Prognostic evaluation of high sensitivity-C reactive protein in peripheral T-cell lymphoma
-
摘要:
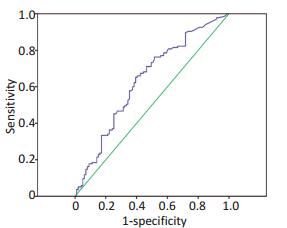
目的 探讨超敏C反应蛋白(high sensitivity-C reactive protein,Hs-CRP)水平在外周T细胞淋巴瘤(peripheral T-cell lymphoma,PTCL)患者预后中的意义。 方法 回顾性分析2005年1月1日至2016年12月31日浙江大学医学院附属第一医院就诊的初治PTCL患者247例,其中在随访过程中失访13例,实际入组234例,患者中位年龄48岁;治疗前检测Hs-CRP水平,同时完善相关检查以明确肿瘤分期及国际预后指数(international prognostic index,IPI),中位随访时间23个月,观察Hs-CRP水平与患者总生存期(overall survival,OS)的关系。 结果 Hs-CRP水平与IPI评分(r=0.132,P < 0.01)、Ann Arbor分期(r=0.183,P=0.005)、B症状(r=0.225,P=0.001)、乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH)(r=0.169,P=0.009)呈正相关(P < 0.05);与血浆白蛋白水平(r=-0.343,P < 0.001)、血红蛋白浓度(r=-0.239,P < 0.001)、血小板计数(r=0.131,P=0.045)呈负相关(P < 0.05);与年龄、性别、体能(ECOG)评分、白细胞计数无显著相关性(P>0.05),血清Hs-CRP≤10 mg/L较Hs-CRP>10 mg/L患者具有更好的OS(P < 0.05)。单因素分析及多因素Cox回归模型显示血小板计数、Hs-CRP、白蛋白水平、IPI评分是OS的独立预后不良因素(P < 0.05)。 结论 PTCL患者治疗前血清Hs-CRP水平可以和IPI评分一样作为PTCL预后的指标。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the prognostic significance of high sensitivity-C reactive protein (Hs-CRP) in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). Methods A total of 234 newly diagnosed PTCL patients with a median age of 48 years were analyzed retrospectively. Serum Hs-CRP levels and other factors, including tumor stage and international prognostic index (IPI), were determined. After a median follow-up of 23 months, the relationship between Hs-CRP and overall survival (OS) was observed. Results Serum Hs-CRP level positively correlated with IPI score (r=0.132, P < 0.001), tumor stage (r=0.183, P=0.005), B symptoms (r=0.225, P=0.001), and lactic dehydrogenase (r=0.169, P=0.009), but negatively correlated with plasma albumin levels (r=-0.343, P < 0.001), hemoglobin concentration (r=-0.239, P < 0.001), and platelet count (r=0.131, P=0.045), and is uncorrelated with age (P>0.05), gender (P>0.05), fitness score (P>0.05), and leukocyte count (P>0.05). Patients with serum Hs-CRP levels ≤10 mg/L had better OS than patients with serum Hs-CRP levels>10 mg/L. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models showed that platelet count, Hs-CRP, albumin levels, and IPI score were independent adverse prognostic factors. Conclusion The baseline Hs-CRP level can serve as a major indicator of prognosis in PTCL patients. -
Key words:
- lymphoma /
- T-cell /
- peripheral /
- high sensitivity-C reactive protein /
- prognostic evaluation
-
表 1 PTCL患者不同亚型之间生存期的比较
Table 1. Comparison of OS in different PTCL subtypes

表 2 血清Hs-CRP与其他用于判断PTCL预后指标的关系
Table 2. Clinical characteristics and serum Hs-CRP of 234 patients

表 3 应用Cox模型进行多因素生存分析
Table 3. COX multivariate regression analysis in PTCL patients

表 4 Hs-CRP水平与PTCL各亚型OS相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis of Hs-CRP and OS of different PTCL subtypes

-
[1] Armitage JO. The aggressive peripheral T-cell lymphomas: 2012 update on diagnosis risk stratification and management[J]. Am J Hematol, 2012, 87(5):511-519. doi: 10.1002/ajh.v87.5 [2] Sum J, Yang Q, Lu Z, et al. Distribution of lymphoid neoplasms in China:analysis of 4 638 cases according to the world health organizationclassification[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2012,138(3):429-434. doi: 10.1309/AJCP7YLTQPUSDQ5C [3] Li YJ, Li ZM, Xia Y, et al. Serum c-reactive protein (CRP) as a simple and independent prognostic factor in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(5):1-9. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC3665788 [4] Troppan KT, Schlick K, Deutsch A, et al. C-reactive protein level is a prognostic indicator for survival and improves the predictive ability of the R-IPI score in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients[J]. Bri J Cancer, 2014,111(1):55-60. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.277 [5] Cao Y, Shi YX, Chen JO, et al. Serum c-reactive protein as an important prognostic variable in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma[J].Tumor Biol, 2012, 33(4):1039-1044. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0337-z [6] Akr SZ, Suyam E, Bildacr Y, et al. Prognostic role of pre-transplantation serum c-reactive protein levels in patients with acute leukemia undergoing myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation[J]. Clin Transplant, 2012, 26(5):513-521. doi: 10.1111/ctr.2012.26.issue-5 [7] Kanda J, Mizumoto C, Ichinohe T, et al. Pretransplant serum ferritin and C-reactive protein as predictive factors for early bacterial infection after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2011, 46(2):208-216. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2010.108 [8] Remberger M, Mattson J. c-reactive protein levels before reducesintensity conditioning predict outcome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation[J]. Int J Hematol, 2010, 92(1):161-167. doi: 10.1007/s12185-010-0632-7 [9] Barbui T, Carobbio A, Finazzi G, et al. Elevated c-reactive protein is associated with shortened leukemia-free survival in patients with myelofibrosis[J]. Leukemia, 2013, 27(10):2084-2086. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.207 [10] 黄琴, 王增胜, 李燕, 等.血清C反应蛋白在弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤预后中的意义[J].肿瘤研究与临床, 2016, 28(4):244-247 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10023-1015353326.htmHuang Q, Wang ZS, Li Y, et al. Prognostic significance of serum c-reactive protein in diffuse large B-celllymphoma[J]. Cancer ResClin, 2016, 28(4):244-247. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10023-1015353326.htm [11] O'Dowd C, McRae LA, McMillan DC, et al. Elevated preoperative creactive protein predicts poor cancer specific survival in patients undergoing resection for non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2010, 5(7):988-992. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181da78f9 [12] Pierce BL, Ballard-Barbash R, Bernstein L, et al. Elevated biomarkers of inflammation are associated with reduced survival among breast cancer patients[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2009, 27(21):3437-3444. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.9068 [13] 王永芹, 李治国.血清脂联素、TNF-α、CRP在脓毒症患者中的临床应用价值分析[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2014, 30(4):528-530. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXZ201404026.htmWang YQ, Li ZG. Clinical application value analysis of serum adiponectin, TNF-α, CRP in patients with sepsis[J]. Chin J Immun, 2014, 30(4):528-530. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXZ201404026.htm [14] Guthrie GJ, Roxburgh CS, Horgan PG, et al. Does interleukin-6 link explain the link between tumour necrosis, local and systemic inflammatory responses and outcome in patients with colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2013, 39(1):89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.07.003 [15] Ravishankaran P, Karunanithi R. Clinical significance of preoperative serum interleukin-6 and c-reactive protein level in breast cancer patients[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2011, 9(18):10-18. doi: 10.1186%2F1477-7819-9-18.pdf [16] Groblewska M, Mroczko B, Sosnowska D, et al. Interleukin 6 and creactive protein in esophageal cancer[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2012,413(19-20):1583-1590. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.05.009 [17] Hong S, Kang YA, Cho BC, et al. Elevated serum c-reactive protein as a prognostic marker in small cell lung cancer[J]. Yonsei Med J, 2012, 53(1):111-117. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.111 [18] Hall WA, Nickleach DC, Master VA, et al. The association between creactive protein (CRP) level and biochemical failure-free survival in patients after radiation therapy for nonmetastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate[J]. Cancer, 2013,119(18):3272-3279. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28185 [19] Toiyama Y, Fujikawa H, Koike Y, et al. Evaluation of preoperative c-reactive protein aids in predicting poor survival in patients with curative colorectal cancer with poor lymph node assessment[J]. Oncol Lett, 2013, 5(6):1881-1888. https://www.spandidos-publications.com/ol/5/6/1881 [20] Szkandera J, Stotz M, Absenger G, et al. Validation of c-reactive protein levels as a prognostic indicator for survival in a large cohort of pancreatic cancer patients[J]. Br J Cancer, 2013,110(1):183-188. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3887299/?tool=pmcentrez [21] 马丽娜, 刘晓彦, 胡彦超, 等.血清超敏C反应蛋白在慢性乙型肝炎进展中的意义[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2015, 23(7):498-501.Ma LN, Liu XY, Hu YC. Clinical significance of high-sensitivity c-reactive protein in development of chronic hepatitis B[J].Chin J Hepatol, 2015, 23(7):498-501. [22] Oda Eiji. High-sensitivity c-reactive protein, but not white blood cell count, independently predicted incident diabetes in a Japanese health screening population[J]. Acta Diabetol, 2015, 52(5):983-990. doi: 10.1007/s00592-015-0788-y [23] Le-Ha C, Beilin LJ, Burrows S, et al. Gender and the active smoking and high-sensitivity c-reactive protein relation in late adolescence[J]. J Lipid Res, 2014, 55(4):758-764. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P045369 [24] Gacouin A, Roussel M, Le PJ, et al. Acute alcohol exposure has an independent impact on c-reactive protein levels, neutrophil CD64 expression, and subsets of circulating white blood cells differentiated by flow cytometry in nontrauma patients[J]. Shock, 2014, 42(3):192-198. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000195 -




 下载:
下载: