Suppression on invasion and migration of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma after knocking down EZH2 expression
-
摘要:
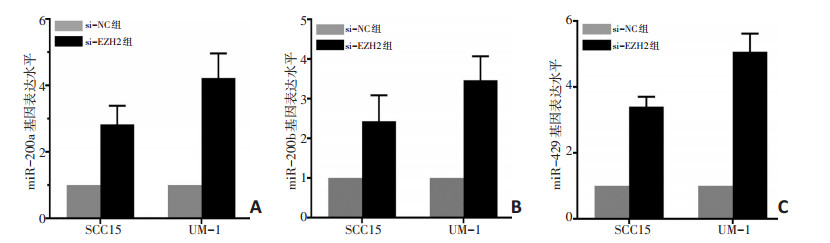
目的 探究Zeste同源增强子(enhancer of zeste homolog 2,EZH2)能否调控miR-200b/a/429的表达,进而影响人舌鳞状细胞癌的侵袭和转移。 方法 利用小干扰RNA(siRNAs)敲低舌鳞状细胞癌SCC15和UM-1细胞系中EZH2的表达。Western blot法检测EZH2和上皮-间质转化(EMT)相关蛋白的表达水平。q-PCR检测敲低EZH2后miR-200b/a/429的表达水平。Transwell实验和划痕实验检测舌鳞癌细胞的侵袭和迁移能力。最后通过免疫荧光实验观测细胞骨架的改变。免疫组织化学法和q-PCR检测人舌鳞状细胞癌标本中EZH2的表达。 结果 siRNAs能够显著地敲低EZH2表达,进而使miR-200b/a/429表达水平升高;E-cadherin表达水平升高,而N-cadherin、Vimentin、MMP-2、MMP-9蛋白表达水平下降;si-EZH2组肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移能力明显降低。淋巴结转移阳性的人舌鳞状细胞癌标本中EZH2表达水平高于淋巴结转移阴性(P < 0.01)。 结论 EZH2通过抑制miR-200b/a/429的表达水平,进而促进了人舌鳞状细胞癌的侵袭和迁移。 -
关键词:
- 人舌鳞状细胞癌 /
- 侵袭 /
- 转移 /
- EZH2 /
- miR-200b/a/429
Abstract:Objective To explore whether EZH2 can regulate the expression of miR-200b/a/429 and, thus, affect human tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC). Methods EZH2 was knocked down in TSCC lines SCC15 and UM-1 with siRNA (si-EZH2) method. The expression levels of EZH2 and epithelial mesenchymal transition related proteins were detected by Western blot. qPCR was used to determine the expression level of miR-200b/a/429 after knockdown of EZH2. Transwell and wound-healing assays were employed to detect the invasion and migration ability of tumor cells. The cytoskeleton was observed with an immunofluorescence assay. EZH2 expression in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) was detected by an immunofluorescence assay and qPCR. Results EZH2 was significantly knocked down by siRNA, thus the expression level of miR-200b/a/429 and E-cadherin increased. While the expression of the N-cadherin, Vimentin, MMP2, and MMP9 proteins decreased; the migration and invasion of HNSCC cells in the si-EZH2 group was markedly inhibited. The EZH2 expression level in patients with lymph node metastasis in HNSCC specimens was higher than those without lymph node metastasis (P < 0.01). Conclusions EZH2 inhibits the expression of miR-200b/a/429 and promotes the invasion and migration of TSCC cells. -
Key words:
- human tongue squamous cell carcinoma /
- invasion /
- metastasis /
- EZH2 /
- miR-200b/a/429
-
表 1 EZH2的表达与95例舌鳞癌患者临床病理特征的关系

-
[1] Pulte D, Brenner H. Changes in survival in head and neck cancers in the late 20th and early 21st century: a period analysis[J]. Oncologist, 2010, 15(9):994-1001. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0289 [2] Lam L, Logan RM, Luke C. Epidemiological analysis of tongue cancer in South Australia for the 24-year period, 1977-2001[J]. Aust Dental J, 2006, 51(1):16-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2006.tb00395.x [3] Liang L, Luo X, Lian Z, et al. Lymph node metastasis in head and neck squamous carcinoma: Efficacy of intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging for the differential diagnosis[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2017, 90:159-165. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.02.039 [4] Garcia J, Lopez M, Lopez L, et al. Validation of the pathological classification of lymph node metastasis for head and neck tumors according to the 8th edition of the TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors[J]. Oral Oncol, 2017, 70:29-33. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.05.003 [5] Talmi YP, Takes RP, Alon EE, et al. Prognostic value of lymph node ratio in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Head Neck, 2018[Epub ahead of print] http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29394461 [6] Strojan P, Vermorken JB, Beitler JJ, et al. Cumulative cisplatin dose in concurrent chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer: A systematic review[J]. Head Neck, 2016, 38(Suppl 1):2151-2158. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25735803 [7] Haigentz M Jr, Vermorken JB, Forastiere AA, et al. When is chemotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma not indicated [J]? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 272(4):781-787. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-2894-9 [8] Margueron R, Reinberg D. The polycomb complex PRC2 and its mark in life[J]. Nature, 2011, 469(7330):343-349. doi: 10.1038/nature09784 [9] Sun N, Zhang Q, Xu C, et al. Molecular regulation of ovarian cancer cell invasion[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35(11):11359-11366. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2434-7 [10] Sossey-Alaoui K, Bialkowska K, Plow EF. The miR200 family of microRNAs regulates WAVE3-dependent cancer cell invasion[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(48):33019-33029. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.034553 [11] Xue X, Zhang Y, Zhi Q, et al. MiR200-upregulated Vasohibin 2 promotes the malignant transformation of tumors by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2014, 12:62. doi: 10.1186/s12964-014-0062-x [12] Ning X, Shi Z, Liu X, et al. DNMT1 and EZH2 mediated methylation silences the microRNA-200b/a/429 gene and promotes tumor progression[J]. Cancer Lett, 2015, 359(2):198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.01.005 [13] Zhou X, Ren Y, Kong L, et al. Targeting EZH2 regulates tumor growth and apoptosis through modulating mitochondria dependent celldeath pathway in HNSCC[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(32):33720-33732. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail?id=PeriodicalPaper_PM26378043 [14] Abdelrahman AE, Arafa SA, Ahmed RA. Prognostic Value of Twist-1, E-cadherin and EZH2 in Prostate Cancer: An Immunohistochemical Study[J]. Turk Patoloji Derg, 2017, 1(1):198-210. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28272687 [15] Wang X, Hu B, Shen H, et al. Clinical and prognostic relevance of EZH2 in breast cancer: A meta-analysis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2015, 75:218-25. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.07.038 [16] Chen Z, Yang P, Li W, et al. Expression of EZH2 is associated with poor outcome in colorectal cancer[J]. Oncology Lett, 2018, 15(3):2953-2961. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7647/download [17] Li S, Sun S, Yu S, et al. Association between EZH2 genetic variants and hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese han population[J]. Clin Lab, 2018, 64(1):85-91. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29479874 [18] Zhang J, Chen L, Han L, et al. EZH2 is a negative prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in glioblastoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2015, 356(2 Pt B):929-936. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304383514006582 [19] Chang JW, Gwak SY, Shim GA, et al. EZH2 is associated with poor prognosis in head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma via regulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and chemosensitivity [J]. Oral Oncol, 2016, 52:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.11.002 [20] Zhang K, Sun X, Zhou X, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes glioblastoma cell cycle progression in an EZH2 dependent manner[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(1):537-546. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4381613/ [21] Zhou X, Ren Y, Zhang J, et al. HOTAIR is a therapeutic target in glioblastoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(10):8353-8365. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25823657 [22] Liu Z, Sun M, Lu K, et al. The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR contributes to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via downregualtion of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression[J]. PloS One, 2013, 8 (10):e77293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077293 [23] Chang CJ, Yang JY, Xia W, et al. EZH2 promotes expansion of breast tumor initiating cells through activation of RAF1-beta-catenin signaling[J]. Cancer Cell, 2011, 19(1):86-100. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.10.035 [24] Bracken AP, Pasini D, Capra M, et al. EZH2 is downstream of the pRBE2F pathway, essential for proliferation and amplified in cancer[J]. EMBO J, 2003, 22(20):5323-5335. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg542 [25] Tsouko E, Wang J, Frigo DE, et al. miR-200a inhibits migration of triple-negative breast cancer cells through direct repression of the EPHA2 oncogene[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2015, 36(9):1051-1060. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv087 [26] Wang J, Yang X, Ruan B, et al. Overexpression of miR-200a suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer stem cells[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(4):2447-2456. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2856-2 [27] Ming J, Zhou Y, Du J, et al. Identification of miR-200a as a novel suppressor of connexin 43 in breast cancer cells[J]. Biosci Rep, 2015, 35(5): 251. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC4613673/?report=reader [28] Mateescu B, Batista L, Cardon M, et al. miR-141 and miR-200a act on ovarian tumorigenesis by controlling oxidative stress response [J]. Nat Med, 2011, 17(12):1627-1635. doi: 10.1038/nm.2512 [29] Liu YN, Yin JJ, Abou-Kheir W, et al. miR-1 and miR-200 inhibit EMT via Slug-dependent and tumorigenesis via Slug-independent mechanisms[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(3):296-306. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.58 [30] Chen J, Wang L, Matyunina LV, et al. Overexpression of miR-429 induces mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) in metastatic ovarian cancer cells[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2011, 121(1):200-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.12.339 [31] Yuan D, Xia H, Zhang Y, et al. P-Akt/miR200 signaling regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion in circulating gastric tumor cells[J]. Int J Oncol, 2014, 45(6):2430-2438. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2644 [32] Xiao P, Liu W, Zhou H. miR-200b inhibits migration and invasion in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells via targeting FSCN1[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 14(2):1835-1840. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5421 [33] Holzner S, Senfter D, Stadler S, et al. Colorectal cancer cell-derived microRNA200 modulates the resistance of adjacent blood endothelial barriers in vitro[J]. Oncol Rep, 2016, 36(5):3065-3071. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5114 [34] Izumchenko E, Chang X, Michailidi C, et al. The TGFbeta-miR200-MIG6 pathway orchestrates the EMT-associated kinase switch that induces resistance to EGFR inhibitors[J]. Cancer Res, 2014, 74(14):3995-4005. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0110 [35] Enkhbaatar Z, Terashima M, Oktyabri D, et al. KDM5B histone demethylase controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells by regulating the expression of the microRNA-200 family[J]. Cell Cycle, 2013, 12(13):2100-2112. doi: 10.4161/cc.25142 [36] Davalos V, Moutinho C, Villanueva A, et al. Dynamic epigenetic regulation of the microRNA-200 family mediates epithelial and mesenchymal transitions in human tumorigenesis[J]. Oncogene, 2012, 31 (16):2062-2074. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.383 [37] Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E, et al. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2[J]. Genes Dev, 2008, 22(7):894-907. doi: 10.1101/gad.1640608 [38] Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2008, 10(5):593-601. doi: 10.1038/ncb1722 [39] Damiano V, Brisotto G, Borgna S, et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-200c in breast cancer is associated with aggressiveness and is modulated by ZEB1[J]. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 2017, 56(2):147-158. doi: 10.1002/gcc.v56.2 -




 下载:
下载: