SVEP1, PKHD1, and P53 expression in primary liver cancer and its clinical significance
-
摘要:
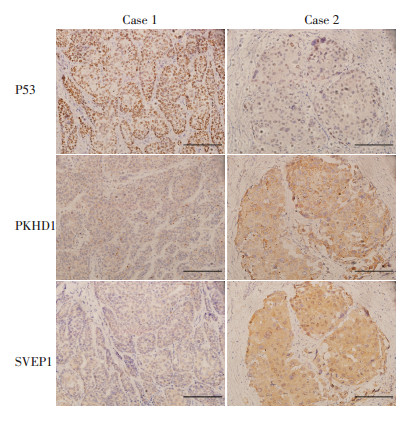
目的 使用免疫组化法检测SVEP1、PKHD1与P53在原发性肝癌组织中的表达, 结合临床病理因素分析其预测肝癌患者术后复发情况的临床意义。 方法 回顾性分析2013年1月至2014年1月于天津医科大学肿瘤医院行手术切除且随访资料完整的103例原发性肝癌患者的临床资料。以ROC曲线为主要统计方法探究不同指标的免疫组化评分对于患者预后的预测效果。根据其临界值将患者分为高危组和低危组, 以无瘤生存期主要研究指标比较两组间的差异。 结果 患者中位年龄为55(21~88)岁, 中位AFP水平70.6(1.03~718 840.0)μg/L, 中位CA19-9水平22.89(0.6~1 000.0) kU/L, 中位肿瘤大小4.5(1.0~27.0) cm。通过免疫组化法检测SVEP1、PKHD1、P53在原发性肝癌中的表达情况, 表达水平使用免疫组化评分进行量化, 三个指标免疫组化评分的ROC曲线中AUC面积分别为0.861、0.829、0.716, 临界值分别为4、4、1分(P < 0.001)。SVEP1高危组(≤4分)与低危组(>4分)3年无瘤生存率分别为4.1%和51.7%;PKHD1高危组(≤4分)与低危组(>4分)3年无瘤生存率分别为5.3%和51.9%;P53高危组(>1分)与低危组(≤1分)3年无瘤生存率分别为6.3%和27.3%, 每个指标两组间差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.001, < 0.001, 0.003)。PKHD1与SVEP1联合应用时, 其ROC曲线的AUC面积为0.897(P < 0.001), 敏感性为76.5%, 特异性为94.4%。 结论 P53预测原发性肝癌复发的准确性不足, 不推荐首选使用。SVEP1、PKHD1预测原发性肝癌复发准确性较高, SVEP1特异性较高, PKHD1敏感性较强, 两者联用效果更佳。 Abstract:Objective To detect the expression of SVEP1, PKHD1 and P53 in primary liver cancer tissues by immunohistochemistry for predicting the recurrence of liver cancer. Methods The clinical data of 103 patients with primary liver cancer who underwent surgical resection at Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital were gathered from January 2013 to January 2014 and analyzed retrospectively.Expression values of three different proteins were used to develop separate immunohistochemical scores for the prognosis of recurrence in patients.The patients were classified into either a high-risk or a low-risk group based on their immunohistochemical scores through ROC curve analysis.The difference in recurrence ratio between the two groups was then compared using the common research index of disease-free survival (DFS). Results The median age of the total patients was 55 years (range 21-88 years), the median AFP level was 70.6(range 1.03-718840.0)μg/L, the median CA19-9 level was 22.89(range 0.6-1000.0) kU/L, and the median tumor size was 4.5(1.0-27.0) cm.The expression levels of SVEP1, PKHD1, and P53 in primary liver tumors were detected by immunohistochemistry and assigned separate immunohistochemical scores.The areas under the ROC curves of the immunohistochemical scores of SVEP1, PKHD1, and P53 were 0.861, 0.829, and 0.716, respectively.The critical values of SVEP1, PKHD1, and P53 were 4, 4, and 1 point, respectively (P < 0.001).The three-year DFS rates among the SVEP1 high-risk (expression ≤ 4 points) and low-risk groups (expression > 4 points) were 4.1% and 51.7%, respectively.Similarly, the three-year survival rates among the PKHD1 high-risk (expression ≤4 points) and low-risk groups (expression >4 points) were 5.3% and 51.9%, respectively.The three-year DFS rates among the P53 high-risk (expression >1 point) and the low-risk group (expression ≤1 point) were 6.3% and 27.3%, respectively.The survival differences between all the pairs were statistically significant (P < 0.001, < 0.001, and 0.003 respectively).When PKHD1 was used in combination with SVEP1, the ROC curve had an area of 0.897(P < 0.001) with a sensitivity of 76.5% and a specificity of 94.4%. Conclusions The accuracy of P53 data for predicting primary liver cancer recurrence is insufficient and therefore it is not recommended for use.SVEP1 and PKHD1 data achieve sufficient accuracy for predicting the recurrence of primary liver cancer.Since SVEP1 data impart a higher specificity and PKHD1 data impart a higher sensitivity to the prognosis scores, the combined use of the two markers is better than being used individually. -
Key words:
- primary liver cancer (PLC) /
- surgical resection /
- disease-free survival (DFS) /
- SVEP1 /
- PKHD1 /
- P53
-
表 1 103例原发性肝癌患者的基线水平分析

-
[1] Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al.Global cancer statistics, 2012[J].CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(2):87-108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262 [2] 原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2011年版)[J].临床肝胆病杂志.2011, (11):1141-1159.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2011.11.004 [3] Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J.Hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Lancet, 2018, 391(10127):1301-1314. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30010-2 [4] Glait-Santar C, Benayahu D.Regulation of SVEP1 gene expression by 17β-estradiol and TNFα in pre-osteoblastic and mammary adenocarcinoma cells[J].J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2012, 130(1-2):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.12.015 [5] Ward CJ, Wu Y, Johnson RA, et al.Germline PKHD1 mutations are protective against colorectal cancer[J].Hum Genet, 2011, 129(3):345- 349. doi: 10.1007/s00439-011-0950-8 [6] Koifman G, Shetzer Y, Eizenberger S, et al.A mutant p53-dependent embryonic stem cell gene signature is associated with augmented tumorigenesis of stem cells[J].Cancer Res, 2018, 78(20):5833-5847. [7] Sasaki Y, Yamada T, Tanaka H, et al.Risk of recurrence in a long-term follow-up after surgery in 417 patients with hepatitis B-or hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Ann Surg, 2006, 244(5):771-780. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000225126.56483.b3 [8] Nishio T, Hatano E, Sakurai T, et al.Impact of Hepatic Steatosis on Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Non-B Non-C Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Hepatic Resection[J].Ann Surg Oncol, 2015, 22(7):2226-2234. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-4181-9 [9] Jing JS, Ye W, Jiang YK, et al.The Value of GPC3 and GP73 in Clinical Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J].Clin Lab, 2017, 63(11):1903- 1909. [10] Liu T, Zu CH, Wang SS, et al.PIK3C2A mRNA functions as a miR-124 sponge to facilitate CD151 expression and enhance malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J].Oncotarget, 2016, 7(28):43376- 43389. [11] Ke AW, Zhang PF, Shen YH, et al.Generation and characterization of a tetraspanin CD151/integrin α6β1-binding domain competitively binding monoclonal antibody for inhibition of tumor progression in HCC[J].Oncotarget, 2016, 7(5):6314-6322. [12] Liu JJ, Li Y, Chen WS, et al.Shp2 deletion in hepatocytes suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis driven by oncogenic β-Catenin, PIK3CA and MET [J].J Hepatol, 2018, 69(1):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.02.014 [13] Bleau AM, Redrado M, Nistal-Villan E, et al.miR-146a targets c-met and abolishes colorectal cancer liver metastasis[J].Cancer Lett, 2018, 414: 257-267. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.008 [14] Karpanen T, Padberg Y, van de Pavert SA, et al.An evolutionarily conserved role for polydom/svep1 during lymphatic vessel formation [J].Circ Res, 2017, 120(8):1263-1275. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308813 [15] Morooka N, Futaki S, Sato-Nishiuchi R, et al.Polydom is an extracellular matrix protein involved in lymphatic vessel remodeling[J].Circ Res, 2017, 120(8):1276-1288. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308825 [16] Nakada TA, Russell JA, Boyd JH, et al.Identification of a nonsynonymous polymorphism in the SVEP1 gene associated with altered clinical outcomes in septic shock[J].Crit Care Med, 2015, 43(1):101-108. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000604 [17] Shur I, Zemer-Tov E, Socher R, et al.SVEP1 expression is regulated in estrogen-dependent manner[J].J Cell Physiol, 2007, 210(3):732-739. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4652 [18] Zhang YL, Xing X, Cai LB, et al.Integrin α9 Suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by rho GTPase signaling[J].J Immunol Res, 2018, 2018:4602570. [19] Huhn S, Bevier M, Pardini B, et al.Colorectal cancer risk and patients' survival:influence of polymorphisms in genes somatically mutated in colorectal tumors[J].Cancer Causes Control, 2014, 25(6):759-769. doi: 10.1007/s10552-014-0379-1 [20] Dhar D, Antonucci L, Nakagawa H, et al.Liver cancer initiation requires p53 inhibition by CD44-enhanced growth factor signaling[J].Cancer Cell, 2018, 33(6):1061-1077. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.05.003 [21] Liu X, Li Y, Meng L, et al.Reducing protein regulator of cytokinesis 1 as a prospective therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(5):534. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0555-4 [22] Cao P, Yang A, Wang R, et al.Germline duplication of SNORA18L5 increases risk for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma by altering localization of ribosomal proteins and decreasing levels of p53[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155(2):542-556. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.020 [23] Zhu H, Wang J, Yin J, et al.Downregulation of PRAME suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma through the activation of P53 mediated pathway[J].Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45(3):1121-1135. doi: 10.1159/000487353 -




 下载:
下载: