Role of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 in tumor malignant biological behavior and its clinical application
-
摘要: 胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白(insulin-like growth factor binding protein,IGFBPs)在机体的生长发育和增殖凋亡中发挥重要作用。该家族中,IGFBP2具有调控胰岛素样生长因子(insulin-like growth factor,IGF)的功能。IGFBP2通过自身独特的结构,不仅能与IGF结合,还与细胞外基质相互作用,进而激活下游相关信号通路,在肿瘤的生物学行为中发挥重要的作用。IGFBP2在多种恶性肿瘤中特异性高表达且与患者治疗和预后相关,具备作为诊断标记物和治疗靶点的潜力。本文结合国内外文献,就IGFBP2在肿瘤恶性生物学行为和临床应用中的研究进展进行综述。
-
关键词:
- 胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白 /
- 肿瘤 /
- 恶性进展 /
- 转移
Abstract: Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) are crucial to cell growth, development, proliferation, and apoptosis in humans. Among IGFBPs, IGFBP2 is recognized as a regulator of insulin-like growth factor (IGF). Besides binding with IGF, IGFBP2 also interacts with extracellular matrix through its specific structure. IGFBP2 promotes the malignant phenotype of tumor by activating several important intracellular signal pathways. IGFBP2 is specifically overexpressed in several malignant tumors, and this overexpression is correlated with patient prognosis. IGFBP2 is regarded as a potential biomarker and a therapeutic target. This review briefly summarizes the latest progress of research on the role of IGFBP2 in tumor malignant biological behavior and its clinical application. -
胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2(insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2,IGFBP2)属于胰岛素生长因子(insulin-like growth factor,IGF)蛋白家族成员,在细胞的增殖、分化和凋亡中发挥重要作用。该轴共包括3个部分,2个低分子多肽配体IGF-Ⅰ和IGF-Ⅱ,其特异性受体有IGF-ⅠR和IGF-ⅡR以及6个对IGF具有高亲和性的胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白(IGFBPs)。有研究表明,IGFBP2异常表达与人类肿瘤的各种生物学行为关系密切,是肿瘤生物学领域的一个热点基因。
1. IGFBP2概述
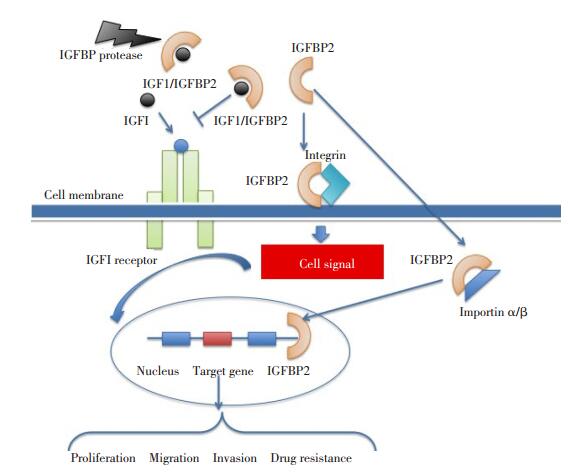
胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2和两种IGF可以在循环中形成二叠体复合物,穿过内皮阻隔并达到局部组织,IGFBP2/IGF复合物能够与整合素或其他细胞外基质组成元件结合[1]。通过与IGFBP2的结合,IGF以复合物的形式保存在局部组织中,因此具备“IGF容器”功能的IGFBP2对调节细胞周围IGF功能具有重要的作用[2]。此外,IGFBP2/IGF复合体和IGFBP2的蛋白水解碎片,在IGF促进的细胞迁移中也发挥重要作用[3]。
2. IGFBP2的结构
成熟的IGFBP2蛋白包括3段结构,富含半胱氨酸的N端和C端,两端中间称为连接区的中间区域。实验证实,IGFBP2的N端和C端都可以与IGF-Ⅰ和IGF-Ⅱ结合,但两端对IGF结合的亲和力不同[4]。
2.1 IGFBP2的整合素结合域
IGFBP2蛋白具有RGD序列(精氨酸-甘氨酸-门冬氨酸),该序列位于人类IGFBP2氨基酸序列中的第265~267位[5]。RGD序列可介导IGFBP2与细胞膜上的整合素结合,目前已知可与IGFBP2结合的整合素包括α5β3和α5β1 [6-7]。
2.2 IGFBP2的肝素结合域
IGFBP2的中间区域包含组成形式为-XBBXBX-(B为基本基团,X为亲水基团)的肝素结合区域(HBD)。这段可以被氨基糖苷识别的保守序列位于人类IGFBP2氨基酸序列中的179~184位[8]。近来发现HBD区是IGFBP2与细胞外基质结合的关键区域,该区域也参与IGFBP2介导的细胞增殖和迁移[9]。
2.3 IGFBP2的核定位序列
IGFBP2可以由核定位序列(nuclear localization sequence,NLS)介导进入细胞核[10]。该NLS位于IGFBP2蛋白的中间连接区,通过与核转入蛋白α/β连接后形成转运复合体被转运入核。
IGFBP2的NLS序列与HBD区域在氨基酸序列的179~184位存在交叉,类似的交叉在IGFBP-3和IGFBP-5中也有报道[11]。这些交叉区域参与了IGFBP2与细胞外基质和其他蛋白如转铁蛋白和纤溶酶原激活物抑制剂等的结合,该结构特点反映出这些区域在不同IGFBP中的多功能性[10]。
3. IGFBP2在肿瘤进展中的作用
血浆中IGFBP2含量在所有IGFBP中排第二,并被证实在多种恶性肿瘤中表达增加,如胶质瘤[12]、前列腺癌[13]、乳腺癌[14]、卵巢癌[15]、肺癌[16]、白血病[17]、直肠癌[18]等。近来研究不断发现IGFBP2表达与肿瘤恶性进展及预后明显相关。体外研究证实IGFBP2参与调节肿瘤细胞的增殖、侵袭和转移。本课题组最近通过体内、外模型和临床数据分析发现,IGFBP2在胰腺癌组织中呈特异性高表达,且与患者淋巴结转移相关,明显影响患者总生存期[19]。
转移是恶性肿瘤最重要的生物学行为之一,研究已证实IGFBP2通过其特殊的结构和生物学特性参与了转移中的多个步骤(图 1)。IGFBP2在不同肿瘤中调控转移的机制略有不同:在直肠癌中,IGFBP2通过激活神经元细胞黏连受体L1促进肿瘤运动并导致肝转移[20];乳腺癌中,IGFBP2通过协同β-catenin促进淋巴结转移[6];胶质瘤细胞中,IGFBP2促进肿瘤细胞表面的板状伪足形成并减少黏着斑形成,增强肿瘤细胞的运动能力并导致转移[21]。
细胞外基质的降解已被证实是肿瘤发生侵袭转移的重要原因之一。IGFBP2可通过激活基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases,MMPs)进而降解细胞外基质成分如胶原蛋白、蛋白多糖、层黏连蛋白和纤连蛋白等[22]。在胶质母细胞瘤中,IGFBP2通过增强MMP2基因的表达导致肿瘤细胞侵袭能力增强。然而,肿瘤细胞核中并未发现IGFBP2,提示MMP的表达可能并非由IGFBP2直接进行转录调控。膀胱癌中也有类似发现[23]。但神经母细胞瘤中IGFBP2过表达可导致MMP2和MMP11的表达显著增高,而且IGFBP2的核定位序列直接参与该转录调控过程。因此,IGFBP2可以通过核内调控和核外促进两种方式调节MMP蛋白的表达[24]。
血管生成是肿瘤转移中的另一重要步骤。研究显示具备较强血管生成能力的肿瘤转移发生率明显提高。胶质母细胞瘤的基因表达谱显示IGFBP2和VEGF与肿瘤的血管生成明显相关,而且原位杂交实验显示IGFBP2与VEGF具备共定位表达,进一步证实IGFBP2与血管新生有关[25]。神经母细胞瘤的基因表达谱提示IGFBP2过表达激活包括VEGF在内的一系列肿瘤血管新生相关基因的表达。IGFBP2可进入细胞核,结合在VEGF的启动子区,增加VEGF mRNA的表达,提示IGFBP2有活化VEGF转录的效应[26]。黑色素瘤细胞与人脐血内皮细胞共培养后,肿瘤分泌的IGFBP2通过与αVβ3整合素结合,激活PI3K/ Akt通路导致促血管新生因子VEGF-A表达上调,最终导致肿瘤血管形成[27]。
4. IGFBP2介导的肿瘤进展相关信号通路
4.1 依赖于IGF/IGFR的肿瘤进展相关信号通路
IGFBP2行使转运IGF-Ⅰ/Ⅱ蛋白的功能,并调控IGF/IGFR信号通路,普遍观点认为IGFBP2可增强IGFR的活性并促进肿瘤进展,但在横纹肌肉瘤细胞中却发现IGFBP2抑制IGF1R的激活。Huang等[28]曾对IGF/IGFR/IGFBP轴的基因多态性与亚洲人群中食管癌和肺癌发病风险的关系进行了Meta分析,并发现二者呈正相关。乳腺癌细胞中,IGFBP2能够通过激活IGF-Ⅰ/IGF-1R信号通路募集内皮细胞至肿瘤周围,而内皮细胞的募集是乳腺癌转移的重要步骤[14]。IGF/IGFR信号通路在肿瘤中经常与其他生长因子通路协同作用,例如IGF/IGFR可通过RASRAF-MAPK通路诱导肿瘤细胞发生上皮间质转化,也可与PI3K/Akt/mTOR协同促进肿瘤转移。
4.2 不依赖于IGF/IGFR的肿瘤进展相关信号通路
前列腺癌[13]中,微阵列表达谱提示IGFBP2表达可导致PTEN表达缺失以及PI3K/Akt的激活。本课题组在胰腺癌中也发现了类似的现象:IGFBP2的表达与PTEN在肿瘤组织及癌旁正常组织中的表达呈明显负相关,而且上调肿瘤细胞中的IGFBP2后,PTEN的表达明显下降,下游PI3K通路显著激活[19];另一方面,在PTEN表达缺失的肿瘤中,IGFBP2表达明显增高,使用PI3K的抑制剂LY294002治疗这些肿瘤细胞时,IGFBP2表达降低至基线水平,该结果提示PI3K/Akt通路参与PTEN缺失肿瘤中的IGFBP2表达调控。在乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7中也发现了类似的结果,PI3K抑制剂处理细胞后,调控IGFBP2表达的转录因子SP-1表达减少,进而导致IGFBP2表达下降[14]。在粒细胞白血病和急性淋巴细胞白血病中,IGFBP2已被证实通过影响PTEN/PI3K/Akt通路导致肿瘤运动能力显著增强[29];一些实体肿瘤如肺腺癌,三阴乳腺癌中,IGFBP2也被发现可激活PI3K/Akt通路,且与肿瘤转移明显相关[14]。
整合素是具备跨细胞膜的异质二聚体结构的蛋白家族。整合素α5和β1亚基可与IGFBP2的RGD序列结合并介导IGF非依赖的下游信号通路[30]。在胶质母细胞瘤和尤文肉瘤中,研究证实IGFBP2过表达后,整合素α5和β1表达增多[31]。胶质瘤中整合素α 5β1与IGFBP2的RGD序列相结合,进而通过整合素相关激酶激活NF-kB信号通路,最终导致体外肿瘤细胞的运动能力明显增强。黏着斑激酶是整合素信号通路的关键激酶,整合素β1亚基可以招募FAK,而FAK在多种肿瘤中呈高表达。之前的研究提示IGFBP2可能通过整合素间接激活FAK诱导肺癌中的dasatinib耐药[32]。此外,IGFBP2在前列腺癌中可以通过整合素β1亚基导致PTEN磷酸化并失活,所以PTEN很可能是IGFBP2/整合素通路的下游调控基因。
IGFBP2在卵巢癌细胞系中激活JNK和ERK1/2信号通路,最终促进肿瘤增殖。IGFBP2过表达的胶质瘤细胞中,JNK和ERK1/2信号通路也都被IGFBP2激活,但是与肿瘤细胞迁移相关的JNK通路受IGFBP2-α5信号通路调控,而ERK1/2并不受该通路影响[33]。Han等[34]研究结果却证实外源性IGFBP2是通过β1信号通路促进胶质瘤细胞的侵袭和转移,当然外源性和内源性IGFBP2的过表达可能通过完全不同的下游信号通路发挥作用。
5. IGFBP2在临床诊治中的应用
5.1 IGFBP2作为肿瘤诊断标记物
IGFBP2在多种肿瘤中的特异性高表达及其在与肿瘤恶性进展相关的多条信号通路中的核心作用引起了学者们的关注,IGFBP2在前列腺癌和卵巢癌中已被作为辅助诊断和临床分期的肿瘤标记物。
乳腺癌患者肿瘤组织中,IGFBP2的表达水平和beta-catenin正相关,而且IGFBP2/beta-catenin高表达的患者淋巴结转移率明显较高[35]。三阴乳腺癌患者IGFBP2升高提示PTEN表达缺失和较晚的临床分期[36]。
Hur等[37]发现在胃癌患者血浆中IGFBP2的水平(805.23±590.56)ng/mL较健康对照(459.61±277.01)ng/mL明显升高,且IGFBP2在较大肿瘤(>6 cm)和较高的T分期(T3/T4)中水平更高,多因素变量Cox回归分析发现IGFBP2可以作为预测胃癌患者远期预后的独立预后因素。因此IGFBP2可能作为胃癌的较特异的生物学标记物。
在胰腺癌中,IGFBP2最先在胰液中被发现较健康人表达明显升高[38]。Kendrick等[39]曾提出在血清中联合检测IGFBP2和间皮素表达对胰腺癌有一定的诊断价值。本课题组前期研究发现,IGFBP2在胰腺癌组织中较癌旁组织和正常胰腺组织中表达均明显增高,且与胰腺周围淋巴结转移明显相关,影响患者的总生存期[19]。
5.2 IGFBP2作为肿瘤预后和疗效评估标记物
内分泌治疗无效的乳腺癌患者中IGFBP2表达显著增高,且IGFBP2高表达的患者预后明显较差,体外试验证实沉默IGFBP2可以逆转肿瘤细胞对他莫西芬的耐药[14]。
前列腺癌合并糖尿病的患者血浆中IGFBP2水平较血糖正常患者明显升高,而且多烯紫杉醇在IGFBP2升高患者组中的客观缓解率减低,提示高糖引起的IGFBP2可能参与前列腺癌对紫杉醇类药物的耐药[40]。
食管癌中,顺铂化疗耐药的患者血浆和肿瘤组织中IGFBP2较化疗敏感患者明显增高,沉默IGFBP2表达联合Akt或MEK抑制剂可以增强顺铂对食管癌细胞的杀伤作用,这一发现提示IGFBP2抑制剂联合顺铂可能作为食管癌化疗的新辅助化疗方案[41]。
McCaffery等[42]提出IGFBP2低表达的胰腺癌肝转移患者对IGF1R的抑制剂ganitumab联合吉西他滨的化疗方案具有极高的治疗应答率,结合本课题组研究结果[19],提示IGFBP2在胰腺癌中的表达增加不仅增加肿瘤负荷和转移风险,也可能是胰腺癌对化疗易于产生耐药的重要原因之一。
5.3 IGFBP2作为肿瘤治疗靶点
多项研究证实IGFBP2在胶质瘤中表达提示肿瘤进展,近来最新研究提示IGFBP2的中和抗体治疗可以明显抑制IGFBP2相关通路的激活,并最终抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖和迁移[12]。IGFBP2的抑制剂OGX-225也在乳腺癌的临床前研究中证实可以逆转乳腺癌细胞的恶性表型。
6. 结语
随着对IGFBP2的结构及其在肿瘤细胞中相关通路的研究不断深入,IGFBP2在肿瘤恶性进展中的作用和相关机制将不断被揭示,相应作用靶点的中和抗体和小分子抑制剂也会不断涌现。IGFBP2在肿瘤辅助诊断、肿瘤生物学行为预测、治疗预后评估和治疗靶效应的肿瘤生物标记物应用中的价值值得进一步研究。
-
[1] Sunderic M, Dukanovic B, Malenkovic V, et al. Molecular forms of the insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in patients with colorectal cancer[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2014, 96(1):48-53. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.11.006
[2] Mitutsova V, Yeo Y, Davaze R, et al. Adult muscle-derived stem cells engraft and differentiate into insulin-expressing cells in pancreatic islets of diabetic mice[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2017, 8(1):86. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-017-0539-9
[3] Kricker JA, Towne CL, Firth SM, et al. Structural and functional evidence for the interaction of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF binding proteins with vitronectin[J]. Endocrinology, 2003, 144(7):2807-2815. DOI: 10.1210/en.2002-221086
[4] DeMambro VE, Le PT, Guntur AR, et al. Igfbp2 Deletion in Ovariectomized Mice Enhances Energy Expenditure but Accelerates Bone Loss[J].Endocrinology, 2015, 156(11):4129-4140. DOI: 10.1210/en.2014-1452
[5] Yoneyama T, Ohtsuki S, Honda K, et al. Identification of IGFBP2 and IGFBP3 As Compensatory Biomarkers for CA19-9 in Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer Using a Combination of Antibody-Based and LC-MS/ MS-Based Proteomics[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(8):e0161009. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161009
[6] Foulstone EJ, Zeng L, Perks CM, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2(IGFBP-2) promotes growth and survival of breast epithelial cells: novel regulation of the estrogen receptor[J]. Endocrinology, 2013, 154(5):1780-1793. DOI: 10.1210/en.2012-1970
[7] Pereira JJ, Meyer T, Docherty SE, et al. Bimolecular interaction of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-2 with alphavbeta3 negatively modulates IGF-Ⅰ-mediated migration and tumor growth[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(3):977-984. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3056
[8] Wiedmer P, Schwarz F, Grosse B, et al. Gender-specific effects on food intake but no inhibition of age-related fat accretion in transgenic mice overexpressing human IGFBP-2 lacking the Cardin-Weintraub sequence motif[J]. J Cell Commun Signal, 2015, 9(2):143-150. DOI: 10.1007/s12079-015-0264-z
[9] Lund J, Sondergaard MT, Conover CA, et al. Heparin-binding mechanism of the IGF2/IGF-binding protein 2 complex[J]. J Mol Endocrinol, 2014, 52(3):345-355. DOI: 10.1530/JME-13-0184
[10] Azar WJ, Zivkovic S, Werther GA, et al. IGFBP-2 nuclear translocation is mediated by a functional NLS sequence and is essential for its pro-tumorigenic actions in cancer cells[J]. Oncogene, 2014, 33(5):578-588. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.630
[11] Russo VC, Schutt BS, Andaloro E, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 binding to extracellular matrix plays a critical role in neuroblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion[J]. Endocrinology, 2005, 146(10):4445-4455. DOI: 10.1210/en.2005-0467
[12] Phillips LM, Zhou X, Cogdell DE, et al. Glioma progression is mediated by an addiction to aberrant IGFBP2 expression and can be blocked using anti-IGFBP2 strategies[J]. J Pathol, 2016, 239(3):355-364. DOI: 10.1002/path.4734
[13] Komisarof J, McCall M, Newman L, et al. A four gene signature predictive of recurrent prostate cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(2):3430-3440. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27966447
[14] Hawsawi Y, Humphries MP, Wright A, et al. Deregulation of IGFbinding proteins -2 and -5 contributes to the development of endocrine resistant breast cancer in vitro[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(22): 32129-32143. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i22
[15] Huang YF, Cheng WF, Wu YP, et al. Circulating IGF system and treatment outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2014, 21(2):217-229. DOI: 10.1530/ERC-13-0274
[16] Hu Q, Huang L, Kuang X, et al. Is insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 associated with metastasis in lung cancer?[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2014, 31(5):535-541. DOI: 10.1007/s10585-014-9647-4
[17] Kuhnl A, Kaiser M, Neumann M, et al. High expression of IGFBP2 is associated with chemoresistance in adult acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Leuk Res, 2011, 35(12):1585-1590. DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2011.08.006
[18] Renehan AG, Jones J, Potten CS, et al. Elevated serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-Ⅱ and IGF binding protein-2 in patients with colorectal cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2000, 83(10):1344-1350. DOI: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1462
[19] Gao S, Sun Y, Zhang X, et al. IGFBP2 Activates the NF-kappaB Pathway to Drive Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Invasive Character in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2016, 76(22):6543-6554. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0438
[20] Ben-Shmuel A, Shvab A, Gavert N, et al. Global analysis of L1-transcriptomes identified IGFBP-2 as a target of ezrin and NF-kappaB signaling that promotes colon cancer progression[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(27):3220-3230. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.340
[21] Wang GK, Hu L, Fuller GN, et al. An interaction between insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2(IGFBP2) and integrin alpha5 is essential for IGFBP2-induced cell mobility[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(20):14085-14091. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M513686200
[22] Wieczorek E, Jablonska E, Wasowicz W, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and genetic mouse models in cancer research: a mini-review[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(1):163-175. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-2747-6
[23] Verma S, Kesh K, Ganguly N, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and gastrointestinal cancers: Impacts of dietary antioxidants[J]. World J Biol Chem, 2014, 5(3):355-376. DOI: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i3.355
[24] Wang X, Zhang Y, Chang Y, et al. Elevation of IGFBP2 contributes to mycotoxin T-2-induced chondrocyte injury and metabolism[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016, 478(1):385-391. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.042
[25] Zhu Z, Zhong H, Zhou Q, et al. Inhibition of PKR impairs angiogenesis through a VEGF pathway[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2015, 308(6):E518-524. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00469.2014
[26] Talbot NC, Caperna TJ. Proteome array identification of bioactive soluble proteins/peptides in Matrigel: relevance to stem cell responses[J]. Cytotechnology, 2015, 67(5):873-883. DOI: 10.1007/s10616-014-9727-y
[27] Das SK, Bhutia SK, Azab B, et al. MDA-9/syntenin and IGFBP-2 promote angiogenesis in human melanoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(2):844-854. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1681
[28] Huang, XP, Zhou WH, Zhang YF. Genetic variations in the IGF-IGFRIGFBP axis confer susceptibility to lung and esophageal cancer[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2014, 13(1):2107-2019. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24615087
[29] Milani M, Laranjeira AB, de Vasconcellos JF, et al. Plasma Hsp90 Level as a Marker of Early Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Engraftment and Progression in Mice[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6):e0129298. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129298
[30] Patil SS, Railkar R, Swain M, et al. Novel anti IGFBP2 single chain variable fragment inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion[J]. J Neurooncol, 2015, 123(2):225-235. DOI: 10.1007/s11060-015-1800-7
[31] Schutt BS, Langkamp M, Rauschnabel U, et al. Integrin-mediated action of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 in tumor cells[J]. J Mol Endocrinol, 2004, 32(3):859-868. DOI: 10.1677/jme.0.0320859
[32] Lu H, Wang L, Gao W, et al. IGFBP2/FAK pathway is causally associated with dasatinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2013, 12(12):2864-2873. DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0233
[33] Mendes KN, Wang GK, Fuller GN, et al. JNK mediates insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2/integrin alpha5-dependent glioma cell migration[J]. Int J Oncol, 2010, 37(1):143-153. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20514406
[34] Han S, Li Z, Master LM, et al. Exogenous IGFBP-2 promotes proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioma cells via the integrin beta1-ERK pathway[J]. Br J Cancer, 2014, 111(7):1400-1409. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.435
[35] Sehgal P, Kumar N, Praveen Kumar VR, et al. Regulation of protumorigenic pathways by insulin like growth factor binding protein2 and its association along with beta-catenin in breast cancer lymph node metastasis[J]. Mol Cancer, 2013, 12:63. DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-63
[36] Dean SJ, Perks CM, Holly JM, et al. Loss of PTEN expression is associated with IGFBP2 expression, younger age, and late stage in triplenegative breast cancer[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2014, 141(3):323-333. DOI: 10.1309/AJCPR11DEAYPTUSL
[37] Hur H, Yu EJ, Ham IH, et al. Preoperative serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 predict prognosis of gastric cancer patients[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(7):10994-11003. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28036255
[38] Chen R, Pan S, Yi EC, et al. Quantitative proteomic profiling of pancreatic cancer juice[J]. Proteomics, 2006, 6(13):3871-3879. DOI: 10.1002/(ISSN)1615-9861
[39] Kendrick ZW, Firpo MA, Repko RC, et al. Serum IGFBP2 and MSLN as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2014, 16(7):670-676. DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12199
[40] Biernacka KM, Uzoh CC, Zeng L, et al. Hyperglycaemia-induced chemoresistance of prostate cancer cells due to IGFBP2[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2013, 20(5):741-751. DOI: 10.1530/ERC-13-0077
[41] Myers AL, Lin L, Nancarrow DJ, et al. IGFBP2 modulates the chemoresistant phenotype in esophageal adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(28):25897-25916. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.v6i28
[42] McCaffery I, Tudor Y, Deng H, et al. Putative predictive biomarkers of survival in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma treated with gemcitabine and ganitumab, an IGF1R inhibitor[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(15):4282-4289. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1840
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 吕建志,曹井贺,刘欢,王鑫哲,石素素,祝海洲. 胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2和细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2在肾透明细胞癌中的表达及其临床意义. 中华诊断学电子杂志. 2022(01): 42-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 高文仓,张月蒙. 胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白相关蛋白1基因甲基化检测联合粪便潜血定量试验在结直肠癌中的诊断价值. 中国医药. 2021(06): 885-889 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李秀焕,李国泰. 分段低强度跑步与持续中强度跑步对糖尿病性骨质疏松大鼠骨密度、胰岛素抵抗的影响研究. 中国骨质疏松杂志. 2020(06): 843-848 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈辉娥,姜训忠,聂鸿,李延东,周芳. 肿瘤特异生长因子检测在恶性肿瘤诊断及治疗中的应用分析. 数理医药学杂志. 2020(11): 1626-1628 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵彩霞,马丽莉,王娟. 血清胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2联合糖链抗原72-4检测对胃癌的诊断价值. 贵州医科大学学报. 2018(05): 613-616+620 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 赵伟,唐辉,邵川,谯飞. 胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2促进神经胶质瘤干细胞的增殖与迁移侵袭. 中国组织工程研究. 2018(29): 4631-4636 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王超,孙燕. 迁移侵袭抑制蛋白在肿瘤发生发展中的作用及其临床意义. 中国肿瘤临床. 2018(03): 146-151 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 赵彩霞,申凤俊. 胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2与消化系统肿瘤的关系. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志. 2017(06): 606-611 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载:
