Association of postoperative radiotherapy and body mass index with the incidence of breast cancer related lymphedema in Chinese patients
-
摘要:
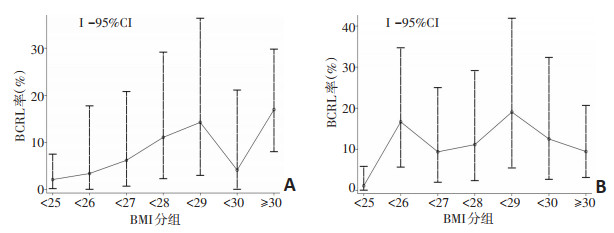
目的 探讨身体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)与放疗前、后乳腺癌相关淋巴水肿(breast cancer related lymphedema,BCRL)的相关性。 方法 分析2013年11月至2015年2月281例于河北医科大学第四医院收治的单侧乳腺癌术后女性患者的前瞻性临床资料,根据BMI < 25、25~27、BMI≥28分为BMI低组(n=94)、中组(n=89)、高组(n=98),比较健患侧上肢体积差(upper limb volume difference,ULVD),采用广义估计方程(GEE)模型和线性逻辑回归模型进行单因素和多因素分析,评估放疗对BCRL(定义为ULVD≥200 mL)的影响,并与其他BMI分界值分组结果进行比较。 结果 放疗前、后ULVD平均值分别为40.6、42.9 mL,中位值均为30.0 mL,二者之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。放疗前(2例缺失)BMI低、中、高组的BCRL发生率分别为2.2%(2/93)、6.8%(6/88)、13.3%(13/98),放疗后(1例缺失)分别为1.1%(1/93)、12.4%(11/89)、12.2%(12/98),GEE模型多因素分析显示放疗未增加BCRL率(P=0.529)。线性逻辑回归模型多因素分析显示,与BMI低组相比中组和高组放疗前(RR=4.199,P=0.693和RR=10.999,P=0.002)、放疗后(RR=13.287,P=0.047和RR=14.308,P=0.029)的BCRL发生率差异具有统计学意义。按BMI < 25、25~29、BMI≥30分组,分析结果与以上类似。 结论 乳腺癌患者术后放疗发生BCRL,中国乳腺癌患者理想的BMI < 28,与国外欧美患者为主的BMI < 30不同。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation between body mass index (BMI) and the incidence of breast cancer (BC) related lymphedema (BCRL) in Chinese patients over the period following postoperative radiotherapy (RT). Methods This study included 281 female patients with single-sided BC who were treated at The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University between November 2013 and February 2015. The clinical data of these patients were collected prospectively and analyzed. Based on their BMI, the patients were classified into three subgroups:low BMI (BMI < 25, n=94), medium BMI (27 > BMI > 25, n=89), and high BMI (BMI ≥ 28, n=98). The upper limb volume difference (ULVD) was compared between the diseased and healthy one. Univariate and multivariate generalized estimating equations (GEE) and linear logistic regression models were used to estimate the effects of RT and BMI on BCRL (defined as a ULVD ≥ 200 mL). In addition, these results were compared among the three BMI subgroups. Results The mean ULVD before and after RT were 40.6 and 42.9 mL, respectively. The median ULVD before and after therapy remained constant at 30.0 mL; no significant difference was observed (P>0.05). Two and single patient respectively lacked one arm volume measurement before and after RT. The BCRL incidence rates in the low, middle, and high BMI subgroups before RT were 2.2% (2/93), 6.8% (6/88), and 13.3% (13/98); the corresponding rates after RT were 1% (1/93), 12.4% (11/89), and 12.2% (12/98), respectively. The GEE model indicated that RT did not cause an increase in the incidence rate of BCRL (P=0.529). Multivariable logistic regression for the middle and high BMI subgroups before RT (RR=4.199, P=0.693 and RR=10.999, P=0.002, respectively) and after RT (RR=13.287, P=0.047 and RR=14.308, P=0.029, respectively) indicated a significantly higher risk of BCRL in the high BMI subgroup. Similar results were obtained from the subgroup analyses of the middle BMI subgroup. Conclusions The incidence and severity of BCRL do not decrease during the period following postoperative RT. Among Chinese BC patients, a lower threshold BMI of 28 kg/m2 appears to be associated with BCRL after RT. This is distinctly different from the commonly reported BMI threshold of 30 kg/m2 in most European and American studies. -
Key words:
- breast cancer related lymphedema /
- BMI /
- upper limb volume /
- postoperative radiotherapy
-
表 1 281例乳腺癌术后放疗患者临床基本特征

表 2 整体和BMI分组患者ULVD与BCRL发生率的关系

表 3 BCRL发生率的线性逻辑回归模型分析

-
[1] Gillespie TC, Sayegh HE, Brunelle CL, et al. Breast cancer-related lymphedema:risk factors, precautionary measures, and treatments[J]. Gland Surg, 2018, 7(4):379-403. doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.11.04 [2] McLaughlin SA, Staley AC, Vicini F, et al. Considerations for clinicians in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of breast cancerrelated lymphedema:recommendations from a multidisciplinary expert ASBrS panel:part 1:definitions, assessments, education, and future directions[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017, 24(10):2818-2826. doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-5982-4 [3] Shaitelman SF, Cromwell KD, Rasmussen JC, et al. Recent progress in the treatment and prevention of cancer-related lymphedema[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(1):55-81. doi: 10.3322/caac.21253 [4] Armer JM, Ballman KV, McCall L, et al. Factors associated with lymphedema in women with node-positive breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and axillary dissection[J]. JAMA, 2019[Epub ahead of print]. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e1854fe5cd12be27b21b6a782c0c0990&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] Fu MR, Axelrod D, Guth AA, et al. Patterns of obesity and lymph fluid level during the first year of breast cancer treatment:a prospective study[J]. J Pers Med, 2015, 5(3):326-340. doi: 10.3390/jpm5030326 [6] Jammallo LS, Miller CL, Singer M, et al. Impact of body mass index and weight fluctuation on lymphedema risk in patients treated for breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2013, 142(1):59-67. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2715-7 [7] Ridner SH, Dietrich MS, Stewart BR, et al. Body mass index and breast cancer treatment-related lymphedema[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2011, 19(6):853-857. doi: 10.1007/s00520-011-1089-9 [8] Helyer LK, Varnic M, Le LW, et al. Obesity is a risk factor for developing postoperative lymphedema in breast cancer patients[J]. Breast J, 2010, 16(1):48-54. doi: 10.1111-j.1743-6109.2009.01542.x/ [9] Wang H, Li D, Liuya J, et al. Reference ranges using bioimpedance for detection of lymphedema in Chinese women[J]. Lymphat Res Biol, 2017, 15(3):268-273. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2017.0012 [10] Kwan ML, Darbinian J, Schmitz KH, et al. Risk factors for lymphedema in a prospective breast cancer survivorship study:the pathways study[J]. Arch Surg, 2010, 145(11):1055-1063. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2010.231 [11] Sun F, Hall A, Tighe MP, et al. Perometry versus simulated circumferential tape measurement for the detection of breast cancer-related lymphedema[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2018, 172(1):83-91. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4902-z [12] Shah C, Vicini FA, Arthur D. Bioimpedance spectroscopy for breast cancer related lymphedema assessment:clinical practice guidelines[J]. Breast J, 2016, 22(6):645-650. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12647 [13] McDuff SGR, Mina AI, Brunelle CL, et al. Timing of lymphedema after treatment for breast cancer:when are patients most at risk[J]? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2019, 103(1):62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.08.036 [14] Kilgore LJ, Korentager SS, Hangge AN, et al. Reducing breast cancerrelated lymphedema (BCRL) through prospective surveillance monitoring using bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and patient directed self-interventions[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2018, 25(10):2948-2952. doi: 10.1245/s10434-018-6601-8 [15] Arngrim N, Simonsen L, Holst JJ, et al. Reduced adipose tissue lymphatic drainage of macromolecules in obese subjects:a possible link between obesity and local tissue inflammation[J]? Int J Obes (Lond), 2013, 37(5):748-750. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2012.98 [16] Shaw C, Mortimer P, Judd PA. A randomized controlled trial of weight reduction as a treatment for breast cancer-related lymphedema[J]. Cancer, 2007, 110(8):1868-1874. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22994 -




 下载:
下载: