Cytoreductive surgery combined with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for pseudomyxoma peritonei: a single-center experience with 854 patients
-
摘要:
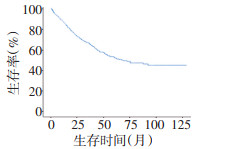
目的 腹膜假黏液瘤(pseudomyxoma peritonei,PMP)是一种罕见的临床综合征,细胞减灭术(cytoreductive surgery,CRS)联合腹腔热灌注化疗(hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy,HIPEC)因其良好的治疗效果已经成为各中心公认的标准治疗方案,航天中心医院从2008年开始致力于PMP患者诊治工作,2016年开始将全腹膜切除应用于临床,本研究通过对既往资料进行收集整理,对PMP治疗经验进行总结。 方法 回顾分析2008年1月到2019年1月航天中心医院腹膜假黏液瘤中心收治并接受手术治疗的PMP患者临床资料及随访结果。对所有患者的手术方式、根治程度及并发症发生情况等临床资料进行搜集整理,并通过随访结果对相关因素进行生存分析,了解CRS+HIPEC在PMP治疗中的临床价值,同时对腹膜切除技术治疗效果进行评价。 结果 共纳入854例患者,平均年龄50岁,中位改良腹膜肿瘤指数(peritoneal cancer index,PCI)为29,其中25.5%的患者接受了根治性手术切除,细胞减灭程度(completeness of cytoreduction,CC)达到0或1。总体并发症发生率为21.7%,围术期死亡率为1.1%。自2016年引进腹膜切除技术后,本中心达CC-0/1的比例由14.3%升至36.5%,且并发症发生率显著下降(16.8%vs.28.8%,P < 0.001)。总体而言,CC-0/1的患者5年和10年生存率分别为77%、64.3%,显著优于CC-2/3患者的45.8%、39.4%。在未达根治的患者中,CC-2和CC-3患者10年生存率也存在明显差异(45.5%vs.34.5%,P=0.006)。对总体生存进行分析,改良腹膜肿瘤指数、手术方式、术中是否行热灌注治疗、病理级别、CA125水平均为影响术后生存的独立危险因素。 结论 细胞减灭术+腹腔热灌注化疗治疗腹膜假黏液瘤安全有效,腹膜切除技术可显著提高根治程度并降低并发症风险;对于无法达到根治切除的患者,最大限度的减瘤亦可延长远期生存。 Abstract:Objective Pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP) is a rare clinical syndrome. Cytoreductive surgery (CRS) combined with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) is gradually being accepted as the standard treatment for PMP. At Aerospace Hospital, we have been treating patients with PMP since 2008 and performing total peritoneal resection since 2016. This study summarizes the experience at our center and collates past data. Methods We performed a retrospective analysis of a prospectively maintained database of all patients who had undergone CRS and HIPEC for PMP at our center. Clinical data, such as the surgical approach, completeness of cytoreduction, and surgical complications, were collected. The results from follow-up were analyzed to simultaneously evaluate the clinical value of CRS+HIPEC and peritonectomy procedures. Results A total of 854 consecutive patients with PMP were included in the study. Their mean age was 50 years. The median modified peritoneal cancer index (PCI) was 29. Of the patients, 25.5% underwent radical surgery with complete cytoreduction (CC) 0/1. The overall complication rate was 21.7%, and the perioperative mortality rate was 1.1%. Since the adoption of peritonectomy from 2016, the proportion of patients who underwent CC-0/1 at our center increased from 14.3% to 36.5%, and the incidence of complications decreased significantly (16.8% vs. 28.8%, P < 0.001). The 5- and 10- year survival rates of patients who had undergone CC-0/1 were 77% and 64.3%, respectively, which were significantly better than those of patients who had undergone CC-2/3 (45.8% and 39.4%, respectively). There was also a significant difference in the survival rate between patients who had undergone CC-2 and those who had undergone CC-3 (10-year OS 45.5% vs. 34.5%, P=0.006). The modified PCI, surgical approach, intraoperative HIPEC, pathological grade, and CA125 levels were independent risk factors for postoperative overall survival. Conclusions CRS+HIPEC is a safe and effective treatment for PMP. The technique of peritoneal resection can significantly improve the degree of radical care, while reducing the risks of complications. For patients in whom radical resection cannot be achieved, maximal tumor reduction may also prolong long-term survival. -
表 1 患者基本临床特征
(n=854) 
表 2 就诊时各区受累情况
(n=854) 
表 3 两种手术方式对比
n(%) 
表 4 单因素分析结果
(n=854) 
表 5 多因素分析结果

-
[1] Sugarbaker PH. Pseudomyxoma peritonei. A cancer whose biology is characterized by a redistribution phenomenon[J]. Annal Surg, 1994, 219(2):109-111. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199402000-00001 [2] Carr NJ, Cecil TD, Mohamed F, et al. A consensus for classification and pathologic reporting of pseudomyxoma peritonei and associated appendiceal neoplasia:the results of the peritoneal surface oncology group international (PSOGI) modified delphi process[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2016, 40(1):14-26. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000535 [3] Baratti D, Kusamura S, Milione M, et al. Pseudomyxoma peritonei of extra-appendiceal origin:A comparative study[J]. Annal Surg Oncol, 2016, 23(13):4222-4230. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5350-9 [4] Prayson RA, Hart WR, Petras RE. Pseudomyxoma peritonei. A clinicopathologic study of 19 cases with emphasis on site of origin and nature of associated ovarian tumors[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 1994, 18(6):591-603. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d035f3228d0a49c7d9ab56444baca5da&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] Ronnett BM, Shmookler BM, Diener-West M, et al. Immunohistochemical evidence supporting the appendiceal origin of pseudomyxoma peritonei in women[J]. Int J Gynecol Pathol, 1997, 16(1):1-9. doi: 10.1097/00004347-199701000-00001 [6] Young RH, Giks CB, Scully RE. Mucinous tumors of the appendix associated with mucinous tumors of the ovary and pseudomyxoma peritonei:A Clinicopathologic analysis of 5 cases supporting an appendiceal origin[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 1991, 15(5):415-429. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199105000-00001 [7] Szych C, Staebler A, Connolly DC, et al. Molecular genetic evidence supporting the clonality and appendiceal origin of pseudomyxoma peritonei in women[J]. Am J Pathol, 1999, 154(6):0-1855. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a929ae0fcbeefd119d1bbf3f65c6aae7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [8] Smeenk RM, van Velthuysen ML, Verwaal VJ, et al. Appendiceal neoplasms and pseudomyxoma peritonei:A population based study[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2008, 34(2):196-201. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2007.04.002 [9] Gough DB, Donohue JH, Schutt AJ, et al. Pseudomyxoma peritonei long-term patient survival with an aggressive regional approach[J]. Ann Surg, 1994, 219(2):112-119. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199402000-00002 [10] Spratt J. Clinical delivery system for intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemotherapy[J]. Cancer Res, 1980, 40(2):256-260. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=663330bc9eaba9d772fd329497cc0b7d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] Sugarbaker PH. Peritonectomy procedures[J]. Ann Surg, 1995, 12(3):703-727. [12] Sugarbaker PH. Peritoneal metastases, a frontier for progress[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 2018, 27(3):413-424. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=47af49acb32a377244708dd4519ef282&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications:A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey[J]. Ann Surg, 2004, 240(2):205-213 doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae [14] Sugarbaker PH, Chang D. Results of treatment of 385 patients with peritoneal surface spread of appendiceal malignancy[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 1999, 6(8):727-731. doi: 10.1007/s10434-999-0727-7 [15] Chua TC1, Moran BJ, Sugarbaker PH, et al. Early-and long-term outcome data of patients with pseudomyxoma peritonei from appendiceal origin treated by a strategy of cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2012, 30(20):2449-2456. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7d605243986e05a4dcf8723f95c448f8 [16] Ansari N, Chandrakumaran K, Dayal S, et al. Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in 1000 patients with perforated appendiceal epithelial tumours[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2016, 42(7):1035-1041. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.03.017 [17] Rebecca F, Renehan AG, Grant P, et al. Referral and treatment pathways for pseudomyxoma peritonei of appendiceal origin within a national treatment programme[J]. Colorectal Dis, 2018, 20(10):888-896. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7dcb943f867576510e88229f678eb32f [18] 李鑫宝, 林育林, 姬忠贺, 等.肿瘤细胞减灭术加腹腔热灌注化疗治疗腹膜假黏液瘤182例分析[J].中国肿瘤临床, 2018, 45(18):943-949. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2018.18.607 [19] Narasimhan V, Wilson K, Britto M, et al. Outcomes following cytoreduction and hipec for pseudomyxoma peritonei:10-year experience[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2019, doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04239-4. [20] Bhatt A, Mehta S, Seshadri RA, et al. The Initial indian experience with cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC in the treatment of peritoneal metastases[J]. Indian J Surg Oncol, 2016, 7(2):160-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8120339779b73ce63b6494ee8481ce6c [21] Youssef H, Newman C, Chandrakumaran K, et al. Operative findings, early complications, and long-term survival in 456 patients with pseudomyxoma peritonei syndrome of appendiceal origin[J]. Colon Rectum, 2011, 54(3):293-299. doi: 10.1007/DCR.0b013e318202f026 [22] Bartlett DJ, Thacker PG, Grotz TE, et al. Mucinous appendiceal neoplasms:classification, imaging, and HIPEC[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2019, 44(5):1686-1702. doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-01888-y [23] Votanopoulos KI, Bartlett D, Moran B, et al. PCI is not predictive of survival after complete crs/hipec in peritoneal dissemination from high-grade appendiceal primaries[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017, 25(3):674-678. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=feb128be17b15abd0418f21ea0d40325&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [24] Kusamura S, Hutanu I, Baratti D, et al. Circulating tumor markers:Predictors of incomplete cytoreduction and powerful determinants of outcome in pseudomyxoma peritonei[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2013, 108(1):1-8. doi: 10.1002/jso.23329 [25] Kusamura S, Baratti D, Hutanu I, et al. The role of baseline inflammatory-based scores and serum tumor markers to risk stratify pseudomyxoma peritonei patients treated with cytoreduction (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC)[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2015, 41(8):1097-1105. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=88cc3126b38bed657c8f31d0358fe020 [26] Huang Y, Alzahrani NA, Liauw W, et al. Early postoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy for low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasms with pseudomyxoma peritonei:is it beneficial?[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017, 24(1):176-183. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5529-0 [27] Huang Y, Alzahrani NA, Liauw W, et al. Early postoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy is associated with survival benefit for appendiceal adenocarcinoma with peritoneal dissemination[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2017, 43(12):2292-2298. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.09.002 [28] Dayal S, Taflampas P, Riss S, et al. Complete cytoreduction for pseudomyxoma peritonei is optimal but maximal tumor debulking may be benefcial in patients in whom complete tumor removal cannot be achieved[J]. Dis Colon Rectum, 2013, 56(12):1366-1372. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0b013e3182a62b0d [29] Funder JA, Jepsen KV, Stribolt K, et al. Palliative Surgery for Pseudomyxoma Peritonei[J]. Scand J Surg, 2015, 105(2):84-89. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=75de3b14d4611e4fa891fabffa143537&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [30] Delhorme JB, Elias D, Varatharajah S, et al. Can a benefit be expected from surgical debulking of unresectable pseudomyxoma peritonei[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2016, 23(5):1618-1624 doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-5019-9 -




 下载:
下载: