Effects of HDAC5 on the proliferation and apoptosis of the gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901
-
摘要:
目的 探讨HDAC5在胃癌细胞中的表达及其对胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖和凋亡的影响。 方法 通过Western blot检测HDAC5和Twist1在胃癌细胞株及正常胃黏膜上皮细胞中的表达。使用MTT及流式细胞术分别检测HDAC5和Twist1对胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖和凋亡的影响。 结果 HDAC5和Twist1在胃癌细胞株中的表达量均明显高于正常胃黏膜上皮细胞(P < 0.05)。沉默HDAC5的表达可使胃癌SGC-7901细胞中Twist1表达降低,并抑制其增殖、促进凋亡;而过表达HDAC5作用相反(P < 0.05)。此外,沉默Twist1可抑制SGC-7901细胞的增殖、促进其凋亡(P < 0.05)。 结论 HDAC5可能通过上调Twist1的表达水平促进胃癌细胞的增殖、抑制凋亡,从而促进胃癌的发生发展。 Abstract:Objective To investigate HDAC5 expression in gastric cancer cell lines and its effects on the proliferation and apoptosis of the gastric cancer line SGC-7901. Methods The expression patterns of HDAC5 and Twist1 in gastric cancer cell lines and normal gastric mucosal cells were detected by Western blot. The effects of HDAC5 and Twist1 on the proliferation and apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells were analyzed by MTT and flow cytometry, respectively. Results The expression of HDAC5 and Twist1 in gastric cancer cell lines were significantly higher than that in normal gastric mucosal cells (P < 0.05). HDAC5 knockdown significantly down-regulated Twist1 expression, inhibited cell proliferation, and induced apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells, whereas HDAC5 overexpression exhibited an opposite effect (P < 0.05). Moreover, Twist1 knockdown significantly inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells (P < 0.05). Conclusion HDAC5 may promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by upregulating Twist1 expression, thus promoting the initiation and development of gastric cancer. -
Key words:
- gastric cancer /
- proliferation /
- apoptosis /
- HDAC5 /
- Twist1
-
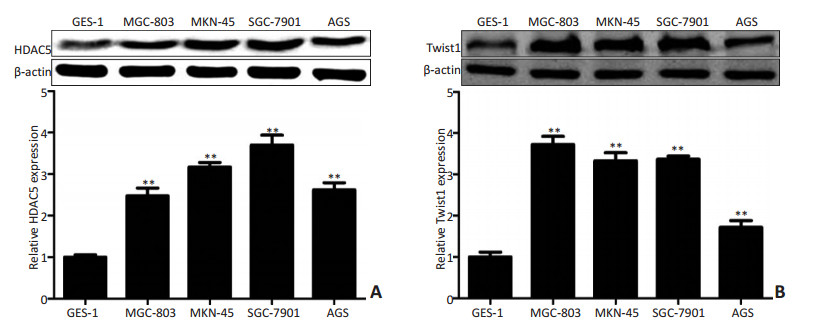
图 1 HDAC5和Twist1在胃癌细胞株中的表达
Figure 1. Expression of HDAC5 and Twist1 in gastric cancer cell lines
A. Representative Western blot image and the relative quantification of HDAC5 expression in gastric cancer cell lines and normal gastric mucosal GES-1 cells; B. Representative Western blot image and the relative quantification of Twist1 expression in gastric cancer cell lines and normal gastric mucosal GES-1 cells. **P < 0.01
图 2 HDAC5对胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖及凋亡的影响
Figure 2. Effects of HDAC5 on the proliferation and apoptosis of the gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901
A. Expression of HDAC5 and Twist1 in SGC-7901 cells during the knockdown or overexpression of HDAC5; B. Effects of HDAC5 knockdown on the proliferation of SGC-7901 cells; C, D. Effects of HDAC5 knockdown on the apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01
图 3 Twist1对胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖及凋亡的影响
Figure 3. Effects of Twist1 on the proliferation and apoptosis of the gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901
A. Twist1 expression in SGC-7901 cells after knockdown; B. Effects of Twist1 knockdown or HDAC5 overexpression on the proliferation of SGC-7901 cells; C, D. Effects of Twist1 knockdown or HDAC5 overexpression on the apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01
-
[1] Lin X, Zhao Y, Song WM, et al. Molecular classification and prediction in gastric cancer[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2015, 13:448-458. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2015.08.001 [2] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2011, 61(2):69-90. doi: 10.3322/caac.v61:2 [3] Ang TL, Fock KM. Clinical epidemiology of gastric cancer[J]. Singapore Med J, 2014, 55(12): 621-628. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2014174 [4] 黄克楠, 刘冬艳, 王爱民, 等.胃癌组织中MCM2、PCNA mRNA表达变化及意义[J].山东医药, 2015, 55(31):69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2015.31.028Huang KN, Liu DY, Wang AM, et al. The mRNA expression and significance of MCM2 and PCNA in gastric cancer tissues[J]. Shandong Medical Journal, 2015, 55(31):69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2015.31.028 [5] Yang L, Zhu J, Huang H, et al. PFTK1 promotes gastric cancer progression by regulating proliferation, migration and invasion[J]. PloS One, 2015, 10(10):e0140451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140451 [6] Carcas LP. Gastric cancer review[J]. J Carcinog, 2014, 13:14. doi: 10.4103/1477-3163.146506 [7] Kahali S, Sarcar B, Chinnaiyan P. The emerging role of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in UPR regulation[J]. Methods Enzymol, 2011, 490:159-174. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385114-7.00010-6 [8] De Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, et al. Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family[J]. Biochem J, 2003, 370(Pt 3):737-749. http://www.biochemj.org/content/370/3/737 [9] Vigushin DM, Coombes RC. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer treatment[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2002, 13(1):1-13. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200201000-00001 [10] Song SH, Han SW, Bang YJ. Epigenetic-based therapies in cancer: progress to date[J]. Drugs, 2011, 71(18): 2391-2403. doi: 10.2165/11596690-000000000-00000 [11] Milde T, Oehme I, Korshunov A, et al. HDAC5 and HDAC9 in medulloblastoma: novel markers for risk stratification and role in tumor cell growth[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2010, 16(12):3240-3252. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0395 [12] Feng GW, Dong LD, Shang WJ, et al. HDAC5 promotes cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma by up-regulating Six1 expression[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2014, 18(6):811-816. https://www.europeanreview.org/article/7141 [13] He P, Liang J, Shao T, et al. HDAC5 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation by up-regulating DLL4 expression[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8(4):6510-6516. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26131280 [14] Shi J, Qu YP, Hou P. Pathogenetic mechanisms in gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(38):13804-13819. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13804 [15] Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2006, 24(14):2137-2150. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.2308 [16] Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2006, 5(9): 769-784. doi: 10.1038/nrd2133 [17] Balliu M, Guandalini L, Romanelli MN, et al. HDAC-inhibitor (S)-8 disrupts HDAC6-PP1 complex prompting A375 melanoma cell growth arrest and apoptosis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2015, 19(1):143-154. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.2014.19.issue-1 [18] Wei TT, Lin YC, Lin PH, et al. Induction of c-Cbl contributes to anticancer effects of HDAC inhibitor in lung cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(14):12481-12492. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget [19] Khan MA, Chen HC, Zhang D, et al. Twist: a molecular target in cancer therapeutics[J]. Tumour Biol, 2013, 34(5):2497-2506. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1002-x [20] Qin Q, Xu Y, He T, et al. Normal and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying molecular mechanisms[J]. Cell Res, 2012, 22(1):90-106. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.144 [21] Lv N, Shan Z, Gao Y, et al. Twist1 regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the NF-kappaB pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Endocrine, 2016, 51(3):469-477. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0714-7 [22] Zhu DJ, Chen XW, Zhang WJ, et al. Twist1 is a potential prognostic marker for colorectal cancer and associated with chemoresistance [J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2015, 5(6):2000-2011. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC4529619/ [23] Sung CO, Lee KW, Han S, et al. Twist1 is up-regulated in gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts with poor clinical outcomes[J]. Am J Pathol, 2011, 179(4):1827-1838. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.06.032 [24] Qian J, Luo Y, Gu X, et al. Twist1 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation through up-regulation of FoxM1[J]. PloS One, 2013, 8(10): e77625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077625 [25] Yang MH, Wu KJ. TWIST activation by hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): implications in metastasis and development[J]. Cell Cycle, 2008, 7(14):2090-2096. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.14.6324 -




 下载:
下载: