Clinical observation of caffeic acid in the treatment of thrombocytopenia (CIT) caused by cancer chemotherapy
-
摘要:
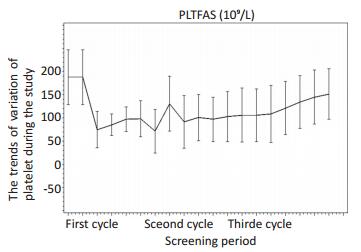
目的 观察咖啡酸片治疗肿瘤化疗所致血小板减少症(chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia,CIT)的临床疗效及安全性。 方法 采用自身对照的方法,选取上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院等11家三级甲等医院2016年1月22日至2017年1月10日收治的60例肿瘤化疗所致CIT患者。给予咖啡酸片/模拟剂治疗,均为3片/次,3次/d。第1个化疗周期(阴性对照期)于化疗开始第1d给予咖啡酸片模拟剂;第2、3个化疗周期(药物治疗期)需要接受与第1个化疗周期相同方案及剂量的化疗,分别于化疗开始第1d给予咖啡酸片。 结果 药物治疗期最低血小板(platelet,PLT)的升高值显著高于阴性对照期(P < 0.001);药物治疗期化疗后,PLT恢复后最高值显著高于阴性对照期(P < 0.001);药物治疗期PLT < 50×109/L的持续天数与阴性对照期无显著性差异,但有缩短趋势(P>0.05);药物治疗期化疗后PLT恢复至≥75×109/L和≥100×109/L,所需的天数较阴性对照期均明显减少(P < 0.001);试验期间无患者行PLT输注。 结论 咖啡酸片用于肿瘤化疗所致CIT患者,疗效确切,不良反应较少,具有广泛的临床应用前景。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of caffeic acid for thrombocytopenia induced by cancer chemotherapy. Methods A total of 60 patients received the same chemotherapy treatment on cycles 1, 2, and 3.They were given mimetic agentas negative control on the first course.On the second and third cycles, caffeic acid tablets were given from the first day of chemotherapy. Results The lowest and highest platelet levels of the treatment group during the drug treatment period were significantly higherthan those of the negative control group(P < 0.001).No significant difference in the period of days of PLT < 50×109/L was observed between the groups, although a decreasing trend(P>0.05) was observed.After chemotherapy, the days required for platelet recovery toPLT≥75×109/L and PLT≥100×109/L in the treatment group was significantly fewer than in the negative control group(P < 0.001).All thepatients did not receive any platelet transfusion during the trial. Conclusion Caffeic acid tablets were safe and effective for thrombocytopenia induced by tumor chemotherapy -
Key words:
- caffeic acid tablets /
- tumor chemotherapy /
- thrombocytopenia
-
表 1 第1、2、3个周期化疗后PLT计数的比较(109/L)
Table 1. Difference in the platelet counts among the first, second, andthird cycle chemotherapy(109/L)

表 2 第1、2、3个周期化疗后最低PLT计数的比较(109/L)
Table 2. Difference in minimum platelet count among the first, second, and third cycle of chemotherapy(109/L)

表 3 第1、2、3个周期化疗后最高PLT计数的比较(109/L)
Table 3. Difference in maximum platelet count among the first, second, andthird cycle of chemotherapy(109/L)

表 4 第1、2、3个周期化疗后PLT < 50×109/L持续天数的比较
Table 4. Difference in the platelet < 50×109/L duration among the first, second, and third cycle of chemotherapy

表 5 第1、2、3个周期化疗后PLT恢复至≥75×109/L所需天数的比较
Table 5. Difference in platelet ≥75×109/L duration among the first, second, and third cycle of chemotherapy

表 6 第1、2、3个周期化疗后PLT恢复至≥100×109/L所需天数的比较
Table 6. Difference in platelet ≥100×109/L duration among the first, second, and third cycle of chemotherapy

表 7 第1、2、3个周期化疗后血小板输注情况
Table 7. Condition of platelet transfusion after the second and third cycle of chemotherapy

-
[1] 李金成, 黄星尧.中西药物治疗化疗致血小板减少的临床研究[J].中国当代医药, 2015, 22(17):15-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGUD201517006.htmLi JC, Huang XY.Clinical study of Chinese and western medicine inthe treatment of thrombocytopenia caused by chemotherapy[J].China Modern Medi, 2015, 22(17):15-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGUD201517006.htm [2] 马军, 秦叔逵, 吴一龙.肿瘤化疗所致血小板减少症诊疗中国专家共识(2014版)[J].中华肿瘤杂志, 2014, 36(11):876-879] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2014.11.016Ma J, Qin SK, Wu YL.Consensus of Chinese experts on the diagnosis and treatment of chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia2014[J].Chin J Oncol, 2014, 36(11):876-879. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2014.11.016 [3] Kaushansky K.The thrombocytopenia of cancer.Prospects for effective cytokine therapy[J].Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 1996, (10):431-455. doi: 10.1016/S0889-8588(05)70346-4 [4] Elting LS, Rubenstein EB, Martin CG, et al.Incidence, cost, and outcomes of bleeding and chemotherapy dose modification amongsolid tumor patients with chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia[J].J Clin Oncol, 2001, 19(4):1137-1146. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2001.19.4.1137 [5] Kuter DJ, Begley CG.Recombinant human thrombopoietin: basic biology and evaluation of clinical studies[J].Blood, 2002, (100):3457-3469. http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/100/10/3457?variant=figures-only&sso-checked=1 [6] Saroj Vadhan-Raj.Management of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia current status of thrombopoic agents[J].Seminars inHematology, 2009, 46(2):s26-32. http://www.seminhematol.org/article/S0037-1963(08)00206-0/abstract [7] 张苗海, 张英羽.中医药防治化疗后血小板减少症的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2009, 18(23):2868-2870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2009.23.088Zhang MH, Zhang YY.The research progress of Chinese medicine inthe prevention and treatment of thrombocytopenia caused by chemotherapy[J].Mod J Int Tradi Chin West Medi, 2009, 18(23):2868-2870. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2009.23.088 [8] 孙红, 李占东, 薛冬, 等.中药鹿血晶治疗化疗后血小板减少症的临床观察[J].中国医院用药评价与分析, 2011, 12(9):832-833. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYPF201209024.htmSun H, Li ZD, Xue D, et al.Clinical efficacy of Chinese medicine cervus blood granule for thrombocytopenia induced bychemotherapy[J].Evaluationand Analysis of Drug-Use in Hospitals of China, 2011, 12(9):832-833. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYPF201209024.htm [9] 孙婷, 方明治.化疗致血小板减少症临床治疗进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报, 2013, 15(3):244-247. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB201303107.htmSun T, Fang MZ, Clinical therapy progress in throm bocytopenia after chem otherapy[J].J Liao ning Uni TCM, 2013, 15(3):244-247. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB201303107.htm [10] Xie CG, Wang JF, Xiang Y, et al.Marrow mesenchymal stem cellstransduced with TPO/FL genes as support for ex vivo expansion ofhematopoietic stem/progenitor cells[J].Cell Mol Life Sci, 2005, 62(21):2495-2507. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5274-1 [11] 蔡锐刚, 徐兵河, 黄镜.重组人血小板生成素预防化疗引起血小板减少症的临床观察[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2009, 16(9):707-709. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL200909018.htmCai RG, Xu BH, Huang J.Recombinant human thrombopoietin in prevention of chemotherapy-induced thromcytopenia[J].Chin J Cancer Pre Tre, 2009, 16(9):707-709. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL200909018.htm [12] Tsimberidou AM, Giles FJ, Khouri I, et al.Low-dose interleukin-11 inpatients with bone marrow failure: update of the M.D.AnderonCancer Center experience[J].Ann Oncol, 2005, 16(1):139-145. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdi007 [13] Isaacs C, Robert NJ, Bailey FA, et al.Randomized placebocontrolled study of recombinant human interleukin-11 to prevent chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with breast cancer receiving dose-intensive cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin[J].J ClinOncol, 1997, 15(11):3368-3377. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.11.3368 [14] 马军.重组人白细胞介素11在血液病实体瘤血小板减少症合理应用的专家共识[J].中华肿瘤杂志, 2010, 32(12):948-950.Ma J.Expert consensaus on rational use of recombinant human IL-11 for thrombocytopenia in solid tumor patients[J].Chin J Oncol, 2010, 32(12):948-950. -




 下载:
下载: