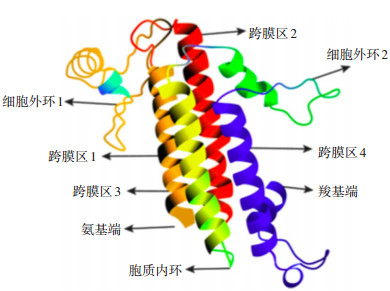
|
[1]
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. doi: 10.3322/caac.v68.6
|
|
[2]
|
Lee YT, Tan YJ, Oon CE. Molecular targeted therapy: Treating cancer with specificity[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2018, 834:188-196. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.07.034
|
|
[3]
|
Lyons TG, Ku GY. Systemic therapy for esophagogastric cancer: targeted therapies[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2017, 6(5):48. doi: 10.21037/cco
|
|
[4]
|
Singh P, Toom S, Huang Y. Anti-claudin 18.2 antibody as new targeted therapy for advanced gastric cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0473-4
|
|
[5]
|
Günzel D. Claudins: vital partners in transcellular and paracellular transport coupling[J]. Pflugers Arch, 2017, 469(1):35-44. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gwyx-slblkxylcfc200602006
|
|
[6]
|
Colpitts CC, Baumert TF. Claudins in viral infection: from entry to spread[J]. Pflugers Arch, 2017, 469(1):27-34. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1908-4
|
|
[7]
|
Hayashi D, Tamura A, Tanaka H, et al. Deficiency of claudin- 18 causes paracellular H + leakage, up- regulation of interleukin- 1β, and atrophic gastritis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 142(2): 292-304. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.10.040
|
|
[8]
|
Li G, Flodby P, Luo J, et al. Knockout mice reveal key roles for claudin 18 in alveolar barrier properties and fluid homeostasis[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2014, 51(2):210-222. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=88699f5a34c9f2700b778979062a13c8
|
|
[9]
|
Türeci Ӧ, Mitnacht-Kraus R, Wöll S, et al. Characterization of zolbetuximab in pancreatic cancer models[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2019, 8(1):e1523096. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1523096
|
|
[10]
|
Sentani K, Oue N, Tashiro T, et al. Immunohistochemical staining of Reg Ⅳ and claudin-18 is useful in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal signet ring cell carcinoma[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2008, 32(8):1182- 1189. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318163a8f8
|
|
[11]
|
Kumar V, Soni P, Garg M, et al. Emerging Therapies in the Management of Advanced-Stage Gastric Cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9:404. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00404
|
|
[12]
|
Wöll S, Schlitter AM, Dhaene K, et al. Claudin 18.2 is a target for IMAB362 antibody in pancreatic neoplasms[J]. Int J Cancer, 2014, 134(3):731-739. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28400
|
|
[13]
|
Micke P, Mattsson Johanna SM, Edlund K, et al. Aberrantly activated claudin 6 and 18.2 as potential therapy targets in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Int J Cancer, 2014, 135(9):2206-2214. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28857
|
|
[14]
|
Jovov B, Van Itallie CM, Shaheen N, et al. Claudin-18: a dominant tight junction protein in Barrett's esophagus and likely contributor to its acid resistance[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2007, 293(6):G1106-1113. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ahykdxxb201412024
|
|
[15]
|
Jiang H, Shi Z, Wang P, et al. Claudin18.2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor Engineered T Cells for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2018, 111(4):1-10.
|
|
[16]
|
Tabariès S, Siegel PM. The role of claudins in cancer metastasis[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(9):1176-1190. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=595327f51b9068e99e0a5a338e3fbc0b
|
|
[17]
|
Türeci O, Koslowski M, Helftenbein G, et al. Claudin-18 gene structure, regulation, and expression is evolutionary conserved in mammals[J]. Gene, 2011, 481(2):83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.04.007
|
|
[18]
|
Zhang X, Odom DT, Koo SH, et al. Genome-wide analysis of cAMPresponse element binding protein occupancy, phosphorylation, and target gene activation in human tissues[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2005, 102(12):4459-4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501076102
|
|
[19]
|
Ito T, Kojima T, Yamaguchi H, et al. Transcriptional regulation of claudin-18 via specific protein kinase C signaling pathways and modification of DNA methylation in human pancreatic cancer cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2011, 112(7):1761-1772. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23095
|
|
[20]
|
Wan YL, Dai HJ, Liu W, et al. miR-767-3p Inhibits Growth and Migration of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Regulating CLDN18[J]. Oncol Res, 2018, 26(4):637-644. doi: 10.3727/096504017X15112639918174
|
|
[21]
|
Klamp T, Schumacher J, Huber G, et al. Highly specific auto-antibodies against claudin-18 isoform 2 induced by a chimeric HBcAg viruslike particle vaccine kill tumor cells and inhibit the growth of lung metastases[J]. Cancer Res, 2011, 71(2):516-527. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2292
|
|
[22]
|
Maron SB, Catenacci Daniel VT. Novel Targeted Therapies for Esophagogastric Cancer[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 2017, 26(2):293-312. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2016.10.002
|
|
[23]
|
Schuler MH, Zvirbule Z, Lordick F, et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of the first-in-class antibody IMAB362 targeting claudin 18.2 in patients with metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinomas[J]. ASCO Meet Abstr, 2013, 31:4080. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6ac63773a661c7f0e0e5a7fb90e620a9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
|
[24]
|
Sahin U, Al-Batran S-E, Hozaeel W, et al. IMAB362 plus zoledronic acid (ZA) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) in patients (pts) with advanced gastroesophageal cancer (GEC): clinical activity and safety data from the PILOT phase I trial[J]. ASCO Meet, 2015, 33:e15079.
|
|
[25]
|
Sahin U, Schuler M, Richly H, et al. A phase I dose-escalation study of IMAB362 (Zolbetuximab) in patients with advanced gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction cancer[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2018, 100:17- 26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.05.007
|
|
[26]
|
Minacht-Kraus R, Kreuzberg M, Utsch M, et al. Preclinical characterization of IMAB362 for the treatment of gastric carcinoma[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28:126.
|
|
[27]
|
Al-Batran S, Schuler M, Zvirbule Z, et al. FAST: an international, multicenter, randomized, phase Ⅱ trial of epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine (EOX) with or without IMAB362, a first-in-class antiCLDN18.2 antibody, as first-line therapy in patients with advanced CLDN18.2+ gastric and gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma[J]. J CO, 2016, 34:LBA4001. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc200906033
|
|
[28]
|
Trarbach T, Schuler M, Zvirbule Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of multiple doses of IMAB362 in patients with advanced gastroesophageal cancer: results of a phase Ⅱ study[J]. Ann Oncol, 2014, 25(4):iv218. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313342706_636PEFFICACY_AND_SAFETY_OF_MULTIPLE_DOSES_OF_IMAB362_IN_PATIENTS_WITH_ADVANCED_GASTRO-ESOPHAGEAL_CANCER_RESULTS_OF_A_PHASE_II_STUDY
|
|
[29]
|
Al-Batran S-E, Schuler M, Zvirbule Z, et al. LBA-06. IMAB362: a novel immunotherapeutic antibody targeting the tight- junction protein component CLAUDIN18.2 in gastric cancer. Ann Oncol, 2016, 27(2):ii141-142. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313337603_LBA-06IMAB362_a_novel_immunotherapeutic_antibody_targeting_the_tight-junction_protein_component_CLAUDIN182_in_gastric_cancer
|
|
[30]
|
Moran D, Maurus D, Rohde C, et al. Prevalence of CLDN18.2, HER2 and PD-L1 in gastric cancer samples[J]. Ann Oncol, 2018, 29(8):103.
|




 下载:
下载: