-
摘要:目的 探讨双克隆型淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤(lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma,LPL)的临床特征及诊疗疗效。方法 收集1993年6月至2017年10月就诊于中国医学科学院血液病医院5例双克隆型LPL患者的临床资料并进行分析。结果 5例患者中男性4例、女性1例。3例为华氏巨球蛋白血症国际预后指数(ISSWM)分期高危患者,4例患者表达免疫球蛋白G(IgG)和免疫球蛋白M(IgM),3例患者表达不同类型轻链。5例患者的血清免疫固定电泳均为双克隆,骨髓均可见异常淋巴细胞及浆细胞浸润。5例患者确诊双克隆LPL后,2例CD20阳性者接受利妥昔单抗为基础的化疗方案、1例伊布替尼口服治疗、1例苯达莫司汀治疗效果不佳改用沙利度胺+地塞米松+环磷酰胺(TCD)治疗、1例使用司莫司汀+环磷酰胺+马法兰+地塞米松+长春新碱(M2)化疗。5例患者中4例达到微小缓解(minimal response,MR)及以上疗效,中位随访时间为44.1个月,中位无进展生存期(median progression-free survival,mPFS)为52.4个月,中位总生存期(median overall survival,mOS)为 52.4个月。截至 2022 年5月随访结束,2例患者部分缓解(partial response,PR),2例患者死亡。结论 双克隆LPL非常罕见,对该疾病的临床特征、诊断、治疗转归及预后尚缺乏深刻一致的认识,仍需更多的临床病例总结分析。
-
关键词:
- 淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤 /
- 双克隆淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤 /
- 华氏巨球蛋白血症 /
- 免疫固定电泳
Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical features and treatment efficacy of bi-clonal lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL).Methods We collected clinical data from five patients with bi-clonal LPL who visited Institute of Hematology & Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College from 1993 to 2017 and reviewed the relevant literature.Results Four of the five patients were male, and three were high-risk patients according to ISSWM staging. Bi-clonal serum immunofixation electrophoresis was performed. Abnormal lymphocytes and plasma cell infiltration were observed in the bone marrow of all five patients. Additionally, four patients expressed IgG and IgM antibodies, while three patients expressed different types of light chains. Serum immunofixation electrophoresis was biclonal in all five patients, and abnormal lymphocytes and plasma cell infiltration were observed in the bone marrow of all five patients. After bi-clonal LPL was confirmed in all patients, varied treatment strategies were employed. Two CD20-positive patients received rituximab-based chemotherapy regimens, one was treated with ibrutinib, one was treated with TCD because of the poor effect of bendamustine, and one was treated with M2. Four of the five patients achieved minimal response (MR) or greater. After a median follow-up time of 44.1 months, a median progression-free survival (mPFS) of 52.4 months, and a median overall survival (mOS) of 52.4 months were observed. At the end of the follow-up, two patients maintained partial response (PR) while two passed away.Conclusions Occurrence of bi-clonal LPL is very rare, and deep and consistent understanding of the clinical features, diagnosis, treatment regression, and prognosis of this disease is lacking. Therefore, more summary and analysis of clinical cases is required. -
淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤(lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma,LPL)是一种罕见的惰性B细胞淋巴瘤,其在非霍奇金淋巴瘤(non-Hodgkin's lymphoma,NHL)中占1%~2%,常侵犯骨髓,少数侵犯淋巴结和脾脏,同时不符合其他伴小B淋巴细胞样肿瘤的诊断标准。90%~95%的LPL分泌单克隆性免疫球蛋白M(IgM),称为华氏巨球蛋白血症(Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia,WM),仅少部分LPL患者分泌单克隆性免疫球蛋白A(IgA)、免疫球蛋白G(IgG)或不分泌单克隆免疫球蛋白,同时表达两种或两种以上免疫球蛋白的LPL称为双克隆型LPL[1]。双克隆型LPL发病率极低,国内外多见于个案报道,预后情况尚未明确,缺乏大宗的数据资料报道。本研究旨在通过对中国医学科学院血液病医院收治的5例患者的临床资料进行总结并结合文献予以复习,以提高对该疾病的认识水平。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 临床资料
收集1993年6月至2017年10月就诊于中国医学科学院血液病医院的5例双克隆型LPL患者的临床资料。WM的诊断依据第二届国际WM工作组标准[2]。5例双克隆LPL患者均行骨髓病理学检查确诊,免疫球蛋白定量及定性检测。收集的临床资料包括患者的性别、初诊年龄、首发症状、血常规、生化常规、免疫球蛋白等实验室检查,以及治疗方案、疗效、预后、随访时间等。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 疗效评价及随访
参照华氏巨球蛋白血症国际研讨会(IWWM)推荐的疗效评价标准进行疗效评价及随访疗效评价[3]。目前,双克隆LPL暂无统一的疗效评价标准,主要参考单克隆LPL,结合患者血清蛋白定量及影像学进行评估。随访采用查阅患者住院病历及电话随访的形式,5例患者均完成随访。随访时间截至2022年5月。
1.2.2 生存指标定义
无进展生存期(progression-free survival,PFS)定义为LPL患者治疗至疾病进展、复发、死亡的时间,总生存时间(overall survival,OS)定义为患者确诊为LPL至随访/死亡时间。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS Statistics 26软件进行统计学分析。患者临床特征基线资料采用中位数进行描述。
2. 结果
2.1 临床表现及体征
5例患者中男性4例、女性1例,中位诊断年龄为73(45~80)岁。5例患者中4例可行ISSWM分期为中危组1例、高危组3例,RIPSSWM评分为中危组2例、高危组1例、极高危组1例。5例患者中乏力3例,出血3例,高黏滞血症1例。
2.2 实验室检查
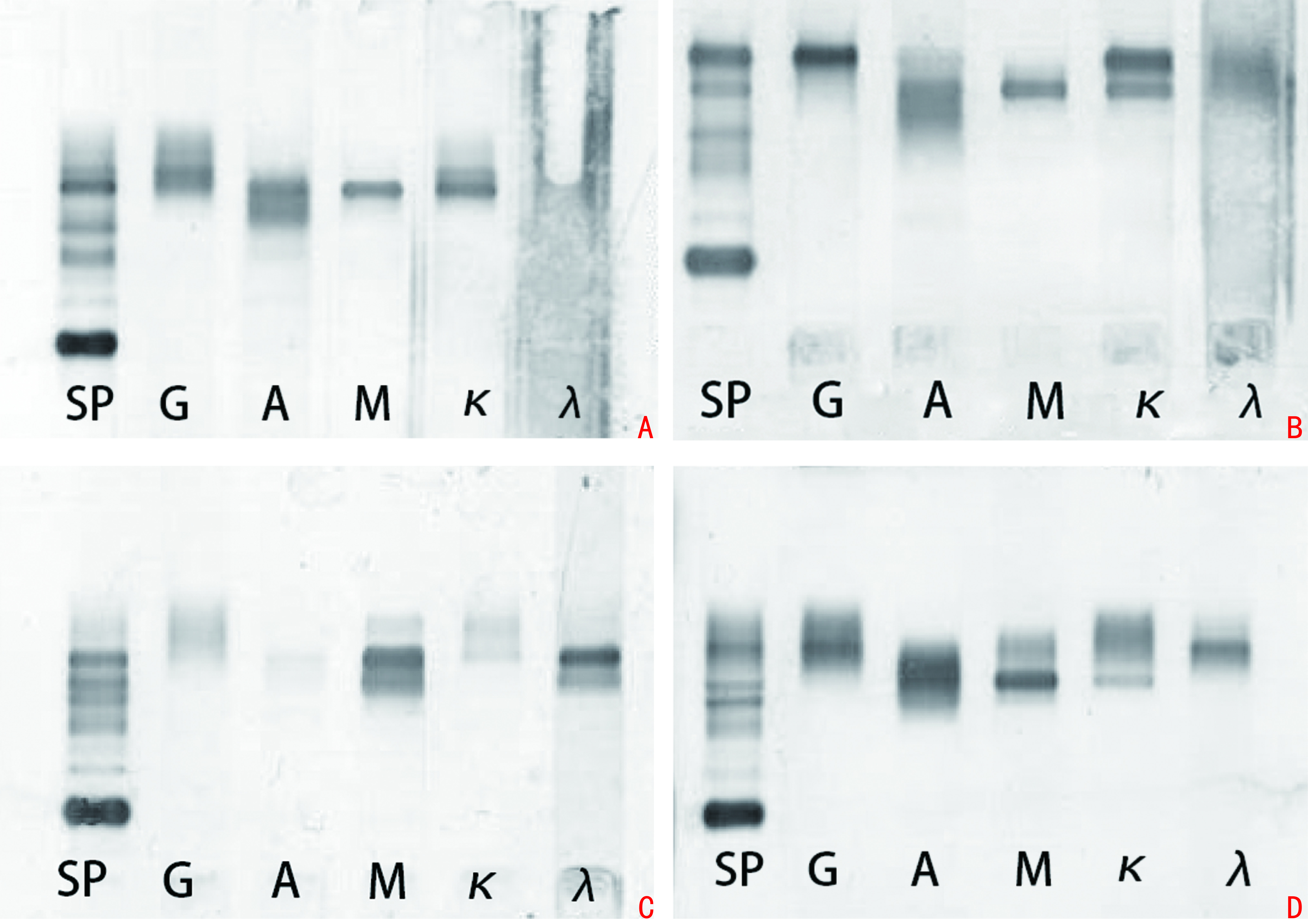
5例患者中位白细胞计数为6.26(1.80~7.21)×109/L,中位血红蛋白为 83(47~216)g/L,中位血小板为62(22~216)×109/L;β2微球蛋白升高4例,中位β2微球蛋白为4.46(3.11~12.60)mg/L;5例患者乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)均无异常,均未见多发性骨质破坏,中位LDH水平为173.3(58.0~239.0)U/L;中位初诊血清IgM为 10.1(4.58~51.50)g/L,IgG为14.20(5.45~41.00)g/L,IgA 为0.62(0.44~1.36)g/L;5例患者中3例MYD88L265P阳性、1例阴性、1例未检测MYD88L265P;5例患者血清免疫固定电泳均为双克隆,4例患者表达IgG和IgM(图1),3例患者表达不同类型轻链。患者临床资料见表1。
表 1 患者M蛋白类型分析患者编号 性别 年龄(岁) 血红蛋白(g/L) 血小板(×109/L) M蛋白类型 初诊IgM(g/L) 初诊IgG(g/L) 1 男 80 117 216 IgGκ和IgMκ 10.10 8.70 2 女 77 98 182 IgGκ和IgMκ 8.12 25.40 3 男 70 47 62 IgGλ和IgMκ 5.89 14.20 4 男 73 83 22 IgMλ和IgMκ 51.50 5.45 5 男 45 61 51 IgGκ和IgMλ 4.58 41.00 6[4] 男 86 36 142 IgAλ和IgMκ 5.71 6.14 7[5] 男 72 75 正常 IgGκ和IgAκ 0.97 51.90 8[6] 男 66 81 84 IgGκ和IgMκ 36.60 14.50 9[7] 女 58 58 148 IgMκ和IgAκ 10.00 13.30 10[8] 男 83 100 正常 IgMλ和IgMκ 34.07 — 2.3 细胞形态学
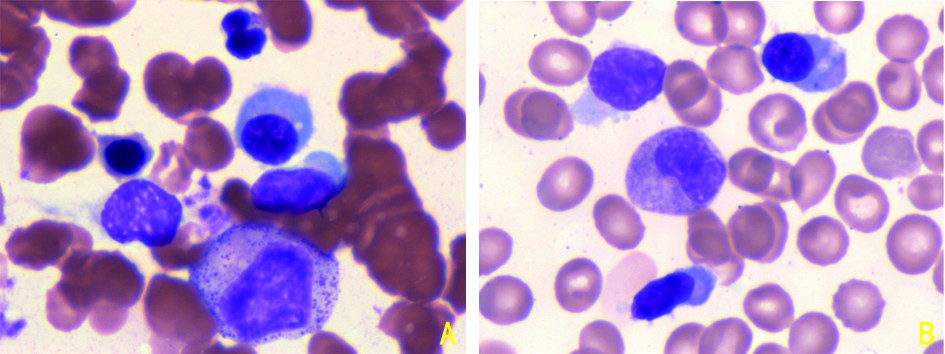
5例患者中2例可见典型淋巴浆细胞浸润(图2),所有患者骨髓均可见异常淋巴细胞及浆细胞浸润,其中位骨髓异常细胞比例:异常淋巴细胞为10.87%(0.48%~79.5%),异常浆细胞为6.81%(0.49%~19.5%),见表2。
表 2 5例患者骨髓异常肿瘤细胞比例及免疫表型患者编号 骨髓流式异常淋巴
细胞比例(%)骨髓流式异常浆
细胞比例(%)免疫表型 1 0.68 0.49 CD20个别+,PAX5少数+,CD3少数+,CD5少数+,CD10-,
CD38浆细胞+,Cyclin D1-2 10.87 6.81 CD20+,PAX5+,CD3-,CD5-,CD10-,CD23-,Cyclin D1-,
CD138+,Kappa+,Lambda-3 12.66 19.29 PAX5+,CD20-,CD3少数+,CD5少数+,CD11c-,CD103-,
CD38少数+,Kappa-,Lambda+,CD23少数+4 0.48 2.94 CD34+,CD19+,HLA-DR+,CD19+,CD20+,CD22+,Kappa+ 5 79.50 19.50 — 2.4 治疗及生存
5例患者中2例CD20阳性者行利妥昔单抗为基础的化疗方案,其中1例行利妥昔单抗+地塞米松(RD)化疗方案7个周期,1例行利妥昔单抗+地塞米松+环磷酰胺(RCD)化疗方案6个周期;其余3例患者中,1例口服伊布替尼治疗,1例使用苯达莫司汀治疗后,血小板波动于(7~36)×109/L,间断性输血治疗,患者疾病无法控制,遂改用沙利度胺+地塞米松+环磷酰胺(TCD)方案治疗,1例使用司莫司汀+环磷酰胺+马法兰+地塞米松+长春新碱(M2)化疗方案3个周期,出现高黏滞血症,予以血浆置换及环磷酰胺(CEP)及马法兰+泼尼松(MP)方案治疗。5例患者中4例达到微小缓解(minimal response,MR)及以上疗效,其中3例患者达到部分缓解(partial response,PR)、1例达到MR。中位随访时间44.1(8.3~91.2)个月,中位无进展生存期(median PFS,mPFS)为52.4(6.37~87.70)个月,中位OS(median OS,mOS)为52.4(8.3~91.2)个月。截至2022年5月随访结束,2例患者疾病平稳,仍维持PR疗效;2例患者死亡,其中1例肌酐为602.7 μmoL/L行肾透析治疗时出现心律失常死亡、1例IgM>144 g/L,出现高黏滞血症后因急性心力衰竭死亡;1例患者失访。
3. 讨论
LPL细胞起源于生发中心后向浆细胞分化,在这个阶段免疫球蛋白重链可变区(immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region,IgHV)出现高频突变后,发生免疫球蛋白基因的类别转化,即从初始分泌IgM抗体向IgA/IgG等进行转化[9]。目前,对于双克隆免疫球蛋白的产生机制仍未明确,主要认为表达不同免疫球蛋白是由具有共同克隆起源的两个细胞群产生。Tschumper等[9]分析14例双克隆多发性骨髓瘤(multiple myeloma,MM)及WM患者的信息,发现双克隆存在3种类型,分别是同种重链不同轻链、同种轻链不同重链,及不同重链不同轻链,对患者骨髓通过聚合酶链反应(PCR)检查分析IgHV、恒定区 (immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region,IGHC) 、连接区域(immunoglobulin heavy chain junction region,IGHJ)和互补决定区域(heavy chain complementarity-determining region 3,HCDR3)以及轻链(light chain,LC)的核苷酸序列发现,63%患者的整个IgHV区域和HCDR3区域具有完全相同的核苷酸序列,翻译的氨基酸序列也完全一致,证实双克隆免疫球蛋白具有相关性,表达的两群细胞很可能具有共同的克隆起源。该结论在另一项研究中也获得证实,通过对IgA及IgE的MM患者的免疫球蛋白重链可变区的免疫表型及核酸序列分析表达发现,两者的重链可变区,包括体细胞突变完全相同,证实分泌IgA及IgE的两个细胞群之间具有共同的克隆起源[10]。
LPL临床表现多样,主要是因单克隆免疫球蛋白异常增高、沉积及其诱发的自身免疫反应以及肿瘤细胞浸润各部位所致。研究表明,IgM型和非IgM型LPL的细胞生物学特征及临床特征基本相似[11]。但对于双克隆LPL有学者认为双克隆的临床特征主要取决于含量较高的免疫球蛋白类型,如IgM型的主要症状为出血症状或高黏滞血症等,而非IgM型多以贫血、乏力起病为主[11]。本研究1例IgM升高为主的患者,以血小板降低为主要表现,而3例以IgG升高为主的患者主要起病原因为血红蛋白减少导致的贫血,与上述观点较为一致,但1例患者的IgM含量稍高,以血红蛋白稍低为主要表现。2例患者虽然是以非IgM升高为主,但起病是以血红蛋白减少为主要症状[4,7]。因此,免疫球蛋白的含量与临床症状的相关性尚未明确。
诊断主要与双克隆型意义未明的单克隆免疫球蛋白血症(monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance,MGUS)及MM相鉴别:双克隆MGUS和WM虽然同双克隆LPL一样有血清双克隆蛋白,但MGUS骨髓中无淋巴浆细胞/浆细胞浸润,无淋巴瘤浸润所致的贫血、肝脾淋巴结肿大以及浆细胞所致的溶骨性损害、肾功能损害等症状;而双克隆MM骨髓中通常仅为浆细胞浸润,免疫表型为高表达浆细胞表型,不仅合并溶骨性损害,此外MM常伴有14q32易位,而LPL通常伴有MYD88L265P突变。以上均可作为三者的鉴别诊断[1]。本研究5例患者均可见免疫固定电泳双克隆,骨髓中为两群异常细胞浸润,免疫表型为淋巴细胞及浆细胞异常表型,均未出现骨质破坏,且3例伴有MYD88L265P突变,5例均无14q32易位,本研究5例患者诊断符合双克隆LPL。双克隆LPL的治疗及预后:该病可能无症状,或出现免疫球蛋白骨髓,或出现其他组织浸润时相应症状或并发症。根据IWWM指南,对于无症状的患者观察和定期复查是最主要的治疗策略,LPL治疗指征是指出现IgM相关并发症和(或)肿瘤侵犯骨髓相关症状,如全血细胞减少/躯体症状,以及髓外大包块[12]。由于双克隆的LPL发病率较低,目前仍无特异的治疗策略,治疗选择上与单克隆LPL一致。利妥昔单抗联合化疗药物是初诊LPL患者首选的治疗方案。本研究5例患者中,2例采用R为基础的联合化疗方案,分别为RD与RCD,2例的疗效均达到PR,OS分别为8.3个月和54.3个月。国外一项多中心研究纳入72例有治疗指征的WM患者,行RCD方案治疗6个疗程,治疗结束后总体有效率为83%,其中74%患者达到PR以上疗效,中位随访23.4个月,2年PFS率及OS率分别为67%与81%[13]。对于有高黏滞血症的患者,利妥昔单抗单药治疗可能会导致一过性IgM水平升高,因此对于有这类症状的患者应避免直接使用此方案,对于出现高黏滞血症等并发症的患者首选血浆置换[14]。
双克隆LPL的病例较为罕见,对于双克隆的LPL是否与LPL有相同的临床特征及特异的治疗方案,目前尚未明确,仍需不断积累病例总结学习。
-
表 1 患者M蛋白类型分析
患者编号 性别 年龄(岁) 血红蛋白(g/L) 血小板(×109/L) M蛋白类型 初诊IgM(g/L) 初诊IgG(g/L) 1 男 80 117 216 IgGκ和IgMκ 10.10 8.70 2 女 77 98 182 IgGκ和IgMκ 8.12 25.40 3 男 70 47 62 IgGλ和IgMκ 5.89 14.20 4 男 73 83 22 IgMλ和IgMκ 51.50 5.45 5 男 45 61 51 IgGκ和IgMλ 4.58 41.00 6[4] 男 86 36 142 IgAλ和IgMκ 5.71 6.14 7[5] 男 72 75 正常 IgGκ和IgAκ 0.97 51.90 8[6] 男 66 81 84 IgGκ和IgMκ 36.60 14.50 9[7] 女 58 58 148 IgMκ和IgAκ 10.00 13.30 10[8] 男 83 100 正常 IgMλ和IgMκ 34.07 — 表 2 5例患者骨髓异常肿瘤细胞比例及免疫表型
患者编号 骨髓流式异常淋巴
细胞比例(%)骨髓流式异常浆
细胞比例(%)免疫表型 1 0.68 0.49 CD20个别+,PAX5少数+,CD3少数+,CD5少数+,CD10-,
CD38浆细胞+,Cyclin D1-2 10.87 6.81 CD20+,PAX5+,CD3-,CD5-,CD10-,CD23-,Cyclin D1-,
CD138+,Kappa+,Lambda-3 12.66 19.29 PAX5+,CD20-,CD3少数+,CD5少数+,CD11c-,CD103-,
CD38少数+,Kappa-,Lambda+,CD23少数+4 0.48 2.94 CD34+,CD19+,HLA-DR+,CD19+,CD20+,CD22+,Kappa+ 5 79.50 19.50 — -
[1] 中国抗癌协会血液肿瘤专业委员会,中华医学会血液学分会,中国华氏巨球蛋白血症工作组.淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤/华氏巨球蛋白血症诊断与治疗中国指南(2022年版)[J].中华血液学杂志,2022(8):624-630. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2022.08.002 [2] Owen RG, Treon SP, Al-katib A, et al. Clinicopathological definition of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: consensus panel recommendations from the second international workshop on Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia[J]. Semin Oncol, 2003, 30(2):110-115. DOI: 10.1053/sonc.2003.50082
[3] Treon SP, Gertz MA, Dimopoulos M, et al. Update on treatment recommendations from the Third International Workshop on Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia[J]. Blood, 2006, 107(9): 3442-3446.
[4] 郑力,郭振兴.IgA和IgM双克隆型淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤1例报道[J].国际检验医学杂志,2019,40(24):3070-3072. [5] 支勇金,曾文前,李勤.IgG和IgA双克隆型淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤一例[J].中华血液学杂志,2020,41(10):871-871. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2020.10.017 [6] 何靖,胡莉文,古学奎,等.单克隆IgM及IgG共存的淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤1例并文献复习[J].临床血液学杂志,2019,32(3):219-221. DOI: 10.13201/j.issn.1004-2806.2019.03.015 [7] 蒋菁菁,祁光玉,周美玲,等.伴双克隆M蛋白的淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤一例并文献复习[J].白血病·淋巴瘤,2020(5):291-294. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115356-20190908-00177 [8] Schulz R, David D, Farkas D, et al. Molecular analysis in a patient with Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia reveals a rare case of biclonality[J]. Mol Diagn, 1996, 1(3):159-166. DOI: 10.1016/S1084-8592(96)70001-2
[9] Tschumper RC, Dispenzieri A, Abraham RS, et al. Molecular analysis of immunoglobulin genes reveals frequent clonal relatedness in double monoclonal gammopathies[J]. Blood Cancer J, 2013, 3(4):e112.
[10] Bakkus MHC, Schots R, Gomez La, et al. Clonally related IgA-and IgE-secreting plasma cells in a myeloma patient[J]. Eur J Haematol, 2000, 65(5):348-355.
[11] 于颖,熊文婕,陈佳雯,等.非IgM型淋巴浆细胞淋巴瘤临床及生物学特征[J].中华血液学杂志,2022,43(7):568-574. [12] Dimopoulos MA, Kastritis E. How I treat waldenström macroglobulinemia[J]. Blood, 2019, 134(23):2022-2035. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019000725
[13] Kastritis E, Gavriatopoulou M, KyrtsonisMC, et al. Dexamethasone, rituximab, and cyclophosphamide as primary treatment of Waldenström macroglobulinemia: final analysis of a phase 2 study[J]. Blood, 2015, 126(11):1392-1394.
[14] Gertx MA. Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: tailoring therapy for the individual[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(23):2600-2608. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.00495



 下载:
下载: