miR-30 functions as a tumor suppressor by modulating CD90 in hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要:
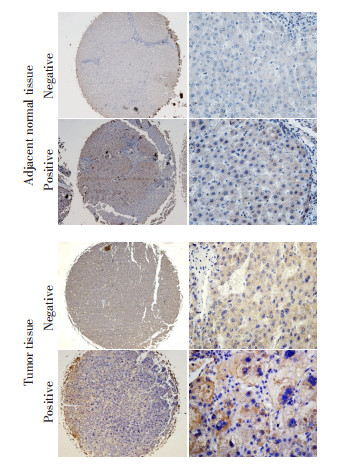
目的 miRNA能通过转录后调节靶基因的表达量,并在致癌过程中发挥抑癌或促癌作用。研究发现miR-30家族在人类肿瘤中起着重要作用,并参与维持干细胞特性的上皮细胞间质化过程,本研究主要识别miR-30家族与肝细胞肝癌的关系。 方法 应用qRT-PCR实验方法检测93例肝细胞肝癌患者癌组织和癌旁正常组织中miR-30c,miR-30b和miR-30e表达水平,另对121例肝细胞肝癌患者癌组织进行miR-30家族的表达及CD90免疫组织化学表达检测,分析miR-30家族与CD90在肝细胞肝癌中的相关性。 结果 本研究发现miR-30c(P < 0.001)、miR-30b(P=0.004)和miR-30e(P < 0.001)与癌旁正常组织相比,癌组织中表达显著下调。CD90蛋白在癌组织中的表达水平显著高于癌旁正常组织(P=0.007)。MiR-30c(P=0.032)和miR-30e(P=0.015)在CD90阴性表达的患者中表达水平显著高于CD90阳性表达的患者。 结论 miR-30家族在肝细胞肝癌中可作为抑癌miRNA,并通过调节CD90蛋白来发挥这一作用。 Abstract:Objective miRNA can post-transcriptionally regulate the expression of target genes and act as oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes in tumorigenesis. Emerging evidence demonstrates that the miR-30 family may perform an important function in human cancers and can regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition, which has a critical role in cancer stem cells. This research was conducted to identify the possible association between the miR-30 family and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Methods The expression of miR-30c, miR-30b, and miR-30e in 93 tumor tissues and adjacent tissues were measured by real-time reverse transcription PCR. Furthermore, 121 tumor tissues from an independent cohort were selected to measure the expression level of miR-30 family and CD90 by immunohistochemistry. The relationship between miR-30 family and CD90 protein expression was analyzed. Results The expression levels of miR-30c (P < 0.001), miR-30b (P=0.004), and miR-30e (P < 0.001) were significantly decreased in tumor tissues compared with adjacent tissues, and the expression level of CD90 in tumor tissues was significantly higher than that in adjacent normal tissues (P= 0.007). In addition, the expression levels of miR-30c (P=0.032) and miR-30e (P=0.015) were significantly high in negative staining for CD90 when compared with positive staining for CD90. Conclusion Taken together, we suggest that the miR-30 family may act as a tumor suppressor in HCC development and may modulate CD90 protein expression. -
Key words:
- hepatocellular carcinoma /
- miR-30 family /
- CD90 /
- cancer stem cell /
- EMT
-
表 1 93例和121例肝细胞肝癌患者一般人口学特征和临床特征
Table 1. Baseline and clinical characteristics of 93 and 121 HCC patients

表 2 miR-30家族和CD90表达情况
Table 2. The expression of miR-30 family and CD90

表 3 CD90蛋白肝癌组织中表达与患者一般人口学和临床特征的关系
Table 3. The expression patterns of CD90 protein in tumor tissues stratified by baseline and clinical characteristics from 121 HCC patients

-
[1] Kerr TA, Korenblat KM, Davidson NO. MicroRNAs and liver disease[J]. TranslRes, 2011, 157(4):241-252. [2] Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/ Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55 (6):1852-1862. doi: 10.1002/hep.25576 [3] Wang J, Li J, Shen J, et al. MicroRNA-182 downregulates metastasis suppressor 1 and contributes to metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2012, 12:227. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-227 [4] Bi Q, Tang S, Xia L, et al. Ectopic expression of MiR-125a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting MMP11 and VEGF[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(6):e40169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040169 [5] Zhang J, Yang Y, Yang T, et al. microRNA-22, downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlated with prognosis, suppresses cell proliferation and tumourigenicity[J]. Br JCancer, 2010, 103(8): 1215-1220. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605895 [6] Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, et al. MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity[J]. Cancer Res, 2009, 69(3):1135-1142. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2886 [7] Peng H, Luo J, Hao H, et al. MicroRNA-100 regulates SW620 colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting RAP1B[J]. Oncol Rep, 2014, 31(5):2055-2062. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3075 [8] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2011, 61(2):69-90. doi: 10.3322/caac.20107 [9] Zhou P, Jiang W, Wu L, et al. miR-301a is a candidate oncogene that targets the homeobox gene Gax in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2012, 57(5):1171-1180. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2099-2 [10] Shao C, Yu Y, Yu L, et al. Amplification and up-regulation of microRNA-30b in oral squamous cell cancers[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2012, 57(8):1012-1017. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2012.04.002 [11] Jiang BY, Zhang XC, Su J, et al. BCL11A overexpression predicts survival and relapse in non-small cell lung cancer and is modulated by microRNA-30a and gene amplification[J]. Mol Cancer, 2013, 12:61. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-61 [12] Jia W, Eneh JO, Ratnaparkhe S, et al. MicroRNA-30c-2* expressed in ovarian cancer cells suppresses growth factor-induced cellular proliferation and downregulates the oncogene BCL9[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2011, 9(12):1732-1745. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0245 [13] Yao J, Liang L, Huang S, et al. MicroRNA-30d promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting Galphai2 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(3):846-856. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9ffcb4ce68c5b2c771521f1e3684d4bd [14] Wang W, Lin H, Zhou L, et al. MicroRNA-30a-3p inhibits tumor proliferation, invasiveness and metastasis and is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2014, 40(11):1586-1594. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2013.11.008 [15] Zhang J, Zhang H, Liu J, et al. miR-30 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocyte by targeting Snail1[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 417(3):1100-1105. [16] Guaita S, Puig I, Franci C, et al. Snail induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumor cells is accompanied by MUC1 repression and ZEB1 expression[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(42): 39209-39216. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206400200 [17] Ouyang G, Wang Z, Fang X, et al. Molecular signaling of the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in generating and maintaining cancer stem cells[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2010, 67(15):2605-2618. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0338-2 [18] Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells[J]. Cell, 2008, 133 (4):704-715. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.027 [19] Rege TA, Hagood JS. Thy-1 as a regulator of cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions in axon regeneration, apoptosis, adhesion, migration, cancer, and fibrosis[J]. FASEB J, 2006, 20(8):1045-1054. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5460rev [20] Yang ZF, Ho DW, Ng MN, et al. Significance of CD90+ cancer stem cells in human liver cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2008, 13(2):153-166. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.01.013 [21] Sukowati CH, Anfuso B, Torre G, et al. The Expression of CD90/ Thy-1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An In Vivo and In Vitro Study[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10):e76830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076830 [22] Bridge G, Monteiro R, Henderson S, et al. The microRNA-30 family targets DLL4 to modulate endothelial cell behavior during angiogenesis[J]. Blood, 2012, 120(25):5063-5072. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-423004 [23] Dang H, Ding W, Emerson D, et al. Snail1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor initiating stem cell characteristics[J]. BMC Cancer, 2011, 11:396. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-396 [24] Pang RW, Poon RT. Cancer stem cell as a potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2012, 12(9): 1081-1094. [25] DeSano JT, Xu L. MicroRNA regulation of cancer stem cells and therapeutic implications[J]. AAPS J, 2009, 11(4):682-692. doi: 10.1208/s12248-009-9147-7 [26] Ji J, Wang XW. Clinical implications of cancer stem cell biology in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Semin Oncol, 2012, 39(4):461-472. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2012.05.011 -




 下载:
下载: