Therapeutic effect of transarterial chemoembolization combined with apatinib on patientswith advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要:
目的 评价肝动脉化疗栓塞术(transarterial chemoembolization,TACE)联合口服阿帕替尼治疗中晚期肝癌的近期疗效。 方法 收集2016年6月至2016年10月于首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院接受TACE联合口服阿帕替尼250 mg/d治疗的21例中晚期原发性肝癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)患者的临床资料;采用影像学中最新修订的实体瘤疗效评价标准(modified responseevaluation criteria in solid tumors,mRECIST),回顾性分析联合治疗1个疗程(平均约28 d)后患者的治疗效果,并对不良反应进行分析。 结果 21例患者中,完全缓解(complete response,CR)3例(14.3%),部分缓解(patial response,PR)6例(28.6%),疾病稳定(stable disease,SD)5例(23.8%)。疾病控制率(disease control rate,DCR)为61.9%,客观缓解率(objective rate,ORR)为38.1%。疾病进展(progressive disease,PD)2例(9.5%)。21例患者治疗中出现的不良反应:乏力17例(94.4%),胃肠道症状14例(66.7%),手足综合征4例(19.0%),血压升高4例(19.0%),并出现不同程度的声音嘶哑、头痛头晕、蛋白尿等。 结论 TACE联合阿帕替尼对中晚期原发性肝癌的临床治疗近期效果满意,治疗过程中不良反应发生率较高,需给予积极处理。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the therapeutic effect of transarterial chemoembolization(TACE)combined with apatinib on patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC). Methods Twenty-one patients were treated with TACE combined with 250 mgof apatinib once a day.Disease classification was assessed by investigators using the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors(mRECIST).The evaluation period was 28 days. Results The therapeutic effects were classified as follows: 3 patients(14.3%)hadcomplete response, 6 patients(28.6%)had partial response, 5 patients(23.8%)had stable disease, and 2 patients(9.5%)had progressive disease.The disease control rate was 61.9%, and the objective response rate was 38.1%.In patients, the most frequent adverseevents were fatigue(94.4%), anorexia(23.8%), diarrhea(19.0%), hypertension(19.0%), and hand-foot syndrome(19.0%). Conclusion The short-term therapeutic effect revealed that the combination of TACE and apatinib could be a promising treatment for patientswith advanced HCC.Adverse events should be closely monitored and provided with active management. -
Key words:
- hepatocellular carcinoma /
- transarterial chemoembolization /
- targeted therapy /
- apatinib
-
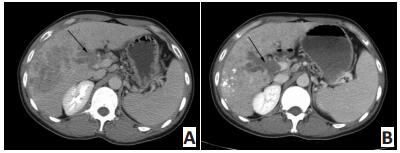
图 1 患者男性,36岁,发现HCC 1个月,CT示TACE联合阿帕替尼治疗后肿瘤变化情况
Figure 1. A 36-year-old male patient diagnosed with HCC for 1 month.CTshowed the tumor change after TACE and apatinib treatment
A.Arrow indicates the enhanced tumor in the right liver and the tumorthrombus in the branch of portal vein.Afterward, the patient was treatedwith one course of TACE and apatinib(250 mg/d); B.Follow-up contrastenhancement CT reveals that all target lesions were deposited with goodlipiodol accumulation
图 2 患者男性,57岁,发现HCC3个月余。CT与DSA显示TACE联合阿帕替尼治疗后肿瘤变化情况
Figure 2. A 57-year old male patient diagnosed with HCC for 3 months.CT and DSA showed tumor change after TACE and apatinib treatment
A.Abdominal CT shows a single enhanced lesion(arrow)in the right lobe; B.Abdominal CT shows no enhancement within the lesion(arrow); C.DSApresents the same rich blood supply lesion(arrow).Afterward, the patient was treated with one course of TACE and apatinib(250 mg/d); D.DSA showsthat the tumor stain disappeared(arrow).The case was regarded as CR by mRECIST
表 1 患者一般资料
Table 1. Patient information

表 2 联合治疗后mRESIST评价结果
Table 2. Results of mRESIST after administering the combined treatment

表 3 联合治疗后实验室检查随访结果
Table 3. Laboratory values after administering the combined treatment

表 4 联合治疗中患者出现的不良反应
Table 4. Adverse events of the combined treatment

-
[1] Lortet-Tieulent J, Soerjomataram I, Lin CC, et al.U.S.burden of cancer by race and ethnicity according to disability-adjusted life years[J].Am J Prev Med, 2016, 51(5):673-681. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2016.07.039 [2] 黄书明, 陈圣开, 张涛.肝癌切除术联合术后TACE对肝癌合并门静脉癌栓患者的治疗效果及预后影响因素分析[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2016(6):160-164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXQY201606023.htmHuang SM, Chen SK, Zhang T.Analysis of the clinical effect andprognostic factors of postoperative TACE combined with hepaticcarcinectomy in the treatment of primary carcinoma of the liverwith portal vein tumor thrombus[J].Chin J Front Med Sci(Electronic Version), 2016(6):160-164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXQY201606023.htm [3] Ter Veer E, Haj MN, van Valkenhoef G, et al.Second-and third-linesystemic therapy in patients with advanced esophagogastric cancer: a systematic review of the literature[J].Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2016, 35(3):439-456. doi: 10.1007/s10555-016-9632-2 [4] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会.原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2017年版)[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, (8):114-126. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLYS201722100.htmNational Health and Family Planning Commission of the People'sRepublic of China.Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma(2017)[J].J Clin Hepat, 2017, (8):114-126. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLYS201722100.htm [5] Mi YJ, Liang YJ, Huang HB, et al.Apatinib(YN968D1) reverses multidrugresistance by inhibiting the efflux function of multiple ATP-bindingcassette transporters[J].Cancer Res, 2010, 70(20):7981-7991. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0111 [6] Ziogas DC, Papadatos-Pastos D, Thillai K, et al.Efficacy and safety ofsorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: age isnot a problem[J].Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 29(1):48-55. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000739 [7] Shiozawa K, Watanabe M, Ikehara T, et al.Efficacy of Sorafenib versus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma refractory to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization[J].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho, 2015, 42(8):953-956. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20565419 [8] Watanabe Y, Nakaba H, Taniguchi E, et al.Successful treatment ofmetastatic hepatocellular carcinoma with sorafenib combined withtranscatheter arterial chemoembolization/hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy[J].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho, 2014, 41(12):2110-2112. [9] Lin C, Wang S, Xie W, et al.Apatinib inhibits cellular invasion andmigration by fusion kinase KIF5B-RET via suppressing RET/Src sig-naling pathway[J].Oncotarget, 2016, 7(37):59236-59244. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i37 [10] Jayson GC, Kerbel R, Ellis LM, et al.Antiangiogenic therapy in oncology:current status and future directions[J].Lancet, 2016, 388(10043):518-529. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01088-0 [11] Fontanella C, Ongaro E, Bolzonello S, et al.Clinical advances in thedevelopment of novel VEGFR2 inhibitors[J].Ann Transl Med, 2014, 2(12):123. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25568876 [12] Zhu XR, Zhu ML, Wang Q, et al.A case report of targeted therapywith apatinib in a patient with advanced gastric cancer and high serum level of alpha-fetoprotein[J].Medi(Baltimore), 2016, 95(37):e4610. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc0911925?query=nextarrow& [13] Mi YJ, Liang YJ, Huang HB, et al.Apatinib(YN968D1) reverses multidrugresistance by inhibiting the efflux function of multiple ATP-bindingcassette transporters[J].Cancer Res, 2010, 70(20):7981-7991. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0111 [14] Shan F, Miao R, Xue K, et al.Controlling angiogenesis in gastric cancer:A systematic review of anti-angiogenic trials[J].Cancer Lett, 2016, 380(2):598-607. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.023 [15] Zhang H.Apatinib for molecular targeted therapy in tumor[J].DrugDes Devel Ther, 2015, (9):6075-6081. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4654530/table/t1-dddt-9-6075/ [16] Kuzuya T, Ishigami M, Ishizu Y, et al.Fever within 2 weeks of sorafenibtherapy predicts favorable treatment efficacy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Oncol, 2016, 91(5):261-266. doi: 10.1159/000449000 [17] Chung SM, Yoon CJ, Lee SS, et al.Treatment outcomes of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma thatinvades hepatic vein or inferior vena cava[J].Cardiovasc Int Radiol, 2014, 37(6):1507-1515. doi: 10.1007/s00270-014-0841-1 -




 下载:
下载: