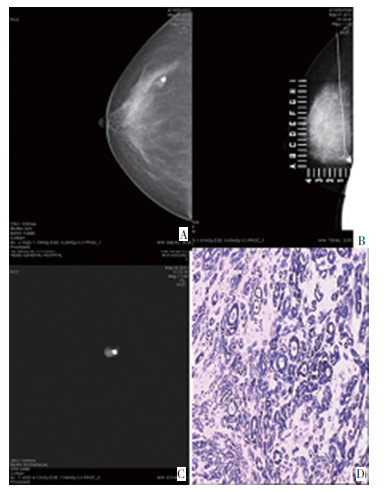
目的 探讨乳腺钼靶X线摄影引导下钩丝定位活检技术对临床触诊阴性或触诊不良的BI-RADS Ⅳ级及以上乳腺病变的诊断意义。 方法 选取2012年1月至2014年8月48例乳腺钼靶BI-RADS Ⅳ级及以上但临床触诊阴性或触诊不良的乳腺病变患者(其中双侧病变4例、单侧病变44例、共计52处病灶),进行钼靶X线摄影引导下钩丝定位活检术。 结果 所有52处病灶中恶性病变13例(均单侧),其中0期占46.15%(6/13),Ⅰ期占38.46%(5/13),Ⅱ期占15.39%(2/13);良性病变39例,乳腺癌检出率为25.0%。钼靶BI-RADS Ⅳ级患者中良性病变39例,恶性病变10例;BI-RADS Ⅴ级患者中良性病变0例,恶性病变3例。Ⅳ、Ⅴ级中乳腺癌的阳性检出率分别为25.6%和100%。 结论 钼靶辅助下钩丝定位活检可以精确切除临床触诊阴性或触诊不良的BI-RADS Ⅳ级及以上乳腺病灶,提高患者生活质量和改善预后,是一种安全、准确、费用低廉的诊断方法,值得国内临床广泛推广。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the diagnosis significance of breast mammography assisted by hook-wire localization biopsy for BI-RADS Ⅳ and above negative or non-palpable breast lesions. Methods A total of 48 cases of mammary molybdenum target with BI-RADS Ⅳ level and above but with clinical-touched negative or non-palpable breast lesions (including 4 bilateral lesions and 44 unilateral lesions; total of 52 lesions) were used in the mammography aided by hook-wire localization biopsy. Results Among the 52 lesions, 13 cases were malignant lesions (single), 6 cases were at Stage 0 (accounted for 46.15%), 5 cases were in Stage I (38.46%), and 2 cases were in Stage Ⅱ (15.39%). The remaining 39 cases were benign lesions. Results showed that the detection rate for breast cancer was 25.0%. A total of 39 cases of benign lesions and 10 cases of malignant lesions were found among mammography BI-RADS Ⅳpatients. Zero cases of benign lesions and 3 cases of malignant change were found among BI-RADS Ⅴ patients. The positive rates of breast cancer among BI-RADS Ⅳand Ⅴ patients were 25.64% and 100%, respectively. Conclusion Breast mammography assisted by hook-wire localization biopsy could precisely excise both BI-RADS Ⅳ and Ⅴ negative/non-palpable breast lesions. This technique can also improve the quality of life and prognosis of patients. It is a safe, accurate, and low-cost diagnostic method. Thus, breast mammography assisted by hook-wire localization biopsy must be widely used in clinical applications in China. -
表 1 乳腺切检术后病理结果
Table 1. Pathological results after breast biopsy

表 2 钼靶BI-RADS分级与乳腺癌分期之间的关系(n=13)
Table 2. Relationship between mammography BI-RADS classification and breast cancer stage(n=13)

表 3 乳腺病变与钼靶BI-RADS分级(n=52)
Table 3. Breast lesions and mammography BI-RADS classification(n=52)

-
[1] Autier P, Boniol M, La VC, et al. Disparities in breast cancer mortality trends between 30 European countries: retrospective trend analysis of WHO mortality database[J]. BMJ, 2010, 341:c3620. doi: 10.1136/bmj.c3620 [2] 张晓耀, 史立晖, 罗燕, 张晓君.触诊阴性乳腺病灶钼靶定位切除的临床应用价值[J].中国医药导报, 2013, (29): 91-94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YYCY201329033.htmZhang XY, Shi LH, Luo Y, et al. Palpation negatie breast lesions the clinical value of molybdenum target positioning resection[J]. Chinese Medicine Herald, 2013, (29): 91-94. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YYCY201329033.htm [3] Hubbard RA, Zhu W, Oneqa TL, et al. Effects of Digital Mammography Uptake on Downstream Breast-related Care Among Older Women[J]. Med Care, 2012, 50(12):1053-1059. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e318269e9c2 [4] Houslleu Demay ML, Monghal C, Bertrand P, et al. An assessment of the performance of elastography for the investigation of BI-RADS 4 and BI-RADS 5breast lesions: Correlations with pathological anatomy findings[J]. Diagn-Interv Imaging, 2012, 93:757-766. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2012.03.015 [5] 王南飞.全数字化X线三维立体导丝定位在乳腺隐匿性病灶中的临床应用[J].疑难和少见病杂志, 2012, 19(2):8-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HSJB201202003.htmWang NF. Fully digital X-ray three-dimensional godet positioning in breast conceals a sexually transmitted disease in the clinical application of oven[J]. Chinese Journal of Difficult and Complicated Cases, 2012, 19(2):8-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HSJB201202003.htm [6] 商建国.钼靶X射线对乳腺疾病的诊断价值[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志, 2012, 15(6):871. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZMGY201206049.htmShang JG. Molybdenum target X-ray diagnostic value of breast disease[J]. China's Journal Of Coal Industry Medical Journal, 2012, 15 (6):871. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZMGY201206049.htm [7] 李旭敏, 李卉.钼靶检查对隐匿性乳腺癌的诊断价值[J], 中国医药导报, 2012, 5(5):2-3. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yycyzx201215051Li XM, Li H. The diagnostic value of molybdenum target inspection of occult breast cancer[J]. China Medical Herald, 2012, 5(5): 2-3. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yycyzx201215051 [8] 王晓军, 李志军, 范志民, 等.钼靶摄影对早期乳腺癌的诊断价值[J].中国妇幼保健, 2013, 11(5):34-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgfybj200608061Wang XJ, Li ZJ, Fang ZM, et al. The diagnostic value of molybdenum target photography for early breast cancer[J]. Maternal & Child Health Care of China, 2013, 11(5):34-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgfybj200608061 [9] 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会.乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2011版)[J].中国癌症杂志, 2013, 23(8):637-693.The Chinese association of breast. The breast cancer diagnosis and treatment guidelines and standards (2011 edition)[J]. Chinese Oncology, 2013, 23(8):637-693.[ [10] Sickers EA. False positive rate of screening mammography[J]. N Engl J Med, 1998, 339(8):561-562. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c4289ae0ef7dd1150176c02756923426&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] 魏冉, 张蓓, 胡文娟, 等.X线导引下乳腺钙化导丝定活检的应用价值[J].中国癌症杂志, 2011, 21(6):473-477. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3969.2011.06.011Wei R, Zhang B, Hu WJ, et al. The X line set of mammary gland calcify godet biopsy guided by application value[J]. Chinese Oncology, 2011, 21(6):473-477. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3969.2011.06.011 [12] Ernster VL, Barclay J, Kerlikowske K, et al. Mortality among women with ductal carcinoma insitu of the breast in the population based surveillance, epidemiology and end results program[J]. Arch Intern Med, 2000, 160 (7):953-958. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.7.953 [13] Adamovich TL, Simmons RM. Ductal carcinoma in situ with micro invasion[J]. Am J Surg, 2003, 186(2):112-116. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(03)00166-1 [14] 韩志刚, 王士甲, 张国福, 等.乳腺微钙化术前导丝定位效果评价及钙化形态分析[J].上海医学影像, 2012, 21(2):96-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-617X.2012.02.005Han ZG, Wang SJ, Zhang GF, et al. Breast microcalcification godet preoperative localization effect evaluation and calcification morphological analysis[J]. Shanghai Medical Imaging, 2012, 21(2):96-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-617X.2012.02.005 [15] Kouskos E, Guig P, Mantas D, et al. Wire localisation biopsy of non-palpable breast lesions: reasons for unsuccessful excision[J]. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol, 2006, 27(3):262-266. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f20f1ed9148a34b4b09b7e28a55afe36&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [16] American College of Radiology. Breast imaging reporting and data system atlas (BI-RADS atlas)[M]. 4Ed. Reston: Am Coll Radiol, 2003: 1-257. [17] 赵丽丽, 王家平.BI-RADS系统钼靶X线摄影诊断对乳腺疾病的应用价值对微钙化病变征象描述及评估分类的临床应用研究[J].云南医药杂志, 2012, 33(1):45-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YNYY201201038.htmZhao LL, Wang JP. BI - RADS molybdenum target X-ray photography system the application value of the diagnosis of mammary gland disease of microcalcification lesion signs description and classification of evaluation of clinical research[J]. Medicine and Pharmacy of Yunnan, 2012, 33(1):45-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YNYY201201038.htm [18] 安彦虹, 叶兆祥, 李弋, 等.乳腺影像报告和数据系统在国人女性乳腺癌筛查中的应用价值[J].中华放射学杂志, 2011, 45(4):353-357. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2011.04.007An YH, Ye ZX, Li Y, et al. Breast imaging reporting and data system application value in the Chinese female breast cancer screening [J]. Chinese Journal of Radiology, 2011, 45(4):353-357. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2011.04.007 [19] Michel SC, Low R, Singer G, et al. Stereotaclic Mammotome breast biopsy: routine clinical experience and correlation with BI-RADS classification and histopathology[J]. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax, 2007, 96(39):1459-1474. -




 下载:
下载: