Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition Cell Proliferation and Cell Apoptosis in Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma with a Micropapillary Pattern
-
摘要:目的 探讨伴微乳头成分的肺腺癌(pulmonary adenocarcinoma with a micropapillary pattern, MPPAC)上皮间质转化和增殖调亡特征, 为临床评价其恶性潜能提供理论依据。方法 根据2011年发表的肺腺癌新分类诊断标准, 以是否伴有微小乳头状结构(micropapillary pattern, MPP)将120例肺腺癌病例分为64例MPP阳性组, 56例MPP阴性组。免疫组织化学法检测Vimentin、E-cadherin、Capase-3、pEGFR的表达。结果 120例肺腺癌病例中pECFR在女性(P=0.035)、非吸烟(P=0.017)患者中高表达。Vimentin在MPP阳性组的表达(28.1%)高于MPP阴性组(16.1%)并且其多表达于微乳头结构腔内散落的细胞; Caspase-3在MPP阳性组高表达(P=0.001)。结论 微乳头结构的腔内散落细胞表现间质表型有利于癌细胞浸润转移, 伴乳头结构的肺腺癌有其独特的分子生物学特征。Abstract:Objective This paper aimed to determine the characteristics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell proliferation, and cell apoptosis in pulmonary adenocarcinoma with a micropapillary pattern(MPPAC).Methods Based on the new diagnostic criteria for lung adenocarcinoma classification(published in 2011), 120 cases of lung adenocarcinoma were divided into micropapillary pattern (MPP)-positive(n=64)and MPP-negative(n=54)groups.The expression of vimentin, E-cadherin, caspase-3, and pEGFR in pulmonary adenocarcinoma tissue specimens was determined by immunohistochemical assay.Results pEGFR expression in 120 cases of lung adenocarcinoma was higher in female(P=0.035)and nonsmoking(P=0.017)patients.Vimentin expression was higher in the MPP-positive(28.1%)than MPP-negative(16.1%)groups, and mostly located in scattered cells in the MPP cavity.Caspase-3 expression was significantly higher in the MPP-positive group(P=0.001).Conclusion Scattered cells in the MPP cavity have a mesenchymal phenotype, which may favor invasion and metastasis, indicating a unique characteristic of MPPAC.
-
国际肺癌研究协会、美国胸科协会、欧洲呼吸协会对肺腺癌进行新的分类, 相关文献于2011年2月发表, 其中大的变动是新增加一个组织学类型: 肺微小乳头状腺癌[1]。本研究用免疫组织化学的方法研究这一特殊亚型肺腺癌E-cadherin、Vimentin、Capase-3和pEGFR的表达状况, 研究肿瘤浸润生长上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition, EMT)现象和增殖凋亡特点, 进一步了解其独特的生物学行为并提供评价预后的指标。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 临床病理资料
选择2009年2月至2010年10月天津医科大学附属肿瘤医院经手术治疗有完整临床病理资料的肺部原发肿瘤病例共120例, 微乳头成分 > 5%[1]的MPP阳性组64例, 年龄34~75岁, 平均年龄58.72岁, 中位年龄59.00岁; 男性35例, 女性29例; 吸烟者37例, 不吸烟者27例; 肿瘤大小0.5~10.0 cm, 最大直径的平均值为3.5 cm, 最大直径中位值为3.0 cm; 临床分期结果显示Ⅰ期26例(Ⅰa期14例, Ⅰb期12例), Ⅱ期11例(Ⅱa期6例, Ⅱb期5例), Ⅲa期27例。微乳头成分 < 5%的MPP阴性组56例病例, 年龄32~74岁, 平均年龄58.16岁, 中位年龄57.50岁; 男性22例, 女性34例; 吸烟者25例, 不吸烟者31例; 肿瘤大小1.1~9.0 cm, 最大直径平均值为3.7 cm, 最大直径中位值为3.0 cm; 临床分期结果显示Ⅰ期31例(Ⅰa期18例, Ⅰb期13例), Ⅱ期3例(Ⅱa期0例, Ⅱb 3例), Ⅲa期22例。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 免疫组织化学染色
采用免疫组织化学链霉素抗生物素蛋白-过氧化物酶(S-P)法。常规石蜡切片脱蜡至水, 高压抗原修复。兔抗人Caspase-3多克隆抗体(1:100)、鼠抗人E-cadherin单克隆抗体(1:100)、鼠抗人Vimentin单克隆抗体(1:100)购自北京中杉金桥生物试剂公司, 鼠抗人pEGFR单克隆抗体(1:1 600)购自美国CST公司, 4℃孵育过夜, PBS漂洗3次×5 min, 生物素标记二抗室温25 min, PBS漂洗3次×5 min, DAB显色, 苏木素复染, 脱水, 透明, 中性树胶封片。用已知阳性切片作阳性对照, PBS代替一抗作为阴性对照。
1.2.2 结果判定
先按染色强度计分: 0分为无色, 1分为淡黄色, 2分为棕黄色, 3分为棕褐色; 再按阳性细胞所占的百分比计分: 0分为阴性, 1分为阳性细胞≤10%, 2分为阳性细胞1 1%~50%, 3分为阳性细胞5 1%~75%, 4分为阳性细胞≥75%。染色强度和阳性细胞百分比的乘积≥3分, 为免疫反应阳性, 否则为阴性[2]。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 16.0统计软件包进行统计分析, 组间数据比较采用χ2检验, P < 0.05定义为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 Vimentin、E-cadherin、Capase-3、pEGFR在肺癌组织中的表达
检测结果显示Vimentin主要表达在胞浆, E-adherin表达在细胞膜或少许胞浆, Caspase-3表达在胞浆和少许胞核, pEGFR表达在胞膜和/或胞浆。
2.2 Vimentin、E-cadherin、Caspase-3与临床病理因素的关系
在120例肺腺癌病例中Vimentin、E-cadherin、Capase-3表达率分别为20.8%、64.2%、70.0%, 这3个标志物的表达与患者的性别、年龄、吸烟状况、浸润转移情况、肿瘤大小、临床分期无明显相关性(P > 0.05)。pEGFR的表达率为34.2%, 其表达与患者的年龄、浸润转移情况、肿瘤大小、临床分期无关(P > 00.05), 在女性患者的表达(42.9%)高于男性(24.6%)(P=0.035);在非吸烟病例表达(44.8%)高于吸烟病例(24.2%, P=0.017, 表 1)。
表 1 Vimentin、E-cadherin、Capase-3、pEGFR表达与120例肺腺癌临床病理参数的相关性 例Table 1. Relationship of Vimentin, E-cadherin, Caspase-3, and pEGFR expression with clinicopathological parameters in 120 cases of lung adenocarcinoma
2.3 Vimentin, E-cadherind, Caspase-3, pEGFR在MPP阳性组及阴性组中表达比较
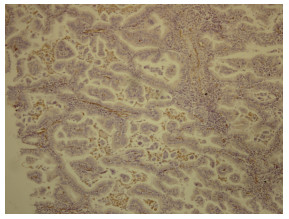
MPP阳性组和阴性组间Vimentin表达率分别为25.0%(16/64)、16.1%(9/56)(P=0.1 15);E-cadherind的表达率分别为62.5%(40/64)、66.1%(37/56)(P=0.684);Caspase-3的表达率分别为82.8%(53/64)、55.4%(31/56)(P=0.001);pEGFR表达率分别为34.4%)(22/64)、33.9%(19/56)(P=0.959) MPP 5性组中Vimentin多表达于微乳头结构腔内散落的细胞(图 1)。
3. 讨论
伴微乳头成分的肺腺癌是一种具有高度恶性潜能[3-4]的独特组织学亚型的癌, 易发生淋巴结转移、淋巴管侵犯、肺内转移、胸膜侵犯及远处转移, 其总体生存期及无病生存期与其他类型的肺腺癌相比有显著差异。多项研究表明肿瘤细胞发生EMT后其深层浸润及远处转移能力明显增加[5], 导致淋巴结转移临床分期进展。Caspase-3的表达水平与肿瘤的恶性度相关[6], pEGFR高表达与肺癌不良的预后相关[7]。本研究通过探讨MPPAC中E-cadherin、Vimentin、Capase-3和pEGFR的表达状况, 为临床评价其恶性潜能提供理论依据。
EMT是指机体细胞在多种因素作用下出现的由上皮细胞向间质细胞转化的现象, 以E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadhe rin等上皮特征蛋白减少和波形蛋白(Vimentin)等间质特征蛋白表达增多为标志[3]。Lee等[8]研究表明, E-cadherin在早期、高分化、无浸润转移的肺癌细胞中高表达。本研究选择120例肺腺癌E-cacdherin和Vimentin的表达率分别为64.2%、20.8%, 研究结果显示二者在肺腺癌中的表达与患者的性别、年龄、吸烟状况、浸润转移情况、肿瘤大小、临床分期无明显相关性。Vimentin在MPP阳性组验组的表达率高于MPP阴性组, MPP阳性组中Vimentin多表达于微乳头结构腔内散落的细胞, 这可能是伴微乳头的肺腺癌易浸润转移能力增强的原因之一。
细胞凋亡的核心成分是半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族(cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase, Caspase), 活化的Caspase能降解细胞的结构蛋白和功能蛋白, 导致细胞凋亡[6]。有研究发现, Caspase-3在肺癌表达与有无淋巴结转移、病理分期、分化程度相关[9]。本实验对120例肺腺癌患者研究Caspase-3在有浸润转移的病例中表达率为74.2%(49/66)高于无浸润转移的病例64.8%(35/54), 但差异无统计学意义。可能由于本研究病例中多为肺腺癌并且伴微乳头结构的肺腺癌占较大比例。Caspase-3在MPP阳性组中表达高于MPP阴性组(P=0.001), 与国外相关研究结果一致[6], 但是这不能解释MPPAC预后较差, 提示MPPAC有独特的分子生物学特点, 有待进一步研究其对临床治疗的意义。
有研究发现按照肺腺癌新分类标准分类后伴微乳头成分的肺腺癌EGFR突变频率高于肺腺癌其他亚型[10]。本实验发现EGFR基因磷酸化的形式pEG-FR在MPP阳性组和MPP阴性组间表达无差异, 与EGFR突变不同, pEGFR的表达与MPPAC无相关性。Dacic等[11]和Kim等[12]研究发现pEGFR在鳞癌中表达高于腺癌, 但与临床各病理学特征均无相关性。于敏等[2]研究发现pEGFR在女性、不吸烟、腺癌患者中高表达。本研究120例肺腺癌中发现pEGFR在女性、不吸烟病例中高表达, 这与EGFR-TKls的临床受益人群基本一致, 说明pEGFR在一定程度上可代替EGFR基因突变作为筛选EGFR-TKls的简易指标。此外, EGFR蛋白过表达和EGFR-TKIs应答的相关性, 有待于进一步研究。
本研究通过探讨MPPAC上皮间质转化和增殖调亡特征, 解释了MPPAC独特的生物学行为, 为临床表现提供了理论指导, 提供评价其恶性潜能及准确判断预后的免疫组织化学指标, 为临床医生制定个体化治疗方案提供了依据。
-
表 1 Vimentin、E-cadherin、Capase-3、pEGFR表达与120例肺腺癌临床病理参数的相关性 例
Table 1 Relationship of Vimentin, E-cadherin, Caspase-3, and pEGFR expression with clinicopathological parameters in 120 cases of lung adenocarcinoma

-
[1] Travis WD, Brambilla E, MD, et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary/Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2011, 6(2): 244-285. DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221
[2] 于敏, 倪琛琛. EGFR、pEGFR蛋白在非小细胞肺癌中的表达意义[J]. 安徽大学学报, 2011, 46(1): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YIKE201101018.htm [3] Amin MB, Tamboli P, Merchant SH, et al. Micropapillary component in lung adenocarcinomas distinctive histologic'feature with possible prognostic significance[J]. Am JSurg Pathol, 2002, 26(3): 358-364. DOI: 10.1097/00000478-200203000-00010
[4] Tsutsumida H, Nomoto M, Goto M, et al. A micropapillary pattern is predictive of a poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. and reduced surfactant apoprotein A expression in the micropapillary pat- tern is an excellent indicator of a poor prognosis[J]. Med Pathol, 2007, 20(6): 638-647. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.3800780
[5] Thiery JP. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2003, 15(6): 740-746. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2003.10.006
[6] Cakir E, Yilmaz A, Demiraq F, et al. Prognostic significance of micropapillary pattern in lung adenocarcinoma and expression of apoptosis-related markers: caspase-3, bcl-2, and p53[J]. APMIS, 2011, 119(9): 574-580. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2011.02778.x
[7] Ohsaki Y, Tanno S, Fujita Y, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression correlates with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with p53 overexpression. Oncol Rep, 2000, 7 (3): 603-607.
[8] Lee YC, Wu CT, Chen CS, et al. The significance of E-cadherin and alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin expression in surgically treated non-small cell lung cancers of 3cm or less in size[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2002, 123(3): 502-507. DOI: 10.1067/mtc.2002.119334
[9] Farina F, Cappello F, Todaro M, et al. Involvement of caspase-3 and GD3 ganglioside in ceramide-induced apoptosis in Farber disease[J]. J Histochem Cytochcm, 2011, 48(2): 57-62.
[10] Shim HS, Lee DH, Park EJ, et al. Histopathologic Characteristics of Lung Adenocarcinomas With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations in the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2011, 135(10): 1329-1334. DOI: 10.5858/arpa.2010-0493-OA
[11] Dacic S, Flangan M, Cieply K, et al. Significance of EGFR protein expression and gene amplification in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomar[J]. AmJ Clinical Pathology, 2006, 125(6): 860-865. DOI: 10.1309/H5UW6CPCWWC92241
[12] Kim SJ, Rabbani ZN, Dong F, et al. Phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor and cyclooxygenase2 expression in localized Non small cell lung cancer[J]. MedOncol, 2010, 27(1): 91-97.



 下载:
下载: