Clinical analysis of third-line combination therapy with S-1 plus apatinib for advanced colorectal cancer
-
摘要:
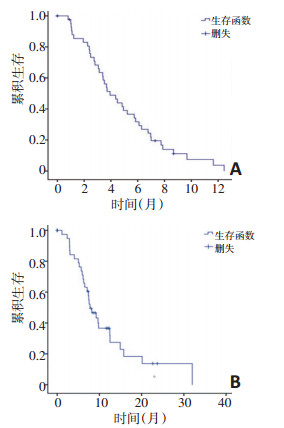
目的 观察替吉奥联合阿帕替尼用于晚期肠癌三线治疗的疗效和安全性。 方法 回顾性分析2016年4月至2018年8月华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院收治的44例采用替吉奥联合阿帕替尼治疗的三线肠癌患者临床病例资料,并进行随访,记录药物使用的有效性及不良反应数据。 结果 全组44例患者中位无进展时间(median progression-free survival time,mPFS)为3.93(2.72~5.15)个月,中位生存时间(median overall survival time,mOS)为7.77(5.36~10.18)个月。左半结肠及直肠癌患者mPFS为4.94个月,右半结肠癌患者mPFS为3.89个月,两组比较差异有统计学意义(P=0.024);左半结肠及直肠癌患者mOS为12.5个月,右半结肠癌患者mOS为7.40个月,两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.080);性别、既往是否使用过贝伐单抗以及是否存在肝转移对于mPFS及mOS无显著影响;初始治疗时ECOG评分0~1分及2分的患者mPFS分别为4.48个月及1.10个月(P < 0.001),mOS分别为9.67个月及2.90个月,两组比较差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。治疗相关性不良反应最普遍的为乏力(52.3%),其次为高血压(45%)、手足综合征(22.7%)、蛋白尿(15.9%)、白细胞下降(15.9%)、血小板下降(22.7%)、转氨酶升高(13.6%)、腹泻(15.9%)。 结论 替吉奥联合阿帕替尼用于肠癌的三线治疗具有较好的疗效,不良反应方面安全可耐受。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the efficacy and toxicity of apatinib combined with S1 as a third-line therapy for advanced colorectal cancer. Methods Forty-four patients with adavanced colorectal cancer from Tongji Hospital Cancer Center were enrolled from April 2016 to August 2018. The median follow-up period was 8 months. Data related to efficacy and adverse effects were recorded. Results The median progression-free survival (PFS) time was 3.93 months (95%CI:2.72-5.15 months), and the median overall survival (OS) time was 7.77 months (95%CI:5.36-10.18 months). Patients with left hemicolon cancer and rectal cancer group had a longer PFS than patients with right hemicolon cancer group (4.94 months vs. 3.89 months, P=0.024); the OS for left hemicolon cancer and rectal cancer was 12.5 months, the OS for right hemicolon cancer was 7.4 months, P=0.080; gender, previous bevacizumab use and liver metastasis had no statistically significant effect on PFS and OS; the PFS was 4.48 months and 1.10 month, in the patients with ECOG 0-1 and ECOG 2; the OS was 9.67 months and 2.90 month, in these two groups respectively. The major adverse effects of the combination therapy were fatigue (52.3%), hypertension (45%), hand-foot syndrome (22.7%), leukopenia (15.9%), and neutropenia (15.9%), thrombocytopenia (22.7%), elevated transaminase levels (13.6%), diarrhea (15.9%). Conclusions The results suggest that the combination of apatinib and S-1 is safe and effective as a third-line treatment for advanced colorectal cancer. -
Key words:
- colorectal cancer /
- S-1 /
- apatinib /
- adverse events /
- clinical observation
-
表 1 44例晚期肠癌患者临床资料

-
[1] 赫杰, 陈万青.2017中国肿瘤登记年报[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2018. [2] Li J, Qin S, Xu J, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase iii trial of apatinib in patients with chemotherapy-refractory advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(13):1448-1454. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.5995 [3] Duan JC, Wang ZJ, Lin L, et al. Apatinib, a novel VEGFR inhibitor plus docetaxel in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients with wild-type EGFR:a phase Ⅰ trial[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2019, 37(4):731-737. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00735-1 [4] Yu Z, Liu W, Deng Y, et al. Significant efficacy of apatinib in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma lung metastases after liver transplantation:a case report[J]. Transplant Proc, 2018, 50(10):4042-4045. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.06.044 [5] Zhen L, Jiali C, Yong F, et al. The efficacy and safety of apatinib treatment for patients with unresectable or relapsed liver cancer:a retrospective study[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(16):2773-2777. doi: 10.7150/jca.26376 [6] Hu X, Zhang J, Xu B, et al. Multicenter Phase Ⅱ study of apatinib, a novel VEGFR inhibitor in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic triplenegative breast cancer[J]. Int J Cancer 2014, 135(8):1961-1969. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28829 [7] Hu X, Cao J, Hu W, et al. Multicenter Phase Ⅱ study of apatinib in nontriple-negative metastatic breast cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14:820. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-820 [8] Miao M, Deng G, Luo S, et al. A Phase Ⅱ study of apatinib in patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2018, 148(2):286-290. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.12.013 [9] Aono N, Ito Y, Nishino K, et al. A retrospective study of the novel combination of paclitaxel and S1 for pretreated advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Chemotherapy, 2012, 58(6):454-460. doi: 10.1159/000345624 [10] Ma L, Liu JM, Zhang J, Li H. A pilot study of oral S-1 for treating heavily pretreated patients with advanced or recurrent cervical cancer among Chinese population[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018, 97(22):e10922. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010922 [11] Aoki Y, Ochiai K, Lim S, et al. Phase Ⅲ study of cisplatin with or without S-1 in patients with stage IVB, recurrent, or persistent cervical cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2018, 119(5):530-537. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0206-7 [12] Yuan P, Di LJ, Liu W, et al. Phase Ⅱ multi-center clinical study on using S-1 to treat advanced breast cancer after resistance to anthracycline and taxane drugs in Chinese patients[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8(2):3072-3079. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=735b5d35d5e71529c7c005b17b3542bf&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A, et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT):an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2013, 381(9863):303-312. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61900-X [14] Li J, Qin S, Xu R, et al. Regorafenib plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care in Asian patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CONCUR):a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(6):619-629. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70156-7 [15] Mayer RJ, Van Cutsem E, Falcone A, et al. Randomized trial of TAS-102 for refractory metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372(20):1909-1919. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414325 [16] Xu J, Kim TW, Shen L, et al. Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase iii trial of trifluridine/tipiracil (TAS-102) monotherapy in asian patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer:the TERRA study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(4):350-358. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.3245 [17] Li J, Qin S, Xu RH, et al. Effect of fruquintinib vs placebo on overall survival in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer:the FRESCO randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 2018, 319(24):2486-2496. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.7855 [18] Tian S, Quan H, Xie C, et al. YN968D1 is a novel and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase with potent activity in vitro and in vivo[J]. Cancer Sci, 2011, 102(7):1374-1380. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01939.x -




 下载:
下载: