In vitro Study on the Mechanism of MLN4924-induced Apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer Cell Line A549
-
摘要:目的 观察MLN4924对人肺腺癌A549细胞增殖、凋亡的影响,探讨MLN4924促进凋亡的作用机制。方法 不同浓度的MLN4924作用细胞不同时间后,采用CCK-8检测细胞增殖抑制率;Hoechst33342荧光染色、流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率及细胞周期;Western blot检测凋亡相关蛋白Caspase-3、NF-κB p65及CDT1相对表达量。结果 MLN4924能够明显抑制A549细胞的增殖,并且具有浓度和时间依赖性。流式细胞仪检测结果显示药物作用后,细胞被阻滞在S期。Western blot结果显示药物作用后细胞内Caspase-3、CDT1蛋白的表达量增加,而NF-κB p65的表达量减少。结论 MLN4924能够明显抑制A549细胞增殖、促进细胞凋亡,其相关机制为MLN4924可阻滞细胞于S期,增加Caspase-3蛋白表达,抑制NF-κB通路的激活。Abstract:Objective To study the effect of MLN4924 on the proliferation and apoptosis of lung epithelial carcinoma A549 cells.Methods A549 cells were treated with MLN4924 at different concentrations and incubation times. The inhibition rate of cell growth was detected using the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Apoptosis was observed using Hoechst 33342 and flow cytometry. The protein expression of the associated proteins in cell apoptosis, including caspase-3, NF-κB p65, and CDT1, was determined through Western blot analysis.Results The proliferation of A549 cells decreased when the concentration of MLN4924 increased or the incubation time was prolonged. MLN4924 induced S phase cell cycle arrest. The protein expression of the associated proteins caspase-3 and CDT1 was higher than that of the control group. NF-κB p65 was lower than that in the control group.Conclusion MLN4924 effectively inhibited the proliferation and induced cell apoptosis in A549 cells. MLN4924 treatment induced the S phase cell cycle arrest, increased the caspase-3 protein expression, and inhibited the NF-κB pathway activation.
-
Keywords:
- MLN4924 /
- Lung cancer /
- Proliferation /
- Apoptosis /
- DNA replication
-
MLN4924是最近报道的一种选择性的NEDD8(neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated)活化酶的小分子抑制剂[1], 能够与NEDD8活化酶结合形成NEDD8活化酶-MLN4924化合物, 从而抑制NEDD8活化酶, 控制部分依赖于CRL (cullin-RING ligase)酶的泛素化途径, 最终影响相关蛋白质的降解[2]。目前有研究显示NEDD8活化酶有望成为抗肿瘤药物的新靶点[3], 而MLN4924作为NEDD8活化酶的抑制剂可能成为新型抗肿瘤药物[4]。目前报道MLN4924抗肿瘤作用与促进细胞凋亡、衰老、自噬有关, 但是具体机制尚不清楚[5-8]。本研究以不同浓度MLN4924作用于人肺腺癌A549细胞, 观察其对于A549细胞形态、增殖、凋亡、细胞周期的影响, 探讨其促进肿瘤细胞凋亡的相关机制, 为其临床应用提供一定的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
A549细胞株为重庆医科大学第一附属医院肺科实验室冻存, 改良型RPM1-1640培养基、胎牛血清、胰酶溶液购自Hyelone公司; DMSO购自Sigma公司; CDT1购自Abgent公司; CCK-8、Hoechst33342染色液、Caspase-3抗体、NF-κB p65抗体、SDS-PAGE凝胶配制试剂盒等均购自碧云天生物技术有限公司。MLN4924购自TCR公司, 用DMSO溶解, -20℃保存, 临用前解冻, 用RPM1-1640培养基稀释到所需浓度, 使DMSO的终浓度 < 0.1%。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养
人肺腺癌A549细胞接种于100 mL培养瓶中, 培养基为含10%的胎牛血清、10 000 U/L的青霉素和0.1 g/L的链霉素的RPM1-1640, 置入37℃、5%CO2培养箱孵育, 待细胞融合度70%~80%, 用胰酶进行消化, 计数、传代。
1.2.2 CCK-8检测细胞增殖抑制率
调整细胞浓度为1500个/100μL, 各取100μL细胞悬液接种于96孔培养板。将培养板移入培养箱, 在37℃、5%CO2及饱和湿度条件下培养24 h, 分别加入含有不同浓度MLN4924的RPM1-1640培养液200μL。设立对照组, 对照组加入200μL的空白培养基。MLN4924组加入不同剂量的MLN4924溶液, 使其终浓度为0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10μmol/L。加药组和对照组均设立3个复孔, 继续将培养板移入培养箱中培养48、72 h后, 每孔加入20μL CCK-8溶液, 在培养箱内继续孵育1.5 h后用酶标仪检测吸光值, 检测波长为450 nm, 测量每孔吸光值(A)。细胞生长抑制率(%)=(1-加药组A值/对照组A值)×100%。
1.2.3 Hoechst33342染色检测细胞凋亡
取对数期细胞制备成细胞悬液, 并按2×104个/孔接种于24孔板中, 待贴壁后加入含不同药物浓度的培养液, 并设置对照组, 置入培养箱中继续培养48h后洗尽培养液, PBS冲洗2次, 每孔加入1 mL Hoechst33342染色液, 培养箱内继续培养30 min, 用PBS洗2次, 置于荧光显微镜下观察。实验重复3次。
1.2.4 流式细胞仪检测细胞周期
取对数期生长的A549细胞, 以浓度1×106个/mL接种于6孔板, 每孔1 mL, 置于培养箱中过夜。按浓度0.25、0.5、1μM加入药物, 同时设立对照组。置于培养箱继续孵育48 h, 胰酶消化, PBS洗涤2次, 1 000 r/min离心5min收集细胞, 70%乙醇4℃固定过夜, 加入RNAase A 3μL至终浓度50μg/mL, 37℃恒温水浴1 h, 碘化丙啶(PI)避光染色, 流式细胞仪测定细胞周期。实验重复3次。
1.2.5 流式细胞仪测定细胞凋亡
细胞处理及分组同细胞周期检测实验。细胞培养48 h后收集细胞, 将细胞悬于500mL的Binding Buffer中, 加入FITC标记的Annexin2V(20μg/mL)5μL以及PI染液(50μg/mL)10μL, 轻轻混匀; 室温、避光、孵育1Omin。在1h进行流式细胞仪检测。实验重复3次。
1.2.6 Western blot检测
取药物处理48 h后的A549细胞, 并设置相应对照组, 用1×SDS裂解, 提取总蛋白, BCA法进行蛋白定量, 取等量蛋白(20μg), 经SDS-PAGE电泳分离, 将蛋白转移到PVDF膜上。5%脱脂奶粉(TBS、0.1%Tween-20)封闭1 h, 分别加入Caspase-3抗体(1:1 000)、CDT1(1:400)、NF-κB p65抗体(1:800)。4℃过夜, 1×TBST (1%Tween-20, TBS)漂洗3次, 10 min/次; 二抗体(1:800), 室温孵育2h。Actin作为内参照。ECL化学发光剂孵育, Bio-Rad凝胶成像系统采集图片, 结果采用Quantity One软件分析。实验重复3次。
1.3 统计学处理
不同药物浓度、处理不同时间的细胞增殖抑制率实验结果, 使用SPSS 19.0进行方差分析, 事后检验采用SNK方法, 检验水平为α=0.01。流式细胞仪检测凋亡率和细胞周期结果以表示, 采用SPSS 19.0统计软件单因素方差分析SNK方法, 检验水平为α=0.01。以P < 0.01为有统计学意义。
2. 结果
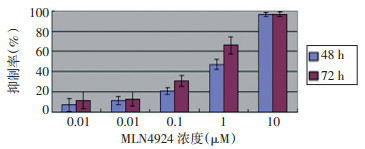
2.1 MLN4924对A549细胞增殖的抑制作用
MLN4924作用48 h时IC50(半数抑制浓度)为0.5μM、72 h IC50约为0.2μM。并且随着剂量增加和时间延长, 抑制效果有增强趋势(图 1)。同一浓度不同时间之间除高浓度10μM组48 h与72 h之间无统计学意义(P > 0.01)外, 其他时间两两比较有显著性统计学差异(P < 0.001);同一时浓度之间比较, 除0.001、0.01μM浓度之间差异无统计学意义外(P > 0.01), 其他浓度两两比较均有显著性差异。
2.2 Hoechst 33342染色检测结果
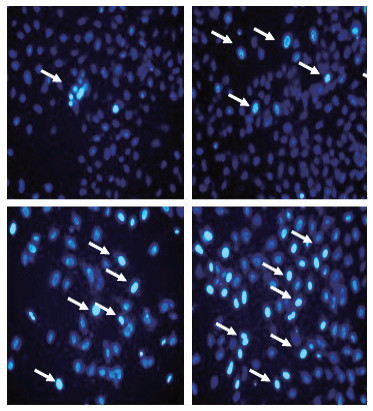
用不同浓度MLN4924处理细胞48 h后, 通过Hoechst 33342染色, 荧光显微镜下观察细胞凋亡效应(图 2)。对照组染色质均匀, 无浓缩现象, 细胞核染色均一, 无明显亮蓝色, 而MLN4924处理组细胞体积变大, 细胞核染色质致密固缩, 聚集于细胞核边缘, 可见境界分明的块状小体, 并有核碎裂出现凋亡小体, 随着浓度增加亮蓝色细胞明显增多(箭头标注)。
2.3 Western blot检测Caspase-3、CDT1及NF-κB p65蛋白相对表达
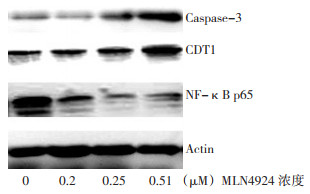
采用Western blot检测Caspase-3、CDT1及NF-κB p65蛋白相对表达。用浓度分别为0、0.25(0.5×IC50)、0.5(IC50)、1μM(2×IC50)的MLN4924处理细胞48 h后, NF-κB p65蛋白表达依次降低, Caspase-3、CDT1蛋白含量逐渐增加(图 3)。
2.4 流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率及周期
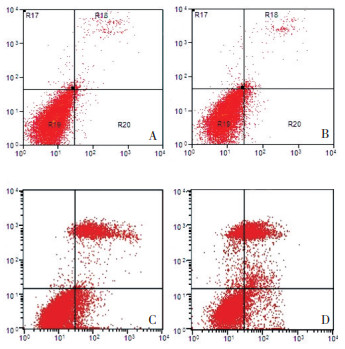
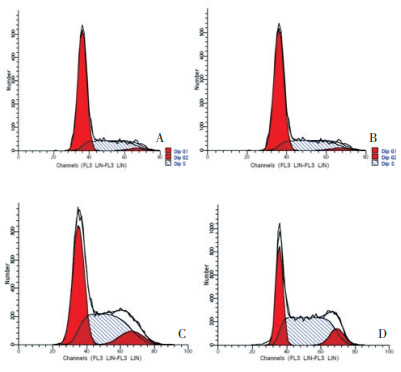
用浓度为分别为0、0.25(0.5×IC50)、0.5(IC50)、1μM(2×IC50)的MLN4924处理细胞48 h后流式细胞仪检测细胞周期及细胞凋亡率。随着MLN4924浓度的增加细胞凋亡率增加, S期细胞所占比例也明显增加, 并且具有统计学意义(表 1, 图 4、5)。
表 1 流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率及细胞周期Table 1. Flow cytometry of the cell cycle and rate of apoptosis after 48 h at different concentrations of MLN4924.*Compared with the control group (P < 0.01)
3. 讨论
MLN4924是AMP (腺嘌呤核苷酸)类似物, AMP与NEDD8活化酶之间存在很高的亲和力, 由于MLN4924与AMP结构非常类似, 能够与NEDD8活化酶结合形成NEDD8活化酶-MLN4924化合物, 从而抑制NEDD8活化酶, 控制部分依赖于CRL酶的泛素化途径, 最终影响相关蛋白质的降解, 从而抑制肿瘤生长[9-10]。临床上用于多发性骨髓瘤患者治疗的硼替佐米可作用于蛋白酶体从而达到抑制肿瘤生长的作用, 而研究发现通过MLN4924特异性干扰NEDD8活化酶通路相比阻断蛋白酶体通路而言, 能更特异性地干扰肿瘤细胞的内环境稳态[4, 11]。
本研究用CCK-8检测不同浓度和不同作用时间MLN4924对肺腺癌A549细胞增殖的影响, 结果显示, MLN4924在体外对A549细胞增殖具有明显的抑制作用, 并且在一定范围内具有时间和浓度依赖性。但是在低浓度范围时(0.001μM、0.01μM)增加药物浓度不能增加其对细胞增殖的抑制作用, 原因可能与浓度太低, 未达到药物作用的有效剂量有关。而在高浓度(10μM)时, 增加药物作用时间, 也不能增加抑制率, 推测可能与以下两个方面有关: 其一观察的时间点设定不够, 继续延长作用时间可能会增加抑制率; 其二可能与MLN4924引起S期细胞DNA再复制, 最终导致DNA损伤, 诱导细胞凋亡这一机制有关, 细胞群中处于或者进入S期的细胞才能触发上述机制, 当MLN4924达到一定浓度后, 抑制DN A复制期细胞增长达到饱和, 故增加作用时间不能增强其抑制作用。为了进一步研究其抑制A549细胞生长的作用机制, 用不同浓度MLN4924处理细胞48h后, 通过Hoechst33342染色, 荧光显微镜下观察细胞, 结果显示随着MLN4924浓度增加, 观察到的凋亡细胞越多。结果说明促进肿瘤细胞凋亡是MLN4924抑制A549细胞增殖的重要机制之一。为研究MLN4924促进A549细胞凋亡的机制, 用Western blot检测了凋亡相关蛋白的表达。因为Caspase-3是Caspase相关凋亡途径中凋亡执行蛋白, 而细胞核内P65是NF-kb信号传导途径激活的直接标志。结果显示随着浓度增加, Caspase-3表达量增加, 而NF-κB p65表达减少。因此推测MLN4924可以通过激活Caspase相关凋亡途径和抑制NF-κB信号传导途径而促进A549细胞凋亡。
同时还检测到细胞周期相关因子CDT1的表达量随MLN4924浓度增加而表达增加。CDT1是一65 kDa蛋白质, 是细胞分裂、增殖的细胞周期的S期DNA复制的控制准许因子之一。所以推测MLN4924可能会对细胞周期产生影响, 因此用流式细胞仪检测不同浓度MLN4924作用下A549细胞的周期和凋亡率。结果显示随着浓度增加细胞凋亡率增加, 与Hoechst 33342染色结果相吻合。不同浓度MLN4924作用A549细胞后, S期细胞比例明显增加, 根据Western blot检测的CDT1蛋白表达增加的结果分析, MLN4924通过抑制NEDD8活化酶活性, 从而控制部分依赖于CRL酶的泛素化途径, 最终影响细胞周期相关因子CDT1蛋白质的降解, 使得CDT1在细胞内蓄积, 进而阻滞细胞于S期, 最终导致肿瘤细胞增殖受到抑制。
本实验结果为以后MLN4924用于肺癌治疗提供一定的理论依据, 下一步将进行动物实验, 进一步评价MLN4924对于肺癌增殖的抑制作用及其安全性。
-
表 1 流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率及细胞周期
Table 1 Flow cytometry of the cell cycle and rate of apoptosis after 48 h at different concentrations of MLN4924.*Compared with the control group (P < 0.01)

-
[1] Leung CH, Chan DS, Yang H, et al. A natural product-like inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme[J]. Chem Commun(Camb), 2011, 47(9): 2511-2513. DOI: 10.1039/c0cc04927a
[2] Petroski MD. Mechanism-based neddylation inhibitor[J]. Chem Biol, 2010, 17(1): 6-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.01.002
[3] Swords RT, Kelly KR, Smith PG. Inhibition of NEDD8-activating enzyme: a novel approach for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Blood, 2010, 115(18): 3796-3800. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-254862
[4] Soucy TA, Smith PG, Milhollen MA, et al. An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer[J]. Nature, 2009, 458(7237). 732-736.
[5] Zhao L, Yue P, Lonial S, et al. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, MLN4924, cooperates with TRAIL to augment apoptosis through facilitating c-FLIP degradation in head and neck cancer cells[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2011, 10(12): 2415-2425. DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0401
[6] Luo Z, Yu G, Lee HW, et al. The Nedd8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor MLN4924 Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis to Suppress Liver Cancer Cell Growth[J]. Cancer Res, 2012, 72(13): 3360-3371. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0388
[7] Yang D, Tan M, Wang G, et al. The p21-dependent radiosensitization of human breast cancer cells by MLN4924, an investigational inhibitor of NEDD8 activating enzyme[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(3): e34079. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034079
[8] Zhao Y, Sun Y. Targeting the mTOR-DEPTOR Pathway by CRL E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: Therapeutic Application. Neoplasia, 2012, 14(5): 360-367. DOI: 10.1593/neo.12532
[9] BrownellJE, Sintchak MD, Gavin JM, et al. Substrate-assisted inhibition of ubiquitin-like protein-activating enzymes: the NEDD8 E1 inhibitor MLN4924 forms a NEDD8-AMP mimetic in situ[J]. Mol Cell, 2010, 37(1): 102-111. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.024
[10] Wei D, Li H, Yu J, et al. Radiosensitization of human pancreatic cancer cells by MLN4924, an investigational NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor[J]. Cancer Res, 2012, 72(1): 282-293. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2866
[11] Chen JJ, Tsu CA, Gavin JM, et al. Mechanistic studies of sub strate -assisted inhibition of ubiquitin activating enzyme by adenosine sulfamate analogues[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(47): 40867-40877. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.279984



 下载:
下载: