MiR-200c/141 methylation inhibits the expression of miR-200c and miR-141 in gastric cancer
-
摘要:
目的 探讨胃癌组织中miR-200c/141CpG岛的甲基化水平与miR-200c/141表达水平和临床病理特征的相关性。 方法 运用实时定量PCR(qRT-PCR)和BS-MSP方法检测胃癌组织和癌旁组织中miR-200c/141CpG岛的表达与其基因甲基化水平。统计学分析miR-200c/141CpG岛的甲基化水平与miR-200c/141水平和临床病理特征的关系。 结果 miR-200c/141CpG岛的甲基化水平在胃癌组织中显著升高,miR-200c和miR-141的水平显著降低,miR-200c/141CpG岛的甲基化水平与miR-200c和miR-141的水平呈负相关。 结论 胃癌组织中升高的miR-200c/141CpG岛的甲基化水平诱导miR-200c和miR-141表达降低。 Abstract:Objective This work aims to detect the levels of miR-200c/141 methylation and miR-200c/141 in gastric cancer tissue and investigate the relationship between miR-200c/141 expression and clinical parameters. Methods The methylation status of miR-200c/ 141 CpG island and miR-200c/141 in gastric cancer tissue specimens was evaluated by qRT-PCR or BS-MSP method. We analyzed the relationship among the methylation status of miR-200c/141 CpG island, expression level of miR-200c or miR-141, and clinical parameters. Results The status of miR-200c/141 CpG island methylation in gastric cancer tissue was significantly higher compared with that in paracarcinoma tissue. MiR-200c and miR-141 were markedly decreased in gastric cancer tissue compared with those in adjacent tissue. MiR-200c/141 CpG island methylation was negatively related with the expression of miR-200c and miR-141 in gastric cancer specimens. Conclusion The upregulation of miR-200c/141 CpG methylation inhibits miR-200c/141 expression in gastric cancer tissue. -
Key words:
- gastric cancer /
- methylation /
- miR-200c /
- miR-141 /
- clinicopathological feature
-
图 2 miR-200c和miR-141在胃癌中的表达情况
Figure 2. Differential expression of miR-200c and miR-141 in gastric cancer specimens
A. miR-200c expression in gastric cancer tissue and paired adjacent tissue; B. miR-141 expression in gastric cancer tissue and paired adjacent tissue. Results were normalized to values for the paired adjacent tissue
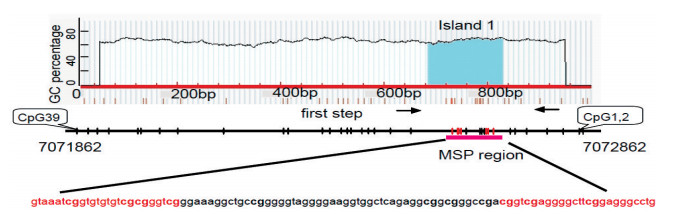
图 3 胃癌标本中miR-200c/141上游CpG岛的甲基化水平
Figure 3. Methylation status of miR-200c/141 CpG island was analyzed by bisulfite conversion-and methylation-specific PCR in gastric cancer tissue and adjacent tissue
A. The methylation and demethylation of miR-200c/141 CpG island were showed by Gel Imaging; B. Methylation status of miR-200c/141 CpG island was showed by histogram. Results were normalized to results for the paired adjacent tissue
表 1 胃癌中miR-200c/141CPG岛甲基化水平与胃癌患者临床病理特征的关系
Table 1. Correlations of the methylation status of miR-200c/141 CpG island in gastric cancer specimens with the clinicopathological feature

表 2 miR-200c/141上游CpG岛的甲基化水平与miR-200c和miR-141表达的相关性
Table 2. Correlations of the expression levels of miR-200c and miR-141 in gastric cancer specimens with the expression level of TGF-β and CpG island cytosine methylation level of miR-200c/141

-
[1] Standart N, Jackson RJ. MicroRNAs repress translation of m7Gpppcapped target mRNAs in vitro by inhibiting initiation and promoting deadenylation[J]. Genes Dev, 2007, 21(16):1975-1982. doi: 10.1101/gad.1591507 [2] Nilsen TW. Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation in animal cells[J]. Trends Genet, 2007, 23(5):243-249. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2007.02.011 [3] Damiano V, Brisotto G, Borgna S, et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-200c in breast cancer is associated with aggressiveness and is modulated by ZEB1[J]. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 2016.[Epub ahead of print]. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22422/abstract [4] Vrba L, Jensen TJ, Garbe JC, et al. Role for DNA methylation in the regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 expression in normal and cancer cells[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(1):e8697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008697 [5] Paterson EL, Kazenwadel J, Bert AG, et al. Down-regulation of the miRNA-200 family at the invasive front of colorectal cancers with degraded basement membrane indicates EMT is involved in cancer progression[J]. Neoplasia, 2013, 15(2):180-191. doi: 10.1593/neo.121828 [6] Liu S, Tetzlaff MT, Wang T, et al. miR-200c/Bmi1 axis and epithelialmesenchymal transition contribute to acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitor treatment[J]. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res, 2015, 28(4):431-441. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12379 [7] Abedi N, Mohammadi-Yeganeh S, Koochaki A, et al. miR-141 as potential suppressor of β-catenin in breast cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(12):9895-9901. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3738-y [8] Wu PP, Zhu HY, Sun XF, et al. MicroRNA-141 regulates the tumour suppressor DLC1 in colorectal cancer[J]. Neoplasma, 2015, 62(5):705-712. doi: 10.4149/neo_2015_084 [9] Zhou H, Tang K, Xiao H, et al. A panel of eight-miRNA signature as a potential biomarker for predicting survival in bladder cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2015, 34(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0167-0 [10] Chen X, Wang X, Ruan A, et al. miR-141 is a key regulator of renal cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by controlling EphA2 expression[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 20(10):2617-2630. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3224 [11] Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101(9):2999-3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307323101 [12] Makunin IV, Pheasant M, Simons C, et al. Orthologous microRNA genes are located in cancer-associated genomic regions in human and mouse[J]. PLoS One, 2007, 2(11):ell33. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.283.7001 [13] Lujambio A, Esteller M. CpG island hypermethylation of tumor suppressor microRNAs in human cancer[J]. Cell Cycle, 2007, 6(12):1455-1459. http://www.citeulike.org/user/capitall/article/1409489 [14] Wu A, Wu K, Li M, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-492 induced by epigenetic drug treatment inhibits the malignant phenotype of clear cell renal cell carcinoma in vitro[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 12(1): 1413-1420. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274258609_Upregulation_of_microRNA-492_induced_by_epigenetic_drug_treatment_inhibits_the_malignant_phenotype_of_clear_cell_renal_cell_carcinoma_in_vitro [15] Yang Y, Huang JQ, Zhang X, et al. MiR-129-2 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma cells by targeting HMGB1 and is down-regulated by DNA methylation[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2015, 404(1-2):229-239. doi: 10.1007/s11010-015-2382-6 [16] Guo W, Zhu TN, Dong ZM, et al. Aberrant methylation and expression of growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible 45G gene inesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma[J]. TUMOR, 2013, 33(1):74-80. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289042249_Aberrant_methylation_and_expression_of_growth_arrest_and_DNA-damage-inducible_45G_gene_in_esophageal_squamous-cell_carcinoma -




 下载:
下载: