The association between the expression and activity of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase and the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer
-
摘要:目的 分析吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶(indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase,IDO)在乳腺癌患者癌组织中表达及其在外周血中活性与新辅助化疗疗效的关系。方法 收集2015年9月至2016年12月天津医科大学肿瘤医院53例行新辅助化疗乳腺癌患者的肿瘤穿刺标本和血液标本,采用免疫组织化学法及高效液相色谱法检测癌组织中IDO表达及外周血中色氨酸(tryptophan,Trp)、犬尿氨酸(kynurenine,Kyn)浓度与IDO活性,分析IDO表达及活性与化疗疗效的相关性。结果 新辅助化疗前乳腺癌组织中IDO表达与临床T分期(P=0.006)、N分期(P=0.020)、临床分期(P=0.045)及ER状态(P=0.014)有关。新辅助化疗前外周血中IDO高活性伴随癌组织中IDO高表达(P=0.004),并与临床T分期(P=0.019)及N分期(P=0.047)有关。单因素分析显示新辅助化疗临床疗效与化疗前临床T分期(P=0.049)、ER状态(P=0.025)及分子分型(P=0.014)有关;病理完全缓解(pathologic complete response,pCR)与化疗前临床T分期(P=0.014)有关。更重要的是新辅助化疗临床疗效及pCR均与化疗前IDO表达及活性有关(均P < 0.05)。多因素分析显示新辅助化疗前外周血中IDO活性是影响pCR的唯一独立因素(P=0.032)。结论 新辅助化疗前乳腺癌组织中IDO表达和外周血中IDO活性与化疗疗效相关,可以为临床预测化疗是否敏感提供一定信息。
-
关键词:
- 乳腺癌 /
- 吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶 /
- 新辅助化疗 /
- 化疗疗效 /
- 病理完全缓解
Abstract:Objective To investigate the association between indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) expression in tumor tissue, its peripheral blood activity, and the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapyin patients with breast cancer.Methods Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) were used to measure IDO protein expression in tumor tissue, and kynurenine (Kyn), tryptophan (Trp), and IDO activity (Kyn/Trp) in peripheral blood before neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 53 patients with breast cancer from Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital between September 2015 and December 2016. The correlations between the expression and activity of IDO and the efficacy of chemotherapy were analyzed.Results In tumor tissue, IDO expressionbefore neoadjuvant chemotherapy was related to clinical tumor stages (P=0.006), node stages (P=0.020), clinical stages (P=0.045), and estrogen receptor (ER) status (P=0.014). High IDO activity before neoadjuvant chemotherapy in peripheral blood was associated with high IDO expression in tumor tissue (P=0.004), and was also correlated with clinical tumor stages (P=0.019) and node stages (P=0.047). Univariate analysis showed that the clinical efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy was associated with pre-chemotherapeutic clinical tumor stages (P=0.049), ER status (P=0.025), and molecular subtype (P=0.014), while pathologic complete response (pCR) was related to pre-chemotherapeutic clinical tumor stages (P=0.014). Importantly, the clinical efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and pCR were both related to IDO expression and activity before chemotherapy (all P < 0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that pre-chemotherapeutic IDO activity in peripheral blood was the only independent factor that affected pCR (P=0.032).Conclusions Tumor tissue IDO expression and peripheral blood IDO activity before chemotherapy were associated with chemotherapy efficacy, and could provide promising information for the clinical prediction of chemotherapy sensitivity. -
吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶(indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase,IDO)是肝脏外唯一可以代谢色氨酸的限速酶,很多恶性肿瘤患者的癌组织中IDO高表达且外周血中IDO活性增加[1-2]。研究发现卵巢癌化疗耐药后IDO表达增高[1],乳腺癌患者外周血IDO活性高于正常人且与化疗疗效有关[2-3]。本研究旨在分析行新辅助化疗乳腺癌患者的癌组织中IDO表达及外周血中IDO活性与化疗疗效的相关性,为临床预测化疗是否敏感提供一定信息。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 标本
收集2015年9月至2016年12月53例于天津医科大学肿瘤医院经粗针穿刺活检术证实为乳腺癌并行新辅助化疗患者的临床病理资料及化疗前肿瘤组织穿刺标本、血液标本。53例患者的年龄为24~68岁,中位年龄50岁。
1.1.2 试剂
IDO抗体Clone 10.1(美国Milliper公司)、DAB显色剂及抗体稀释液ZLI-9030(北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司)、犬尿氨酸(上海君创生物科技有限公司)、L-色氨酸(上海蓝季科技发展有限公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 免疫组织化学法
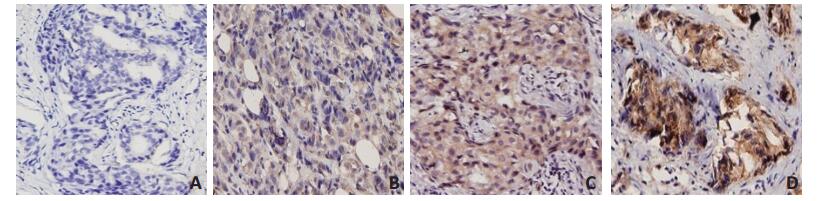
穿刺组织标本经10%福尔马林固定,石蜡包埋后4 μm厚连续切片,SP法进行IDO蛋白免疫组织化学染色,PBS代替一抗作阴性对照。阳性细胞定位于细胞浆染成棕黄色,采用半定量积分法评价。根据每张切片的阳性细胞指数及着色强弱计分:阳性细胞 < 5%(0分),5%~30%(1分),31%~70%(2分),>71%(3分);按着色强弱评分:未着色0分,弱着色1分,中等着色2分,强着色3分。IDO表达最终评分标准:两者评分相加0~1分IDO(-),2~3分IDO(+),4~ 5分IDO(++),6分IDO(+++)。0~3分定义为IDO低表达,4~6分为高表达[4]。阳性细胞指数=阳性细胞数/计数细胞总数×100%。
1.2.2 高效液相色谱法
配制色氨酸(tryptophan, Trp)和犬尿氨酸(kynurenine, Kyn)标准储备液,放入冰箱备用。收集53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前空腹外周静脉血3 mL,分离血清于-80℃冰箱冻存备用。色谱检测条件为色谱柱:Kromasil RP-C18柱(内径4.6 mm,长度150 mm,粒径5 μm);流动相:15 mmol/L乙酸钠-乙酸溶液(含5%乙腈、pH为4.0);流速:1.0 mL/min;柱温:25℃;进样量:20 μL;数据处理:Anstar色谱工作站。Kyn、Trp采用外标法测定峰面积定量分析。外周血IDO活性采用血清Kyn/Trp的比值评估。
1.2.3 化疗疗效评估
标准新辅助化疗疗效从临床疗效及病理完全缓解两方面评估。临床疗效采用实体瘤疗效评价标准RECIST 1.1版评估,分为完全缓解(complete response,CR)、部分缓解(partial response,PR)、疾病稳定(stable disease,SD)和疾病进展(progressive disease,PD)。新辅助化疗临床疗效敏感组为CR与PR,临床疗效不敏感组为SD与PD。病理完全缓解(pathologic complete response,pCR)采用美国乳腺与肠道外科辅助治疗研究组(national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project,NSABP)评估标准。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 20.0软件进行统计学分析。计量资料均数比较采用t检验和单因素方差分析,计数资料采用χ2检验、Fisher确切概率法,多因素分析采用二元Logistic回归。P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 乳腺癌患者临床病理特征
根据AJCC癌症分期手册(第7版)中的TNM分期,53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前Ⅱ期4例,Ⅲ期48例,Ⅳ期1例。新辅助化疗1~8个周期,中位化疗3个周期。紫杉类联合蒽环类化疗方案50例,单纯蒽环类方案2例,单纯紫杉类方案1例。组织学分类中乳腺浸润性癌45例,其他8例。参照2011年St.Gallen共识分子分型,Luminal型35例,HER-2过表达型11例,Basal-like型7例。53例患者中新辅助化疗临床疗效敏感组为30例,pCR组为10例。
2.2 乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前IDO表达及活性
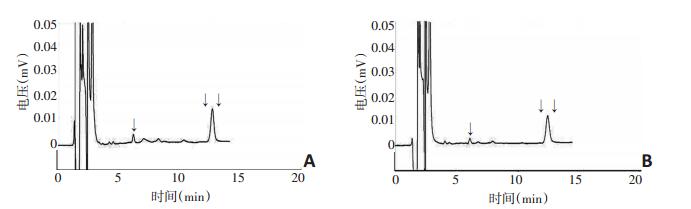
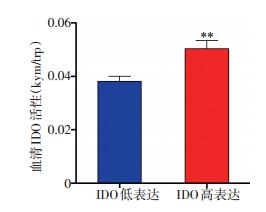
53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前28例癌组织中IDO高表达(52.83%),25例IDO低表达(47.17%),见图 1。新辅助化疗前外周血中IDO平均活性为0.044±0.015,其中患者A外周血IDO高活性为0.052(图 2A),患者B外周血IDO低活性为0.031(图 2B)。新辅助化疗前癌组织IDO高表达者的外周血IDO平均活性为0.050± 0.017,IDO低表达者的IDO平均活性为0.038±0.009,两者比较差异具有统计学意义(t=-3.08,P=0.004,图 3)。
2.3 乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前IDO表达及活性与临床病理特征的相关性分析
新辅助化疗前癌组织中IDO表达随着临床T分期(P=0.006)、N分期(P=0.020)、临床分期(P=0.045)的增高而增强,且ER阳性者IDO高表达(P=0.014);新辅助化疗前外周血中IDO活性同样随着临床T分期(P=0.019)和N分期的增高而升高(P=0.047,表 1)。
表 1 53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前癌组织中IDO表达及外周血中IDO活性与临床病理特征的相关性
2.4 乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前IDO表达及活性与化疗疗效的关系
在新辅助化疗临床疗效不敏感组中,癌组织中的IDO表达较高(P=0.012)且外周血IDO活性较强(P= 0.004);在非pCR组中IDO表达增强(P=0.004)、IDO活性升高(P=0.001,表 2)。
表 2 53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前癌组织中IDO表达及外周血中IDO活性和化疗疗效的关系
2.5 乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗疗效的单因素分析
新辅助化疗临床疗效与化疗前临床T分期(P=0.049)、ER状态(P=0.025)及分子分型(P=0.014)有关,化疗前临床T3、T4期、ER阳性及Luminal型乳腺癌患者化疗敏感性较差;pCR与化疗前临床T分期相关(P=0.014),化疗前临床T1、T2期的患者更易达到pCR(表 3)。
表 3 53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗疗效的单因素分析
2.6 乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗疗效的多因素二元Logistic回归分析
新辅助化疗前外周血中的IDO活性是影响pCR唯一的独立因素(P=0.032)。新辅助化疗临床疗效中分子分型是其独立因素(P=0.041),而外周血中的IDO活性非其独立因素可能与样本数量较少有关(P= 0.053,表 4)。
表 4 乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗疗效的多因素二元Logistic回归分析
3. 讨论
多种恶性肿瘤患者的癌组织中IDO表达增强或外周血中IDO活性升高,研究证实某些癌组织中IDO的表达与肿瘤临床分期、淋巴结转移、激素受体状态等临床病理因素相关[1-2]。本课题组前期研究发现乳腺癌患者癌组织中的IDO高表达与较晚临床分期及淋巴结转移相关[5]。Isla Larrain等[6]研究也证实IDO表达与临床分期呈正相关。本研究中乳腺癌患者癌组织中的IDO表达随着临床T分期、N分期及临床分期的提高而增强;且ER阳性患者IDO表达水平高。
以往研究揭示肿瘤IDO表达和全身Trp代谢相关,肿瘤IDO高表达常伴随外周血中Trp浓度降低、Kyn浓度升高以及异常的Kyn/Trp比值,如在子宫内膜癌组织中IDO mRNA的升高伴随着外周血Kyn/Trp比值的增大[7],在乳腺癌组织中IDO高表达与外周血中Kyn/Trp高比值相关[8]。一项乳腺癌研究发现,外周血中Kyn/Trp比值在肿瘤远处转移组及局部复发组均升高,且远处转移组高于局部复发组、多处转移组高于单一转移组,而远处转移组的生存率明显低于局部复发组[9]。以上研究表明Kyn/Trp比值与局部癌组织中的IDO表达相关,且与肿瘤的进展及预后有关。本研究证实新辅助化疗前外周血中IDO活性与乳腺癌组织中IDO表达及肿瘤T、N分期呈正相关,以Kyn/Trp比值评估IDO活性可以提示局部癌组织中IDO表达及肿瘤进展情况。
研究发现化疗药物对肿瘤细胞IDO表达及活性均有影响,同时IDO酶也与化疗耐药相关[3, 10]。本研究显示,乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前IDO表达及活性与化疗疗效相关,在疗效不敏感及非pCR组中,化疗前肿瘤IDO表达增高、外周血IDO活性增强,且化疗前外周血中IDO活性是影响pCR的独立因素。卵巢癌的研究发现,紫杉醇耐药卵巢癌细胞系及难治性卵巢癌组织中IDO高表达[1]。非小细胞肺癌的研究发现,铂类化疗敏感患者血液单核细胞中IDO表达较低[11],肺癌患者经过铂类或紫杉醇化疗联合放疗后,疗效敏感者Kyn/Trp比值高于不敏感者[12]。在乳腺癌中IDO表达或活性与化疗耐药间的关系尚不明确,但在乳腺癌内分泌治疗中证实使用氟维司群耐药者IDO活性下降不显著[13]。这些均与本研究得到的结论是一致的。
综上所述,新辅助化疗前癌组织中IDO表达及外周血中IDO活性与化疗疗效相关,可以为临床预测化疗是否敏感提供一定信息。
-
表 1 53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前癌组织中IDO表达及外周血中IDO活性与临床病理特征的相关性

表 2 53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗前癌组织中IDO表达及外周血中IDO活性和化疗疗效的关系

表 3 53例乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗疗效的单因素分析

表 4 乳腺癌患者新辅助化疗疗效的多因素二元Logistic回归分析

-
[1] Okamoto A, Nikaido T, Ochiai K, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase serves as amarker of poor prognosis in gene expression profiles of serous ovarian cancer cells[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2005, 11(16):6030-6039. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2671
[2] Lyon DE, Walter JM, Starkweather AR, et al. Tryptophan degradation in women withbreast cancer: a pilot study[J]. BMC Res Notes, 2011, 4:156. DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-156
[3] Sakurai K, Fujisaki S, Nagashima S, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase activityduring neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer[J]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho, 2013, 40(12):1578-1580. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/papers/24393854
[4] Ino K, Yoshida N, Kajiyama H, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase is a novel prognostic indicator for endometrial cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2006, 95(11):1555-1561. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603477
[5] Liu JT, Wei LJ, Yu JP, et al. Expression of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase and its correlation with prognosis in breast cancer patients[J]. Zhong Hua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2011, 33(7):513-516.
[6] Isla Larrain MT, Rabassa ME, Lacunza E, et al. IDO is highly expressed in breast cancer and breast cancer-derived circulating microvesicles and associated to aggressive types of tumors by in silico analysis[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35(7):6511-6519. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-1859-3
[7] Hascitha J, Priya R, Jayavelu S, et al. Analysis of Kynurenine/Tryptophan ratio and expression of IDO1 and 2mRNA in tumour tissue of cervical cancer patients[J]. Clin Biochem, 2016, 49(12):919-924. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2016.04.008
[8] Sakurai K, Amano S, Enomoto K, et al. Study of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenaseexpression in patients with breast cancer[J]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho, 2005, 32(11):1546-1549. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7452889_Study_of_indoleamine_23-dioxygenase_expression_in_patients_with_breast_cancer
[9] Sakurai K, Fujisaki S, Suzuki S, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase activity in breast cancer patients with local recurrence or distant metastases[J]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho, 2014, 41(10):1304-1306.
[10] Ninomiya S, Narala N, Huye L, et al. Tumor indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibits CD19-CAR T cells and is downregulated by lymphodepleting drugs[J]. Blood, 2015, 125(25):3905-3916. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-01-621474
[11] Sim SH, Ahn YO, Yoon J, et al. Influence of chemotherapy on nitric oxide synthase, indole-amine-2, 3-dioxygenase and CD124 expression in granulocytes and monocytes ofnon-small cell lung cancer [J]. Cancer Sci, 2012, 103(2):155-160. DOI: 10.1111/cas.2012.103.issue-2
[12] Creelan BC, Antonia S, Bepler G, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase activity andclinical outcome following induction chemotherapy and concurrent chemoradiation in stage Ⅲnon-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2013, 2(3):e23428. DOI: 10.4161/onci.23428
[13] Sakurai K, Fujisaki S, Suzuki S, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase activity during fulvestrant therapy for aromatase inhibitor-resistant metastatic breast cancer[J]. Gan ToKagaku Ryoho, 2015, 42(10): 1225-1227.



 下载:
下载: